Zero ohm cables offer negligible resistance, ideal for applications demanding minimal signal loss, whereas low impedance cables prioritize controlled impedance to prevent signal reflection in high-frequency environments. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right cable for your specific needs--explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
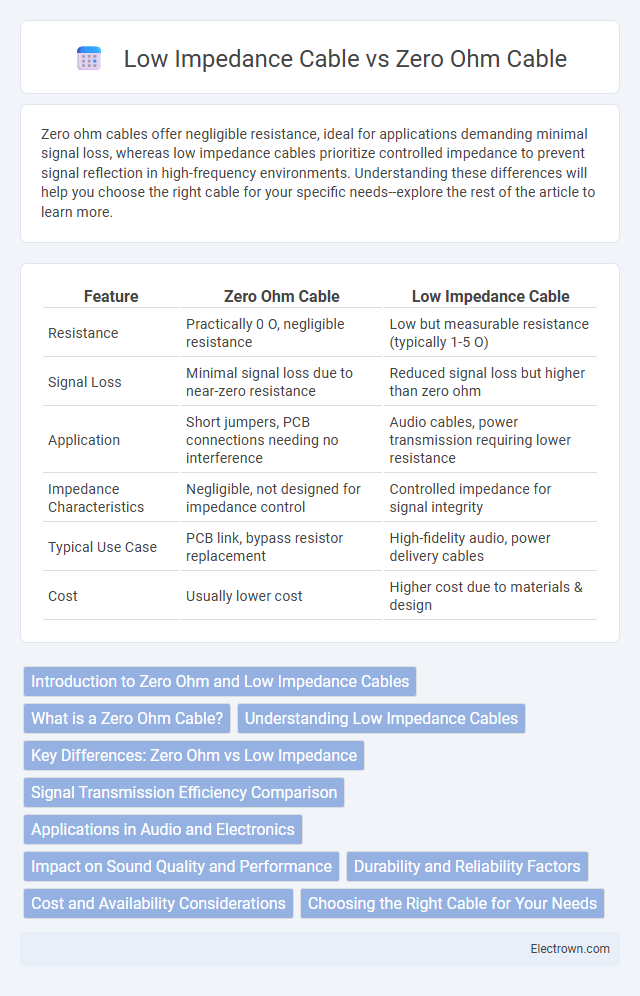
| Feature | Zero Ohm Cable | Low Impedance Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Practically 0 O, negligible resistance | Low but measurable resistance (typically 1-5 O) |
| Signal Loss | Minimal signal loss due to near-zero resistance | Reduced signal loss but higher than zero ohm |
| Application | Short jumpers, PCB connections needing no interference | Audio cables, power transmission requiring lower resistance |
| Impedance Characteristics | Negligible, not designed for impedance control | Controlled impedance for signal integrity |
| Typical Use Case | PCB link, bypass resistor replacement | High-fidelity audio, power delivery cables |
| Cost | Usually lower cost | Higher cost due to materials & design |
Introduction to Zero Ohm and Low Impedance Cables
Zero ohm cables are designed to present negligible resistance, allowing maximum current flow with minimal signal loss, making them ideal for high-frequency and sensitive electronic circuits. Low impedance cables maintain a controlled impedance level, typically between 50 to 75 ohms, ensuring signal integrity and reducing reflections in audio, video, and data transmission applications. Choosing between zero ohm and low impedance cables depends on specific performance requirements, including minimizing resistance versus controlling signal characteristic impedance for optimal system functionality.
What is a Zero Ohm Cable?
A zero ohm cable is designed to provide an almost negligible resistance, effectively acting as a direct electrical connection with minimal voltage drop. Unlike low impedance cables that present a small but measurable resistance, zero ohm cables ensure maximum current flow and signal integrity in sensitive electronic applications. These cables are commonly used in testing environments, circuit board jumpers, and situations where an ideal conductor is essential.
Understanding Low Impedance Cables
Low impedance cables typically range between 20 to 75 ohms, minimizing signal loss and improving audio fidelity in professional and consumer electronics. Unlike zero ohm cables which are essentially jumper wires with negligible resistance used for circuit bridging, low impedance cables optimize performance in high-frequency transmission environments. Understanding low impedance cables involves recognizing their ability to reduce noise interference and maintain signal integrity over longer distances.
Key Differences: Zero Ohm vs Low Impedance
Zero ohm cables essentially function as simple jumper wires with minimal resistance, often used to connect circuit points without affecting the electrical path. Low impedance cables provide a controlled, small but non-zero resistance that helps maintain signal integrity and reduce noise over longer distances. The key difference lies in zero ohm cables offering virtually no resistance, while low impedance cables are designed to optimize performance by balancing resistance and signal quality.
Signal Transmission Efficiency Comparison
Zero ohm cables minimize resistance to nearly negligible levels, ensuring maximal signal transmission efficiency by preventing voltage drops and maintaining signal integrity over short distances. Low impedance cables, while slightly higher in resistance, are designed to match the impedance of connected devices, reducing signal reflections and enhancing performance in complex audio or data systems. Your choice between zero ohm and low impedance cables depends on the specific application, balancing minimal resistance with impedance matching for optimal signal fidelity.
Applications in Audio and Electronics
Zero ohm cables are primarily used as jumpers on circuit boards to connect traces without adding resistance, making them ideal for electronics prototyping and PCB design. Low impedance cables, on the other hand, are essential in audio applications for transmitting signals with minimal loss and reduced noise interference, ensuring high-quality sound reproduction. Choosing the right cable can significantly impact Your audio system's clarity and the reliability of electronic circuits.
Impact on Sound Quality and Performance
Zero ohm cables minimize signal loss by providing virtually no resistance, resulting in a cleaner and more accurate audio transfer with minimal distortion. Low impedance cables, typically under 50 ohms, allow for better current flow, maintaining clarity and dynamic range in sound reproduction, especially over longer distances. Selecting cables with lower impedance values improves overall sound quality by reducing noise and preserving the integrity of the audio signal.
Durability and Reliability Factors
Zero ohm cables feature minimal resistance, enhancing signal integrity and reducing power loss, which directly contributes to greater reliability in electronic circuits. Low impedance cables, designed to maintain consistent impedance, minimize signal reflections and electromagnetic interference, boosting durability in high-frequency applications. Both cable types prioritize durability through robust insulation materials and construction, but low impedance cables offer superior performance in environments where signal stability and noise reduction are critical.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Zero ohm cables generally offer lower costs due to simpler manufacturing requirements and widespread availability in standard configurations. Low impedance cables typically incur higher expenses because of enhanced materials and construction techniques designed to reduce signal loss and interference. Availability of low impedance cables can be limited, especially in specialized applications, influencing overall project budget and delivery timelines.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate cable depends on the specific electrical requirements and signal integrity considerations. Zero ohm cables offer minimal resistance, ideal for high-current applications where voltage drop must be avoided, while low impedance cables are designed to maintain signal quality by minimizing reflections and losses in high-frequency transmissions. Understanding the load characteristics and frequency range ensures optimal performance and reliability in your electrical or communication systems.
zero ohm vs low impedance cable Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com