LPADs provide stable voltage regulation by using a combination of resistors and Zener diodes to create a precise voltage drop, while Zener attenuators primarily focus on reducing signal amplitude without significantly altering the waveform. Understanding the differences between LPAD and Zener attenuators can help you choose the right component for your circuit's voltage regulation or signal attenuation needs; explore the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
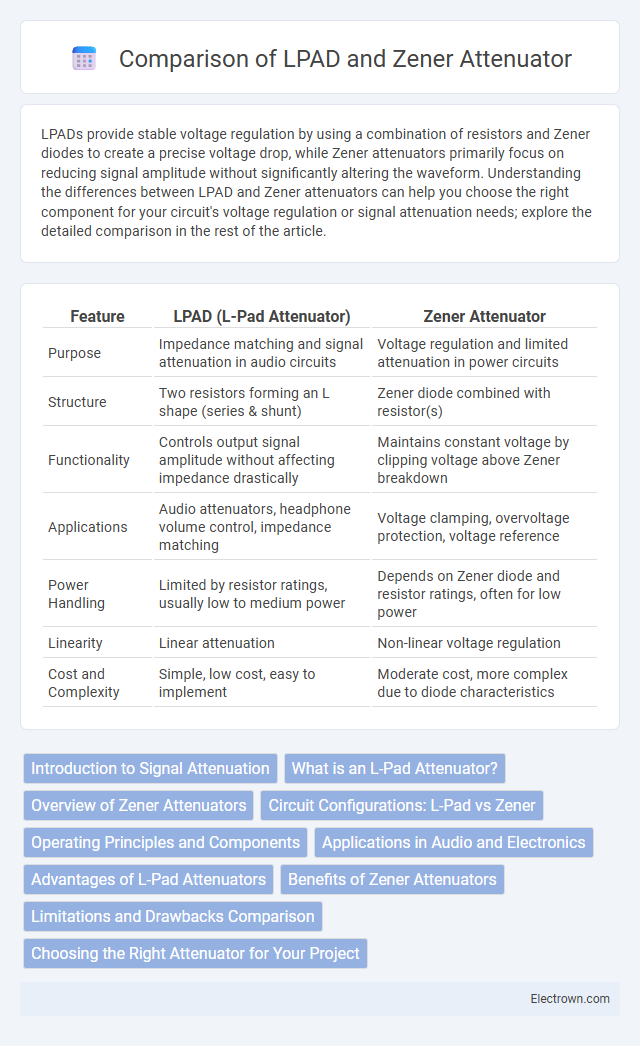
| Feature | LPAD (L-Pad Attenuator) | Zener Attenuator |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Impedance matching and signal attenuation in audio circuits | Voltage regulation and limited attenuation in power circuits |
| Structure | Two resistors forming an L shape (series & shunt) | Zener diode combined with resistor(s) |
| Functionality | Controls output signal amplitude without affecting impedance drastically | Maintains constant voltage by clipping voltage above Zener breakdown |
| Applications | Audio attenuators, headphone volume control, impedance matching | Voltage clamping, overvoltage protection, voltage reference |
| Power Handling | Limited by resistor ratings, usually low to medium power | Depends on Zener diode and resistor ratings, often for low power |
| Linearity | Linear attenuation | Non-linear voltage regulation |
| Cost and Complexity | Simple, low cost, easy to implement | Moderate cost, more complex due to diode characteristics |
Introduction to Signal Attenuation
Signal attenuation reduces the power of an electrical signal to prevent distortion or overload in circuits. An LPAD attenuator uses a combination of resistors arranged in an L-shaped network, providing precise and adjustable attenuation ideal for audio and RF applications. Zener attenuators employ Zener diodes to clamp voltage levels, offering protection and stabilization but are less linear and suitable mainly for limiting voltage spikes rather than precise signal attenuation.
What is an L-Pad Attenuator?
An L-Pad attenuator is a type of passive electrical circuit designed to reduce signal strength while maintaining impedance matching between the source and load. It consists of two resistors arranged in an "L" shape that provide a controlled amount of attenuation without significantly affecting the audio or signal quality. You can use an L-Pad attenuator in audio systems, RF applications, and other scenarios where precise signal level adjustment and impedance consistency are crucial.
Overview of Zener Attenuators
Zener attenuators use Zener diodes to maintain a stable voltage level by exploiting the diode's voltage regulation properties, making them ideal for precise voltage referencing and noise reduction in signal conditioning circuits. Unlike traditional resistive attenuators such as LPAD attenuators, Zener attenuators provide improved voltage stability under varying load conditions due to the diode's ability to clamp voltage at its Zener breakdown level. Their applications are prevalent in calibration, measurement instrumentation, and protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes, highlighting their importance in maintaining signal integrity.
Circuit Configurations: L-Pad vs Zener
The L-pad attenuator employs two resistors arranged in series and parallel to maintain consistent impedance while reducing signal levels, making it ideal for audio and RF applications requiring impedance matching. The Zener attenuator incorporates a Zener diode in shunt with a resistor, providing voltage regulation and limiting voltage spikes, which is advantageous in protective circuits but introduces non-linear characteristics. Unlike the purely resistive L-pad, the Zener configuration combines resistive attenuation with voltage clipping, affecting the linearity and frequency response of the signal.
Operating Principles and Components
LPAD attenuators use resistive pads to reduce signal levels by dissipating energy through fixed resistor networks, maintaining impedance matching in audio and RF circuits. Zener attenuators incorporate Zener diodes to clamp voltage at a predetermined level, providing voltage regulation and protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes. Your choice depends on whether precise attenuation with minimal distortion or voltage stabilization is required in your application.
Applications in Audio and Electronics
LPAD (L-pad attenuator) is widely used in audio applications for impedance matching and volume control without altering tonal balance, making it ideal for speaker level attenuation. Zener attenuators, leveraging Zener diodes, provide voltage regulation and overvoltage protection in electronic circuits by maintaining a stable reference voltage, which is crucial in sensitive audio components and power supply designs. Both components play distinct roles in electronics; LPADs manage audio signal levels and impedance, while Zener attenuators ensure voltage stability and circuit protection.
Advantages of L-Pad Attenuators
L-Pad attenuators offer precise and consistent impedance matching, reducing signal reflection and distortion effectively. Their simple design with fixed resistor values ensures reliable performance and easy integration into audio and RF circuits. You benefit from improved signal control without sacrificing quality, making L-Pads ideal for volume adjustments and impedance bridging.
Benefits of Zener Attenuators
Zener attenuators provide precise voltage regulation and protection by utilizing Zener diodes to maintain a stable output voltage despite input variations, enhancing circuit reliability. They offer superior noise reduction and improved signal integrity compared to simple resistor-based LPADs, making them ideal for sensitive electronic applications. Their ability to clamp voltage spikes safeguards downstream components, increasing overall system durability and performance.
Limitations and Drawbacks Comparison
LPADs exhibit limited frequency response and are prone to impedance mismatch, leading to signal distortion in high-frequency applications. Zener attenuators, while offering better voltage regulation, introduce noise and exhibit nonlinear behavior under varying load conditions. Your choice depends on the specific requirements for linearity and noise tolerance in the attenuation design.
Choosing the Right Attenuator for Your Project
Selecting the right attenuator depends on your project's frequency range and power handling requirements; an LPAD attenuator offers precision and stability for RF applications with lower power levels, while a Zener attenuator excels in voltage regulation and transient protection in high-voltage circuits. LPAD attenuators use a fixed resistor network to provide accurate attenuation without distortion, making them ideal for signal conditioning. Zener attenuators leverage Zener diodes to maintain voltage levels and protect downstream components, which is crucial for sensitive electronic devices operating under variable voltage conditions.
lpad vs zener attenuator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com