Class D amplifiers operate with high efficiency by using pulse-width modulation to switch output transistors fully on or off, minimizing power loss and heat generation, while Class H amplifiers improve efficiency by dynamically adjusting the power supply voltage based on the input signal to reduce wasted energy. Understanding the key differences between Class D and Class H amplifiers can help you choose the ideal option for your audio system; explore the rest of this article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
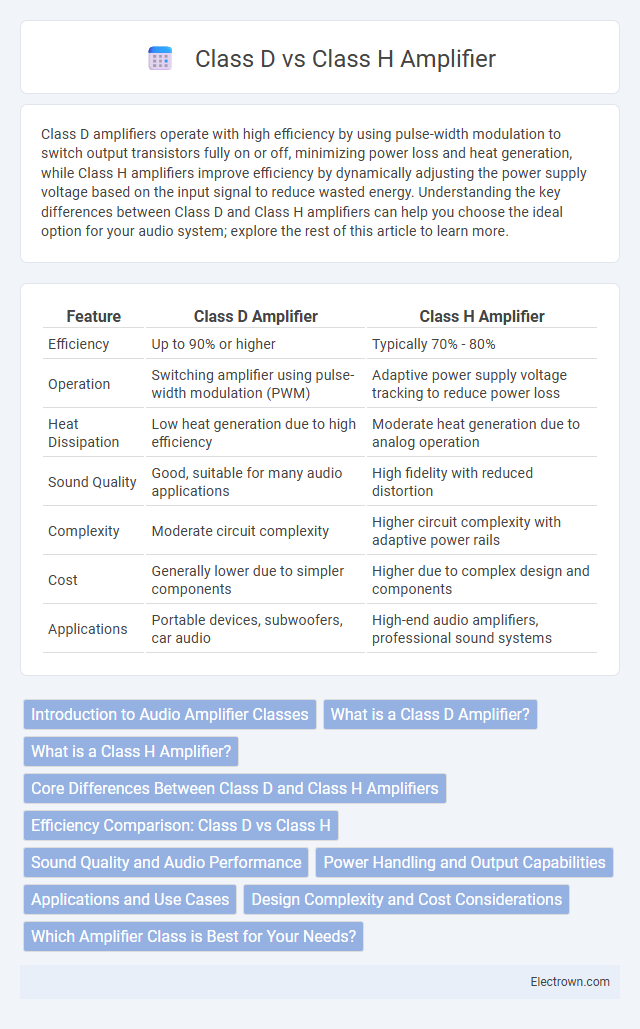
| Feature | Class D Amplifier | Class H Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Up to 90% or higher | Typically 70% - 80% |
| Operation | Switching amplifier using pulse-width modulation (PWM) | Adaptive power supply voltage tracking to reduce power loss |
| Heat Dissipation | Low heat generation due to high efficiency | Moderate heat generation due to analog operation |
| Sound Quality | Good, suitable for many audio applications | High fidelity with reduced distortion |
| Complexity | Moderate circuit complexity | Higher circuit complexity with adaptive power rails |
| Cost | Generally lower due to simpler components | Higher due to complex design and components |
| Applications | Portable devices, subwoofers, car audio | High-end audio amplifiers, professional sound systems |
Introduction to Audio Amplifier Classes
Class D amplifiers utilize pulse-width modulation for efficient, high-power audio amplification with minimal heat dissipation, making them ideal for portable and high-power applications. Class H amplifiers employ dynamic voltage rails that adjust in real-time to the input signal, improving efficiency over traditional Class AB designs while maintaining audio fidelity. Both classes address the trade-off between efficiency and audio quality, with Class D excelling in energy conservation and Class H optimizing performance in high-power scenarios.
What is a Class D Amplifier?
A Class D amplifier operates by rapidly switching its output devices on and off, creating a pulse-width modulated signal that efficiently drives speakers with minimal heat dissipation. This switching method allows Class D amplifiers to achieve higher power efficiency, often above 90%, making them ideal for portable and high-power audio applications. Your choice of a Class D amplifier ensures compact size and energy savings without sacrificing audio performance.
What is a Class H Amplifier?
A Class H amplifier is a type of audio amplifier that optimizes efficiency by modulating the power supply voltage according to the input signal level, reducing power dissipation and heat generation. Unlike Class D amplifiers that use pulse-width modulation for switching transistors on and off, Class H employs dynamic voltage rails to minimize wasted energy during amplification. This approach allows Class H amplifiers to maintain high linearity and audio fidelity while improving power efficiency compared to traditional Class AB amplifiers.
Core Differences Between Class D and Class H Amplifiers
Class D amplifiers use pulse-width modulation to achieve high efficiency by rapidly switching output devices between on and off states, minimizing power loss and heat generation. Class H amplifiers improve efficiency by dynamically adjusting the power supply voltage to the output devices based on the input signal level, reducing voltage drop and power dissipation during operation. Understanding these core differences helps you choose the right amplifier for applications requiring energy efficiency and performance balance.
Efficiency Comparison: Class D vs Class H
Class D amplifiers achieve efficiency levels typically above 90% by using pulse-width modulation to switch output transistors fully on or off, minimizing power loss as heat. Class H amplifiers improve on traditional Class AB designs by dynamically adjusting supply voltage to reduce dissipation, reaching efficiencies around 70-80% under optimal conditions. Your choice depends on whether maximum efficiency with lighter heat management (Class D) or improved linearity with moderate efficiency gains (Class H) better suits your audio application.
Sound Quality and Audio Performance
Class D amplifiers deliver high efficiency and compact design but may exhibit higher distortion levels affecting sound clarity and audio fidelity. Class H amplifiers offer superior sound quality by dynamically adjusting the power supply voltage to reduce distortion, resulting in cleaner audio performance and better handling of dynamic audio signals. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize power efficiency or audiophile-grade sound reproduction in your audio setup.
Power Handling and Output Capabilities
Class D amplifiers excel in high power handling and output efficiency due to their switching mode operation, allowing them to deliver substantial wattage with minimal heat dissipation. Class H amplifiers enhance power efficiency by modulating the supply voltage in real-time, improving output capabilities while reducing power loss compared to traditional Class AB designs. Your choice depends on whether maximum efficiency and compactness in high-power applications (Class D) or dynamic voltage scaling for improved linearity and power performance (Class H) better suits your audio system requirements.
Applications and Use Cases
Class D amplifiers are widely used in portable audio devices, home theaters, and automotive sound systems due to their high efficiency and compact size, making them ideal for battery-operated and space-constrained applications. Class H amplifiers find applications primarily in professional audio equipment and large sound reinforcement systems where high power output and improved thermal management are critical. Both amplifier classes serve distinct purposes, with Class D excelling in energy-efficient consumer electronics and Class H optimized for demanding, high-power environments.
Design Complexity and Cost Considerations
Class D amplifiers feature simpler circuit designs with fewer components, leading to lower manufacturing costs and smaller form factors. In contrast, Class H amplifiers require more complex circuitry to modulate the power supply rails dynamically, resulting in increased design complexity and higher production expenses. The advanced power management in Class H designs enhances efficiency but often demands specialized components, driving up overall costs.
Which Amplifier Class is Best for Your Needs?
Class D amplifiers offer high efficiency and compact size, making them ideal for portable or battery-powered devices where energy conservation is crucial. Class H amplifiers provide improved power efficiency over traditional Class AB designs by dynamically adjusting voltage rails, delivering cleaner sound in high-power audio systems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy savings and compactness (Class D) or superior audio fidelity in demanding environments (Class H).
class d vs class h amplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com