High gain mode amplifies signals or input levels significantly, enhancing sensitivity and output strength, while low gain mode provides a more controlled, stable signal with reduced noise and distortion. Discover how choosing the right gain mode impacts your audio or electronic device's performance by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
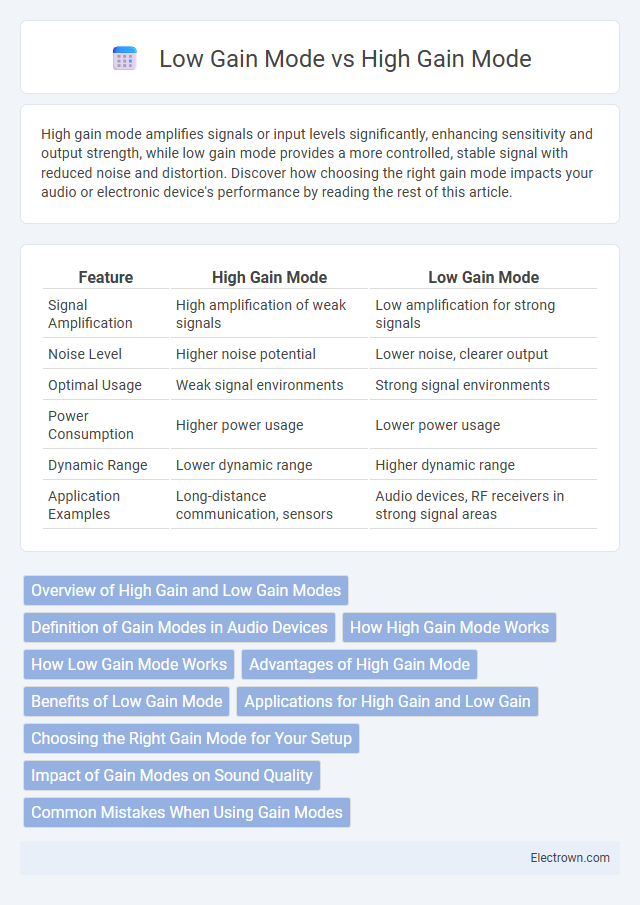
| Feature | High Gain Mode | Low Gain Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Amplification | High amplification of weak signals | Low amplification for strong signals |
| Noise Level | Higher noise potential | Lower noise, clearer output |
| Optimal Usage | Weak signal environments | Strong signal environments |
| Power Consumption | Higher power usage | Lower power usage |
| Dynamic Range | Lower dynamic range | Higher dynamic range |
| Application Examples | Long-distance communication, sensors | Audio devices, RF receivers in strong signal areas |
Overview of High Gain and Low Gain Modes
High gain mode amplifies the input signal to achieve greater sensitivity, commonly used in environments where detecting weak signals is crucial, such as in radio receivers or sensor applications. Low gain mode reduces signal amplification to prevent overload and distortion, offering better performance in high-signal environments by maintaining signal integrity and dynamic range. The choice between high and low gain modes directly impacts system performance by balancing sensitivity and signal clarity depending on the application requirements.
Definition of Gain Modes in Audio Devices
Gain modes in audio devices refer to settings that control the amplification level of the input signal. High gain mode increases signal strength to drive signals harder, ideal for low-output microphones or instruments needing more volume and presence. Low gain mode offers a cleaner, less amplified signal, reducing noise and distortion for sources with strong output levels, helping maintain audio fidelity in your recordings or live sound.
How High Gain Mode Works
High gain mode amplifies the input signal by increasing the sensitivity of the device's preamplifier, allowing it to detect weaker signals with improved clarity. This mode adjusts the gain stages to boost signal strength, which is particularly useful in environments with low signal levels or long cable runs. By enhancing signal amplitude, high gain mode improves overall reception quality but may also increase susceptibility to noise and distortion.
How Low Gain Mode Works
Low gain mode operates by reducing the signal amplification, which minimizes noise and preserves signal integrity for accurate measurements in high-intensity environments. This mode is essential in devices like sensors and amplifiers to prevent saturation when encountering strong input signals. By limiting the gain, low gain mode ensures stable performance and extends the dynamic range of electronic systems.
Advantages of High Gain Mode
High gain mode amplifies weak signals, significantly enhancing reception quality in low-signal environments. It improves sensitivity, allowing your device to capture distant or faint transmissions with greater clarity and reliability. This mode is ideal for boosting performance in challenging scenarios where signal strength is critically low.
Benefits of Low Gain Mode
Low gain mode enhances audio clarity by minimizing distortion and background noise, making it ideal for recording soft or distant sounds. It ensures a cleaner signal, preserving the integrity of the original audio without overwhelming the input. This mode also reduces the risk of audio clipping, providing a more natural and balanced sound quality.
Applications for High Gain and Low Gain
High gain mode is ideal for applications requiring enhanced sensitivity, such as capturing faint astronomical objects or deep-space imaging, where amplifying weak signals is crucial. Low gain mode suits scenarios demanding higher dynamic range and less noise, including bright daylight photography or imaging high-intensity light sources with precise detail. These modes optimize sensor performance based on the specific illumination conditions and desired image quality.
Choosing the Right Gain Mode for Your Setup
Selecting the right gain mode depends on your audio or radio frequency application, where high gain mode amplifies weak signals to enhance sensitivity and clarity in low-signal environments. Low gain mode is ideal for situations with strong signals, preventing distortion and maintaining sound or signal quality by reducing excessive amplification. Your choice between high and low gain modes directly impacts performance, balancing noise levels and signal integrity to optimize your setup.
Impact of Gain Modes on Sound Quality
High gain mode amplifies the input signal, producing a more distorted and aggressive tone favored in heavy metal and hard rock genres, while low gain mode provides cleaner, more transparent sound ideal for jazz and blues. The increased distortion in high gain can introduce noise and reduce clarity, potentially masking subtle audio details, whereas low gain maintains sonic accuracy and dynamic nuance. Understanding the impact of gain modes helps you tailor your sound quality to match the desired musical context and tonal characteristics.
Common Mistakes When Using Gain Modes
Common mistakes when using high gain mode include excessive noise amplification and signal distortion due to overpowering the input stage, which compromises audio clarity. Low gain mode errors often result from insufficient signal strength, causing weak output and reduced dynamic range, especially in quiet environments. Proper adjustment tailored to the input source is essential for optimal performance and avoiding degradation in sound quality.
high gain vs low gain mode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com