A preamp shapes and controls the audio signal, enhancing tone and volume before sending it to a power amp, which then amplifies the signal to drive speakers with enough power for audible sound. Dive into the rest of the article to understand how your audio setup can benefit from the right combination of preamp and power amp.
Table of Comparison
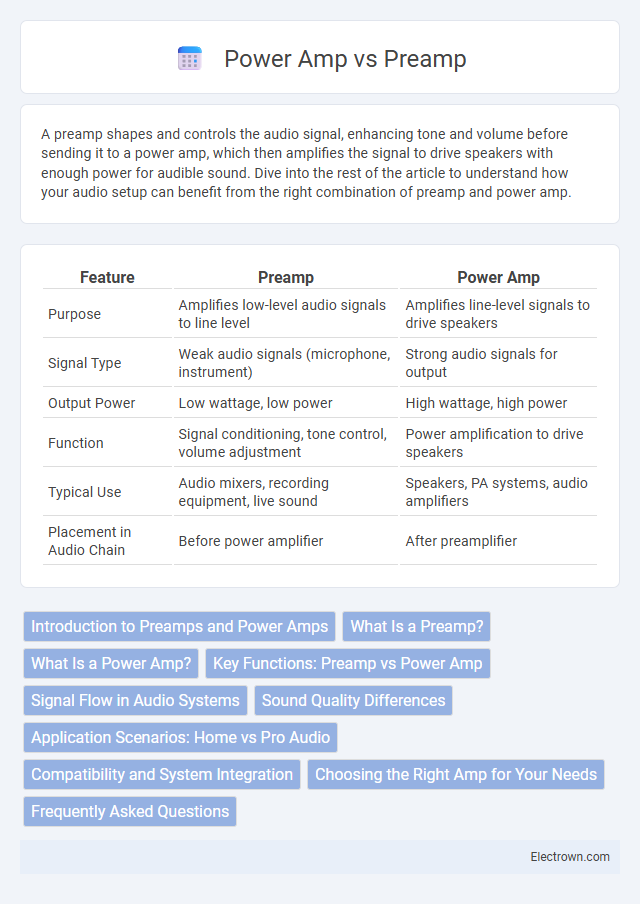
| Feature | Preamp | Power Amp |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Amplifies low-level audio signals to line level | Amplifies line-level signals to drive speakers |
| Signal Type | Weak audio signals (microphone, instrument) | Strong audio signals for output |
| Output Power | Low wattage, low power | High wattage, high power |
| Function | Signal conditioning, tone control, volume adjustment | Power amplification to drive speakers |
| Typical Use | Audio mixers, recording equipment, live sound | Speakers, PA systems, audio amplifiers |
| Placement in Audio Chain | Before power amplifier | After preamplifier |
Introduction to Preamps and Power Amps
Preamps boost low-level audio signals from sources like microphones or instruments to line level, preparing them for further processing or amplification. Power amps increase the line-level signal's power, driving speakers to produce audible sound with sufficient volume and clarity. Understanding the distinct roles of preamps and power amps is essential for optimizing audio system performance.
What Is a Preamp?
A preamp, or preamplifier, boosts weak audio signals from sources like microphones or instruments to line-level strength, ensuring clear sound quality before amplification. It shapes tone and controls volume, offering essential adjustments to your audio signal's character. Unlike power amps, which drive speakers with high power output, preamps prepare your audio for precise and distortion-free amplification.
What Is a Power Amp?
A power amp amplifies the audio signal to a level sufficient to drive speakers, converting low-level signals from the preamp into high-power output. It plays a crucial role in delivering clear, loud sound, especially in home audio systems or live performances. Your choice between preamp and power amp depends on whether you need tone shaping or sheer amplification power.
Key Functions: Preamp vs Power Amp
The preamp amplifies low-level audio signals and shapes the tone by controlling volume, gain, and equalization settings. The power amp receives the processed signal from the preamp and delivers high power output to drive speakers efficiently. Your audio system relies on the preamp for signal clarity and control, while the power amp ensures sufficient power and sound reinforcement.
Signal Flow in Audio Systems
In audio systems, signal flow begins with the preamp, which boosts weak audio signals from sources like microphones or instruments to line level while shaping tone and adding gain control. The power amp then takes this line-level signal and amplifies it significantly to drive speakers with enough power for audible sound output. Understanding this separation ensures Your audio setup achieves optimal clarity and volume control.
Sound Quality Differences
Preamp and power amp components each influence sound quality distinctively, with preamps shaping tone and adding gain, while power amps control volume and drive speakers, affecting dynamic response and clarity. A high-quality preamp maintains signal integrity, providing clean, detailed audio input to your power amp, which then amplifies the signal without distortion or coloration. Understanding the tonal characteristics and transparency of both units ensures your audio system delivers optimal sound fidelity and an immersive listening experience.
Application Scenarios: Home vs Pro Audio
Preamp and power amp serve distinct roles in home and pro audio setups, with preamps primarily shaping sound quality and volume control while power amps drive speakers with necessary wattage. In home audio systems, preamps are often integrated and tailored for convenience and moderate volume levels, whereas professional audio environments demand specialized preamps and high-powered amps to deliver clear, distortion-free sound at large venues. Your choice between preamp and power amp depends on application scenarios, balancing sound clarity, power needs, and system complexity for either intimate home listening or professional stage performance.
Compatibility and System Integration
Preamp and power amp compatibility is crucial for optimal audio system integration, as preamps control signal processing while power amps drive speakers with appropriate voltage and current levels. Ensuring matching input and output impedances between preamp and power amp prevents signal degradation and maximizes sound clarity. Proper integration involves selecting components with harmonized gain structures and connectivity options like balanced XLR or unbalanced RCA, which facilitates seamless signal flow and reduces noise interference.
Choosing the Right Amp for Your Needs
Choosing the right amp depends on your audio setup and performance goals. A preamp controls volume and tone, shaping your sound before sending the signal to the power amp, which delivers the necessary wattage to drive speakers. Your ideal choice balances tonal control with power output, ensuring the best audio quality for your environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions about preamp vs power amp often revolve around their distinct roles in audio systems: the preamp processes and controls audio signals, while the power amp amplifies these signals to drive speakers. Many users wonder if both components are necessary; your setup depends on whether you need signal shaping (preamp) or simply amplification (power amp). Common inquiries also address compatibility, sound quality impact, and optimal configurations for home theater or music systems.
preamp vs power amp Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com