XLR connectors provide superior balanced audio transmission that reduces noise, making them ideal for professional microphones and audio equipment, while BNC connectors are primarily used for video signals and RF applications due to their secure, twist-lock design. To understand the key differences and determine which connector suits Your needs best, explore the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
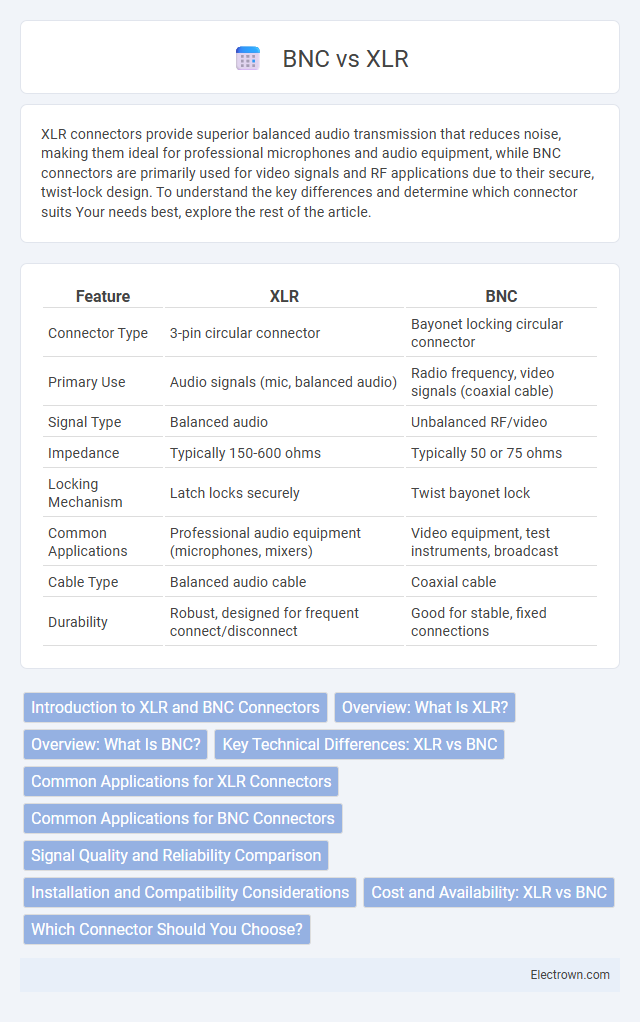
| Feature | XLR | BNC |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Type | 3-pin circular connector | Bayonet locking circular connector |
| Primary Use | Audio signals (mic, balanced audio) | Radio frequency, video signals (coaxial cable) |
| Signal Type | Balanced audio | Unbalanced RF/video |
| Impedance | Typically 150-600 ohms | Typically 50 or 75 ohms |
| Locking Mechanism | Latch locks securely | Twist bayonet lock |
| Common Applications | Professional audio equipment (microphones, mixers) | Video equipment, test instruments, broadcast |
| Cable Type | Balanced audio cable | Coaxial cable |
| Durability | Robust, designed for frequent connect/disconnect | Good for stable, fixed connections |
Introduction to XLR and BNC Connectors
XLR connectors are primarily used in professional audio and microphone equipment, offering secure, balanced connections that reduce noise and interference. BNC connectors, commonly found in video, radio frequency, and networking applications, provide reliable coaxial cable termination with quick twist-lock coupling. Your choice between XLR and BNC connectors depends on the specific requirements for audio fidelity or signal integrity in your setup.
Overview: What Is XLR?
XLR connectors are primarily used in professional audio equipment for balanced audio signals, providing superior noise reduction and signal integrity over long cable runs. Designed with three pins, XLR connectors ensure secure and reliable connections for microphones, mixers, and amplifiers. They differ from BNC connectors, which are mainly used for radio frequency signals and video transmissions.
Overview: What Is BNC?
BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) connectors are coaxial cable connectors widely used in professional video and RF applications for their reliable signal transmission and quick connect-disconnect mechanism. Designed to maintain consistent impedance, typically 50 or 75 ohms, BNC connectors minimize signal loss and interference, making them ideal for radio, television, and test equipment. Compared to XLR connectors, which are primarily used for balanced audio signals, BNC connectors excel in high-frequency and digital video environments.
Key Technical Differences: XLR vs BNC
XLR connectors feature a balanced, three-pin design primarily used for professional audio signals, offering superior noise rejection and secure locking mechanisms to maintain signal integrity. BNC connectors, commonly found in video and RF applications, utilize a bayonet locking system and are designed for unbalanced coaxial cable connections, providing high-frequency signal transmission with minimal loss. Understanding these key technical differences helps you select the appropriate connector type for your audio or video setup, ensuring optimal performance.
Common Applications for XLR Connectors
XLR connectors are predominantly used in professional audio, stage lighting, and broadcasting equipment for balanced audio signal transmission, ensuring minimal noise interference. They are common in microphones, audio mixers, and high-quality sound systems due to their secure locking mechanism and durability. These connectors also support DMX lighting control protocols, making them essential in live event production and studio environments.
Common Applications for BNC Connectors
BNC connectors are widely used in professional video equipment, RF applications, and test instruments due to their reliable quick-connect design and excellent signal integrity at high frequencies. You often find BNC connectors in CCTV camera systems, broadcast television setups, and network test equipment where secure and consistent coaxial cable connections are essential. Their durability and ease of use make BNC connectors ideal for environments requiring frequent cable changes and stable signal transmission.
Signal Quality and Reliability Comparison
XLR connectors provide superior signal quality and reliability in audio applications due to their balanced design, which effectively reduces electromagnetic interference and noise over long cable runs. BNC connectors, commonly used in video and radio frequency transmissions, offer reliable, secure connections but are more susceptible to signal degradation and noise over extended distances. For critical audio signals requiring consistent noise rejection and durability, XLR is generally the preferred choice.
Installation and Compatibility Considerations
XLR connectors, widely used in professional audio and balanced signal applications, require careful alignment due to their three-pin design, ensuring secure and noise-resistant connections. BNC connectors, common in video and RF applications, feature a bayonet-style locking mechanism that simplifies installation with quick twist-lock engagement, providing reliable signal integrity in high-frequency environments. Compatibility depends on the device's input/output ports and signal type, with XLR favored for analog audio systems and BNC preferred for digital video and coaxial transmissions.
Cost and Availability: XLR vs BNC
XLR connectors typically cost more than BNC connectors due to their robust construction and widespread use in professional audio equipment, leading to higher availability in pro audio markets. BNC connectors are generally less expensive and more readily available for video and networking applications, benefiting from mass production for broadcast and telecommunications. Pricing and accessibility largely depend on the intended use, with XLR favored in audio gear and BNC common in video distribution and RF setups.
Which Connector Should You Choose?
Choose an XLR connector for balanced audio signals, professional microphones, and equipment requiring noise reduction and secure locking mechanisms. Opt for a BNC connector when dealing with high-frequency radio, video signals, or digital interface connections like SDI and RF applications. Selecting the right connector depends on your signal type, frequency requirements, and the environment's susceptibility to interference.
xlr vs bnc Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com