Ribbon microphones capture sound with a thin metal ribbon, offering warm, natural tones ideal for studio vocals and instruments, while condenser microphones use a capacitor to deliver a broader frequency response and higher sensitivity, perfect for detailed recordings. Explore the article to understand which mic suits Your recording needs best.
Table of Comparison
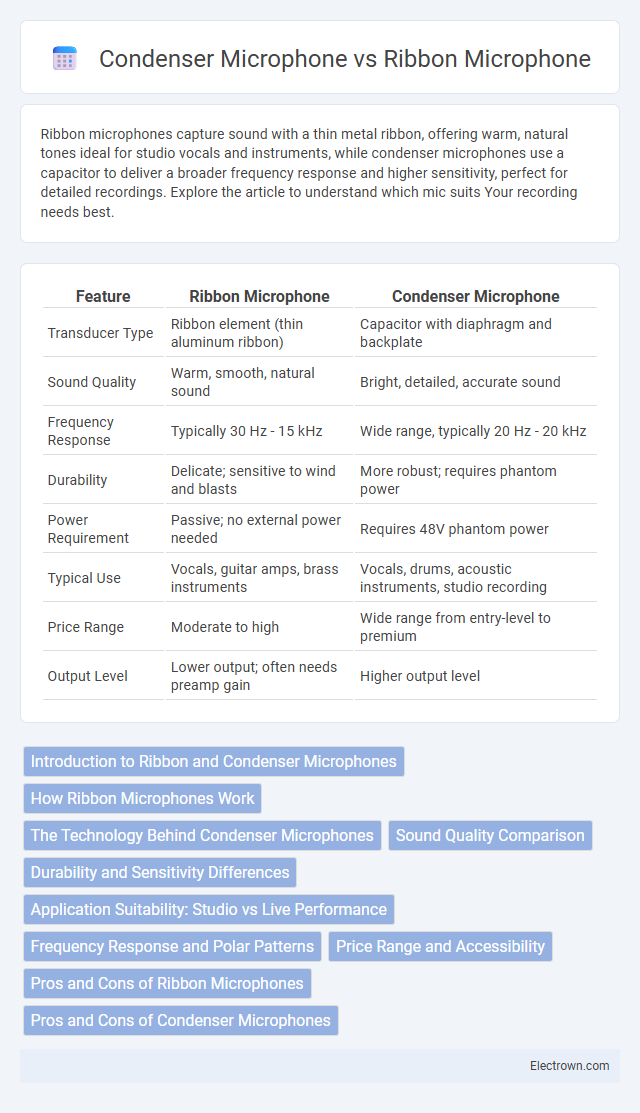
| Feature | Ribbon Microphone | Condenser Microphone |
|---|---|---|
| Transducer Type | Ribbon element (thin aluminum ribbon) | Capacitor with diaphragm and backplate |
| Sound Quality | Warm, smooth, natural sound | Bright, detailed, accurate sound |
| Frequency Response | Typically 30 Hz - 15 kHz | Wide range, typically 20 Hz - 20 kHz |
| Durability | Delicate; sensitive to wind and blasts | More robust; requires phantom power |
| Power Requirement | Passive; no external power needed | Requires 48V phantom power |
| Typical Use | Vocals, guitar amps, brass instruments | Vocals, drums, acoustic instruments, studio recording |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Wide range from entry-level to premium |
| Output Level | Lower output; often needs preamp gain | Higher output level |
Introduction to Ribbon and Condenser Microphones
Ribbon microphones utilize a thin aluminum ribbon suspended within a magnetic field to capture sound vibrations, providing a warm, natural tone ideal for vocals and instruments. Condenser microphones rely on a capacitor system with a charged diaphragm to deliver a precise and detailed audio response, making them popular in studio recording for their clarity and sensitivity. Your choice between ribbon and condenser microphones depends on the desired sound character and recording environment.
How Ribbon Microphones Work
Ribbon microphones utilize a thin aluminum ribbon suspended within a magnetic field that vibrates when sound waves hit it, generating an electrical signal corresponding to the audio source. This design captures sound with a natural, warm quality and excellent transient response, making ribbon microphones ideal for recording vocals and instruments with subtle nuances. Their bidirectional polar pattern distinguishes them from condenser microphones, which rely on capacitance changes between a diaphragm and a backplate to detect sound.
The Technology Behind Condenser Microphones
Condenser microphones utilize a capacitor design where a thin diaphragm acts as one plate of the capacitor, vibrating in response to sound waves and causing variations in capacitance that generate an electrical signal. They require external power, typically provided by phantom power or batteries, to maintain an electrical charge on the capacitor plates. This technology allows condenser microphones to capture high-frequency detail and fast transient response, making them ideal for studio recording and detailed sound capture compared to ribbon microphones.
Sound Quality Comparison
Ribbon microphones deliver a warm, natural sound with smooth high frequencies, making them ideal for capturing vocals and instruments with rich tonal detail. Condenser microphones offer a wide frequency response and higher sensitivity, providing crisp, clear audio with excellent transient response suitable for detailed recording environments. Your choice between ribbon and condenser mics should consider the desired sonic character and recording context for optimal sound quality.
Durability and Sensitivity Differences
Ribbon microphones exhibit greater fragility compared to condenser microphones due to their thin aluminum ribbon elements, making them more susceptible to damage from high sound pressure levels and rough handling. Condenser microphones offer higher sensitivity and can capture a broader frequency range with greater detail, thanks to their active electronic components and capacitor-based design. While condensers are generally more robust and suitable for varied environments, ribbon mics require careful maintenance but provide a unique warm sound character favored in studio settings.
Application Suitability: Studio vs Live Performance
Ribbon microphones excel in studio settings due to their smooth, natural sound and sensitivity to subtle nuances, making them ideal for vocals and acoustic instruments. Condenser microphones offer higher sensitivity and durability, which suits live performances where clarity and feedback rejection are critical. Choosing between ribbon and condenser microphones depends largely on whether the application prioritizes the controlled environment of a studio or the demanding conditions of stage use.
Frequency Response and Polar Patterns
Ribbon microphones typically offer a smooth, natural frequency response with a gentle roll-off in high frequencies, enhancing warmth and vintage tones, making them ideal for capturing rich, detailed sound sources. Condenser microphones provide a broader frequency range with extended high-frequency sensitivity, allowing for crisp and clear recordings, especially in studio environments where precision is key. Your choice depends on whether you need the ribbon mic's warm, figure-8 polar pattern for classic ambiance or the condenser's versatile cardioid and multi-pattern options for focused, isolated sound capture.
Price Range and Accessibility
Ribbon microphones generally fall within a higher price range, often starting around $300 and extending into the thousands, making them less accessible for beginners. Condenser microphones offer a broader price spectrum, with many affordable models available from $50 to $500, providing more options for various budgets. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the desired audio quality and application needs.
Pros and Cons of Ribbon Microphones
Ribbon microphones offer a warm, natural sound with smooth high frequencies, making them ideal for capturing vocals and acoustic instruments with vintage character. Their delicate aluminum ribbon element requires careful handling and often benefits from a transformer or preamp with high gain, limiting use in high-SPL environments. You should consider ribbon mics for studio recording when aiming for rich, detailed audio but avoid them in harsh or live settings due to fragility and sensitivity to moisture.
Pros and Cons of Condenser Microphones
Condenser microphones excel at capturing detailed, high-frequency sounds, making them ideal for studio vocals and acoustic instruments with their wide frequency response and sensitivity. Their main drawbacks include greater fragility and susceptibility to humidity and handling noise, requiring phantom power to operate and sometimes leading to distortion with very loud sound sources. You benefit most from condenser microphones in controlled environments where clarity and accuracy are paramount but should avoid them in rough or outdoor settings due to their delicate build and power needs.
ribbon vs condenser microphone Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com