Optical audio cables transmit digital sound signals through light pulses, offering high-quality audio free from electromagnetic interference, while HDMI cables carry both high-definition video and audio signals through a single connection, supporting advanced audio formats like Dolby Atmos. Discover which connection best suits Your home entertainment setup by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
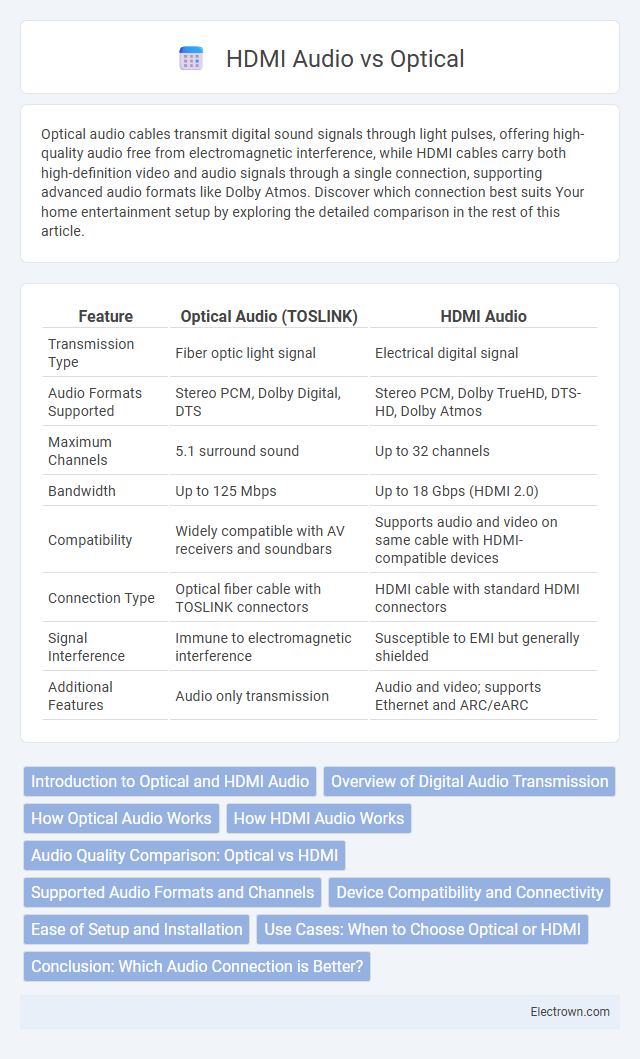
| Feature | Optical Audio (TOSLINK) | HDMI Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Type | Fiber optic light signal | Electrical digital signal |
| Audio Formats Supported | Stereo PCM, Dolby Digital, DTS | Stereo PCM, Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD, Dolby Atmos |
| Maximum Channels | 5.1 surround sound | Up to 32 channels |
| Bandwidth | Up to 125 Mbps | Up to 18 Gbps (HDMI 2.0) |
| Compatibility | Widely compatible with AV receivers and soundbars | Supports audio and video on same cable with HDMI-compatible devices |
| Connection Type | Optical fiber cable with TOSLINK connectors | HDMI cable with standard HDMI connectors |
| Signal Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference | Susceptible to EMI but generally shielded |
| Additional Features | Audio only transmission | Audio and video; supports Ethernet and ARC/eARC |
Introduction to Optical and HDMI Audio
Optical audio uses fiber optic cables to transmit digital audio signals as light pulses, ensuring minimal interference and supporting formats like Dolby Digital and DTS. HDMI audio carries uncompressed multi-channel audio along with video signals on a single cable, supporting advanced audio formats such as Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio. Both technologies offer high-quality sound transmission, but HDMI provides broader compatibility and higher bandwidth for immersive audio experiences.
Overview of Digital Audio Transmission
Optical and HDMI both transmit high-quality digital audio signals, with optical using TOSLINK cables and HDMI employing a single cable for audio and video. Optical cables support formats like Dolby Digital and DTS but are limited to compressed audio, whereas HDMI carries uncompressed multichannel audio, including advanced formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio. Your choice depends on device compatibility and audio format requirements, with HDMI providing greater bandwidth and flexibility for modern home theater systems.
How Optical Audio Works
Optical audio transmits sound using light signals through fiber optic cables, converting electrical audio signals into pulses of infrared light. This method reduces electromagnetic interference, ensuring a clear and high-quality digital audio transmission. Your audio system receives the light pulses and converts them back into electrical signals to produce sound, making optical audio ideal for connecting devices like TVs, soundbars, and gaming consoles.
How HDMI Audio Works
HDMI audio transmits uncompressed digital audio signals alongside video data through a single cable, supporting multiple channels and high-definition sound formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio. Unlike optical audio, which uses light to transfer digital audio but is limited to compressed formats and fewer channels, HDMI enables higher bandwidth and richer audio quality. This integration allows seamless synchronization of audio and video for home theater systems and gaming consoles.
Audio Quality Comparison: Optical vs HDMI
HDMI supports uncompressed audio formats such as Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, delivering superior audio quality compared to optical connections, which are limited to compressed formats like Dolby Digital and DTS. Optical cables cannot transmit high-resolution audio signals, resulting in potential loss of audio fidelity for formats beyond standard surround sound. HDMI's capability to carry both high-definition video and multi-channel audio signals ensures a seamless and enhanced home theater experience with optimal sound clarity.
Supported Audio Formats and Channels
Optical audio cables support compressed surround sound formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, typically handling up to 5.1 channels, whereas HDMI supports a wider range of audio formats including uncompressed PCM, Dolby TrueHD, and DTS-HD Master Audio, allowing for up to 7.1 channels and even immersive formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. HDMI's bandwidth capacity enables transmission of high-resolution multi-channel audio without compression, delivering superior audio quality compared to optical's limited bandwidth and format support. Devices utilizing HDMI benefit from compatibility with modern audio standards, making it the preferred choice for advanced home theater systems requiring immersive and high-fidelity sound.
Device Compatibility and Connectivity
Optical audio supports a wide range of devices including older AV receivers, soundbars, and gaming consoles, offering reliable connectivity through TOSLINK ports. HDMI audio provides superior compatibility with modern devices such as 4K TVs, Blu-ray players, and gaming systems, enabling both high-definition video and multi-channel audio via a single cable. HDMI also supports advanced audio formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X, which optical connections cannot handle due to bandwidth limitations.
Ease of Setup and Installation
Optical audio cables offer straightforward setup with a single, durable cable that transmits high-quality digital sound, making them ideal for standard home theater systems. HDMI cables carry both audio and video signals through one connection, simplifying installation by reducing the number of cables needed and ensuring seamless integration with modern devices like TVs, gaming consoles, and AV receivers. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize simplicity with a single-purpose connection or the convenience of consolidating audio and video into one cable.
Use Cases: When to Choose Optical or HDMI
Optical audio is ideal for connecting older audio equipment or soundbars that lack HDMI ports, providing high-quality digital sound without video signals, making it perfect for simple audio setups or gaming consoles. HDMI audio is preferred when you need to transmit both high-definition video and multi-channel audio through a single cable, commonly used for home theater systems, Blu-ray players, and streaming devices to deliver superior sound formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS:X. Your choice depends on your device compatibility and whether you require integrated audio-video transmission or just audio output.
Conclusion: Which Audio Connection is Better?
Optical audio connections provide reliable, high-quality sound transmission with minimal interference, making them ideal for standard stereo and surround sound setups. HDMI supports higher bandwidth, enabling uncompressed multichannel audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, which enhances your home theater experience. Your choice depends on the audio format compatibility and equipment, but HDMI generally offers superior audio performance for advanced systems.
optical vs hdmi audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com