Sallen-Key filters offer simplicity and ease of design for low-pass high-pass applications, while multiple feedback filters provide greater flexibility and accurate gain control in band-pass and notch filter designs. Explore the rest of the article to understand which filter suits your specific circuit requirements.
Table of Comparison
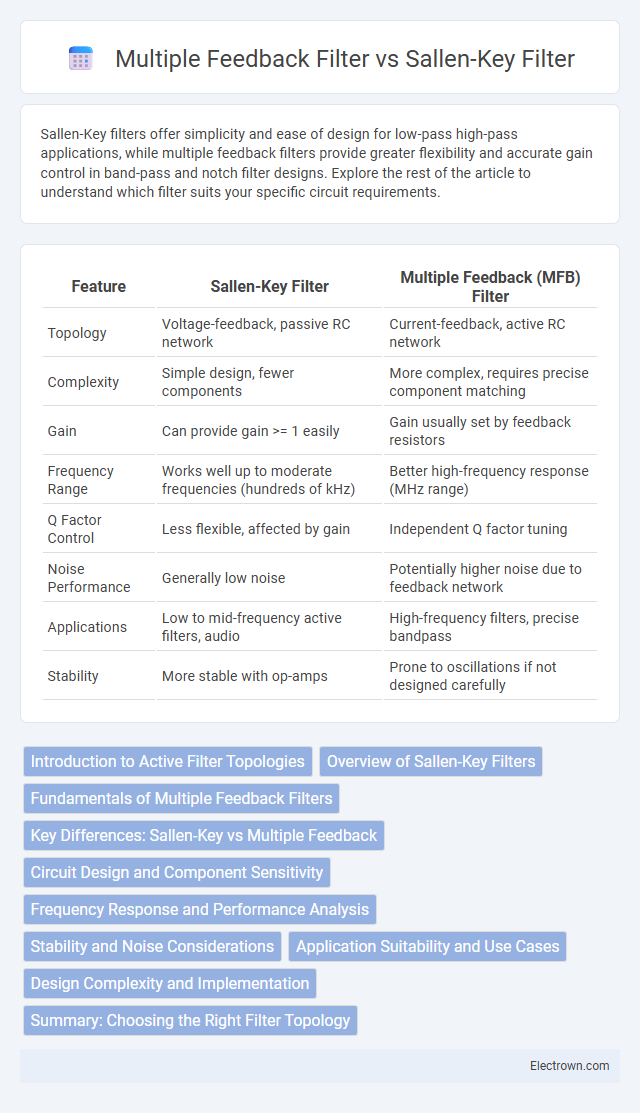
| Feature | Sallen-Key Filter | Multiple Feedback (MFB) Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Topology | Voltage-feedback, passive RC network | Current-feedback, active RC network |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | More complex, requires precise component matching |
| Gain | Can provide gain >= 1 easily | Gain usually set by feedback resistors |
| Frequency Range | Works well up to moderate frequencies (hundreds of kHz) | Better high-frequency response (MHz range) |
| Q Factor Control | Less flexible, affected by gain | Independent Q factor tuning |
| Noise Performance | Generally low noise | Potentially higher noise due to feedback network |
| Applications | Low to mid-frequency active filters, audio | High-frequency filters, precise bandpass |
| Stability | More stable with op-amps | Prone to oscillations if not designed carefully |
Introduction to Active Filter Topologies
Sallen-Key and Multiple Feedback (MFB) filters are two common active filter topologies used in analog signal processing. Sallen-Key filters are favored for their simplicity and ease of design, utilizing operational amplifiers with passive components to achieve low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass responses. Your choice between these topologies depends on factors like filter order, frequency accuracy, and component sensitivity, with MFB filters offering better performance in high-quality factor applications.
Overview of Sallen-Key Filters
Sallen-Key filters are widely used active filters known for their simple design and ease of implementation in low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass configurations. These filters utilize a single operational amplifier combined with resistors and capacitors to achieve a desired frequency response, making them ideal for applications requiring stable gain and predictable cutoff frequencies. Your choice of a Sallen-Key filter ensures a straightforward approach to analog signal processing with minimal component count and reliable performance.
Fundamentals of Multiple Feedback Filters
Multiple feedback filters utilize a feedback topology where the output is fed back through multiple paths to configure the filter's frequency response, enhancing selectivity and stability over the Sallen-Key design. These filters provide precise control over gain, Q factor, and center frequency by adjusting resistor and capacitor values within the feedback loop. Understanding these fundamentals can help you design filters tailored for high-performance applications requiring sharp cutoff slopes and minimal distortion.
Key Differences: Sallen-Key vs Multiple Feedback
The Sallen-Key filter uses a voltage follower configuration that provides high input impedance and simple design, making it ideal for low-frequency applications and low-Q factors. In contrast, the Multiple Feedback (MFB) filter employs feedback through multiple resistors and capacitors, enabling higher Q factors and better performance in narrow-band filters or high-frequency circuits. Sallen-Key designs are more sensitive to component tolerance variations, while MFB filters offer improved stability and precision in frequency response.
Circuit Design and Component Sensitivity
Sallen-Key filters utilize a simple op-amp configuration offering ease of design with fewer components, making them less sensitive to component variations and ideal for low-frequency applications. Multiple Feedback (MFB) filters involve a more complex feedback network that provides higher performance in terms of gain and Q-factor but increases sensitivity to resistor and capacitor tolerances. Component matching is critical in MFB designs to maintain filter accuracy, whereas Sallen-Key circuits offer more robust behavior against component deviations due to their buffered topology.
Frequency Response and Performance Analysis
The Sallen-Key filter exhibits a simpler design with fewer components, delivering a moderately stable frequency response ideal for low to mid-frequency applications, while the Multiple Feedback (MFB) filter offers enhanced frequency selectivity and better high-frequency performance due to its feedback network topology. MFB filters provide superior gain accuracy and higher Q factors, making them suitable for precision filtering and applications requiring sharper cutoff slopes. Frequency response in MFB designs is less susceptible to component variations, translating to improved performance stability over a broader frequency range compared to Sallen-Key configurations.
Stability and Noise Considerations
Sallen-Key filters typically demonstrate superior stability due to their inherently simpler feedback network, which reduces sensitivity to component variations and minimizes the risk of oscillations. Multiple feedback filters tend to introduce higher noise levels because their topology involves active elements in both input and feedback paths, increasing thermal and flicker noise contributions. When designing for low-noise applications, the Sallen-Key topology is often preferred, whereas multiple feedback filters require careful component selection and layout techniques to maintain stability and noise performance.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Sallen-Key filters offer simplicity and low component count, making them ideal for low-frequency applications such as audio tone controls and active crossover networks. Multiple Feedback (MFB) filters provide better frequency stability and higher Q factors, suited for precision narrow-band filtering in RF circuits and sensor signal conditioning. Engineers often choose Sallen-Key for ease of design in general-purpose analog filtering, while MFB is preferred in high-performance applications requiring accurate frequency response and minimal component sensitivity.
Design Complexity and Implementation
Sallen-Key filters offer simpler design with fewer components and straightforward tuning, making them ideal for low-order active filter implementations. Multiple feedback (MFB) filters involve more complex design calculations and additional components, providing greater control over bandwidth and gain but requiring careful consideration of op-amp characteristics. Your choice between Sallen-Key and MFB filters depends largely on the balance between design simplicity and the precision needed in your application.
Summary: Choosing the Right Filter Topology
Sallen-Key and multiple feedback filters each offer distinct advantages for signal processing applications; Sallen-Key filters provide simplicity and ease of design ideal for low-frequency active filter stages, while multiple feedback filters excel in achieving higher Q factors and better performance at higher frequencies. Selecting the right filter topology depends on design requirements such as bandwidth, gain stability, and noise sensitivity. Engineers often prefer Sallen-Key for low-frequency LPF or HPF stages and multiple feedback filters for precise bandpass or notch filters requiring sharper roll-off.
sallen-key vs multiple feedback filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com