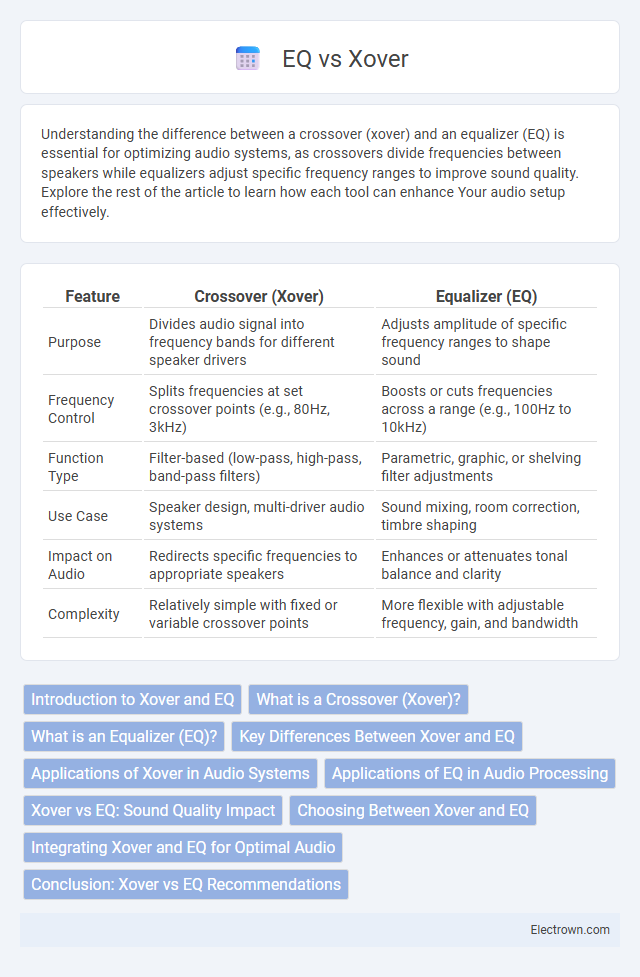
Understanding the difference between a crossover (xover) and an equalizer (EQ) is essential for optimizing audio systems, as crossovers divide frequencies between speakers while equalizers adjust specific frequency ranges to improve sound quality. Explore the rest of the article to learn how each tool can enhance Your audio setup effectively.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Crossover (Xover) | Equalizer (EQ) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Divides audio signal into frequency bands for different speaker drivers | Adjusts amplitude of specific frequency ranges to shape sound |
| Frequency Control | Splits frequencies at set crossover points (e.g., 80Hz, 3kHz) | Boosts or cuts frequencies across a range (e.g., 100Hz to 10kHz) |
| Function Type | Filter-based (low-pass, high-pass, band-pass filters) | Parametric, graphic, or shelving filter adjustments |
| Use Case | Speaker design, multi-driver audio systems | Sound mixing, room correction, timbre shaping |
| Impact on Audio | Redirects specific frequencies to appropriate speakers | Enhances or attenuates tonal balance and clarity |
| Complexity | Relatively simple with fixed or variable crossover points | More flexible with adjustable frequency, gain, and bandwidth |
Introduction to Xover and EQ
Crossovers (Xover) split audio signals into separate frequency bands, directing bass, midrange, and treble to appropriate speakers for clearer sound reproduction. Equalizers (EQ) adjust the amplitude of specific frequencies within the audio signal to enhance or attenuate tones according to your preferences or acoustic needs. Both Xover and EQ play crucial roles in optimizing sound system performance by managing frequency distribution and tonal balance.
What is a Crossover (Xover)?
A crossover (xover) is an electronic filter used in audio systems to split the audio signal into separate frequency bands, directing lows to subwoofers and highs to tweeters. By dividing frequencies accurately, crossovers ensure each speaker operates within its optimal range, improving sound clarity and system efficiency. Unlike a graphic equalizer (EQ), which adjusts the amplitude of specific frequency bands across the whole signal, a crossover focuses solely on frequency separation for targeted speaker output.
What is an Equalizer (EQ)?
An Equalizer (EQ) is an audio processing tool that adjusts the balance of frequency components within a sound signal to enhance or reduce specific frequencies. It enables precise control over bass, midrange, and treble frequencies, allowing for tonal shaping and correction of audio signals. EQs are essential in music production, live sound, and broadcasting to optimize sound clarity and tonal quality.
Key Differences Between Xover and EQ
Xover (crossover) divides audio signals into separate frequency bands for targeted speaker drivers, enhancing clarity and preventing damage, while EQ (equalization) adjusts the amplitude of specific frequency ranges to shape the overall sound. Crossovers work primarily at fixed frequency points to split the audio spectrum, whereas EQs offer flexible frequency manipulation with boosts or cuts across a broad range. The key difference lies in functionality: crossovers manage signal distribution to speakers, and EQs refine tonal balance within those signals.
Applications of Xover in Audio Systems
Crossovers (Xover) play a crucial role in audio systems by dividing the audio signal into separate frequency bands, ensuring that each speaker driver, such as woofers, midrange, and tweeters, receives the appropriate frequencies for optimal performance. This prevents distortion and damage while enhancing sound clarity and balance across the audio spectrum. Your audio system benefits from tailored frequency distribution, resulting in improved overall sound quality and speaker efficiency.
Applications of EQ in Audio Processing
Equalizers (EQ) are essential in audio processing for shaping sound frequencies, correcting tonal imbalances, and enhancing clarity across various applications such as mixing, mastering, and live sound reinforcement. Unlike crossovers that split audio signals into different frequency bands for separate speakers, EQ focuses on adjusting specific frequency ranges within the entire signal to optimize audio quality. Your ability to tailor the frequency response with parametric, graphic, or shelving EQs improves the overall listening experience by emphasizing or attenuating desired sound characteristics.
Xover vs EQ: Sound Quality Impact
Crossover (Xover) and equalizer (EQ) both shape sound quality but influence audio characteristics differently. Xover divides audio signals into distinct frequency bands to optimize speaker performance, reducing distortion and improving clarity. Your sound system benefits from precise frequency allocation, while EQ adjusts tonal balance by boosting or cutting specific frequencies, affecting timbre without separating signal paths.
Choosing Between Xover and EQ
Selecting between a crossover (Xover) and an equalizer (EQ) depends on the specific audio processing needs. Crossovers divide the audio signal into distinct frequency bands, ensuring that speakers receive only the frequencies they can effectively reproduce, which enhances sound clarity and efficiency. Equalizers adjust the amplitude of specific frequency ranges within the audio signal to shape the tonal balance and correct for room acoustics or speaker characteristics.
Integrating Xover and EQ for Optimal Audio
Integrating a crossover (Xover) with an equalizer (EQ) enhances audio performance by precisely dividing frequency bands and fine-tuning tonal balance for each driver. Optimizing crossover points reduces phase interference while EQ adjustments correct room resonances and speaker anomalies, resulting in clearer and more accurate sound reproduction. Combining both tools allows audio systems to achieve superior frequency response and improved overall sound quality.
Conclusion: Xover vs EQ Recommendations
When selecting between a crossover (Xover) and an equalizer (EQ), consider that crossovers efficiently divide audio signals into frequency bands, optimizing speaker performance. EQs provide precise frequency adjustments to shape the sound signature and correct room acoustics. For best results, use crossovers to manage frequency distribution and EQs to fine-tune tonal balance in professional audio setups.
xover vs eq Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com