FLAC offers lossless compression, preserving original audio quality while reducing file size, whereas WAV provides uncompressed audio with the highest fidelity but significantly larger files. Explore the rest of the article to understand which format suits Your needs for audio storage and playback.
Table of Comparison
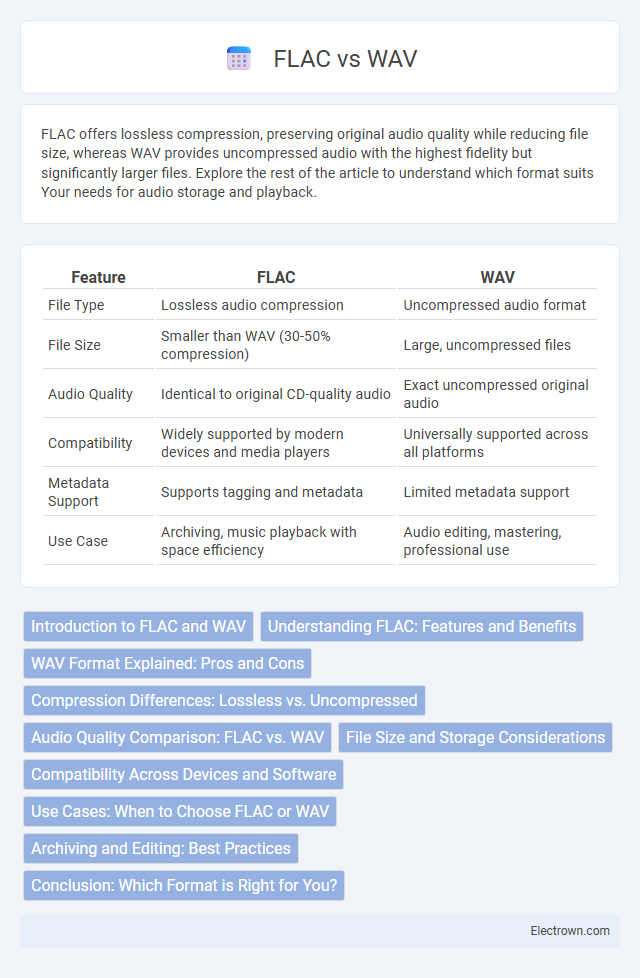
| Feature | FLAC | WAV |
|---|---|---|
| File Type | Lossless audio compression | Uncompressed audio format |
| File Size | Smaller than WAV (30-50% compression) | Large, uncompressed files |
| Audio Quality | Identical to original CD-quality audio | Exact uncompressed original audio |
| Compatibility | Widely supported by modern devices and media players | Universally supported across all platforms |
| Metadata Support | Supports tagging and metadata | Limited metadata support |
| Use Case | Archiving, music playback with space efficiency | Audio editing, mastering, professional use |
Introduction to FLAC and WAV
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) and WAV (Waveform Audio File Format) are popular audio formats used for storing high-quality audio. FLAC compresses audio data without any loss of quality, resulting in smaller file sizes ideal for storage and streaming. WAV files store uncompressed audio data, preserving original sound fidelity but requiring significantly more storage space compared to FLAC.
Understanding FLAC: Features and Benefits
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) is a popular audio format that compresses audio files without any loss in quality, preserving the original sound fidelity. Unlike WAV, which stores uncompressed audio data leading to larger file sizes, FLAC reduces file sizes by approximately 50-60% while maintaining the exact audio quality. If you want to save storage space without sacrificing the accuracy of your music collection, FLAC offers an efficient and convenient solution.
WAV Format Explained: Pros and Cons
WAV format offers uncompressed audio files with high fidelity, making it ideal for professional audio editing and mastering due to its lossless quality. However, WAV files have large file sizes compared to compressed formats like FLAC, which can limit storage and sharing efficiency. Your choice depends on whether audio quality or file size is a higher priority for your needs.
Compression Differences: Lossless vs. Uncompressed
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) employs lossless compression to reduce file size without sacrificing audio quality, maintaining every bit of original data. WAV (Waveform Audio File Format) stores uncompressed audio, preserving raw sound data but resulting in significantly larger files. The primary distinction lies in FLAC's efficient compression algorithm versus WAV's fully uncompressed format, impacting storage requirements and playback compatibility.
Audio Quality Comparison: FLAC vs. WAV
FLAC and WAV both offer lossless audio quality, ensuring the original sound is preserved without degradation. WAV files provide uncompressed audio, delivering perfect fidelity but with large file sizes, whereas FLAC uses compression algorithms to reduce file size by up to 50-60% without sacrificing audio integrity. Audiophiles and professionals often prefer WAV for editing due to its simplicity, but FLAC is favored for storage and streaming because of its efficient file size and identical sound quality.
File Size and Storage Considerations
FLAC files provide lossless compression, reducing file size by approximately 40-60% compared to WAV, which stores audio data in an uncompressed format requiring significantly more storage space. Choosing FLAC optimizes your storage capacity without sacrificing audio quality, making it ideal for limited disk space environments. WAV files demand larger storage, making them less efficient for archiving extensive music libraries or portable devices.
Compatibility Across Devices and Software
WAV files offer broad compatibility across most devices and software due to their uncompressed, standard format widely supported in professional audio environments. FLAC, while providing lossless compression and reduced file sizes, is not natively compatible with all media players and devices, requiring specific support or additional codecs. You should choose WAV for maximum playback compatibility or FLAC for efficient storage with good but slightly limited device support.
Use Cases: When to Choose FLAC or WAV
FLAC is ideal for audiophiles and music streaming services seeking lossless compression with reduced file sizes, enabling efficient storage and transmission without quality loss. WAV is preferred in professional audio production and editing environments where uncompromised, raw audio data is essential for mixing, mastering, and archival purposes. Choose FLAC for personal music libraries and distribution while opting for WAV in scenarios demanding maximum audio fidelity and seamless compatibility with digital audio workstations.
Archiving and Editing: Best Practices
For archiving, FLAC is ideal due to its lossless compression, preserving audio quality while saving storage space compared to uncompressed WAV files. WAV files are preferred in editing workflows because they store raw audio data, allowing for better compatibility with professional audio software and more precise manipulation. When managing your audio library, use FLAC for long-term storage and WAV for detailed editing to balance quality and efficiency.
Conclusion: Which Format is Right for You?
FLAC offers lossless compression, reducing file size without sacrificing audio quality, making it ideal for archiving and streaming where storage and bandwidth matter. WAV delivers uncompressed, high-fidelity sound favored in professional audio editing and situations demanding absolute audio accuracy. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize storage efficiency and compatibility (FLAC) or maximum raw audio quality for detailed sound work (WAV).
flac vs wav Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com