C4 capacitors offer high capacitance with excellent temperature stability, making them suitable for precision analog circuits, while C0G capacitors provide ultra-low loss and negligible capacitance change over temperature, ideal for RF and high-frequency applications. Explore the differences in performance, materials, and best use cases to determine which capacitor meets your specific design needs.
Table of Comparison
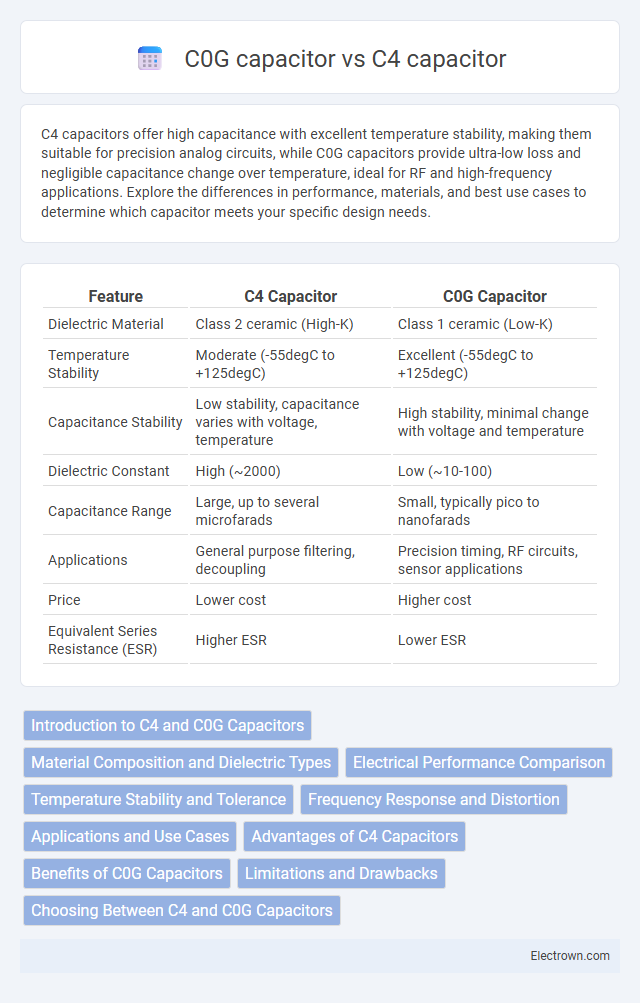
| Feature | C4 Capacitor | C0G Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Material | Class 2 ceramic (High-K) | Class 1 ceramic (Low-K) |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate (-55degC to +125degC) | Excellent (-55degC to +125degC) |
| Capacitance Stability | Low stability, capacitance varies with voltage, temperature | High stability, minimal change with voltage and temperature |
| Dielectric Constant | High (~2000) | Low (~10-100) |
| Capacitance Range | Large, up to several microfarads | Small, typically pico to nanofarads |
| Applications | General purpose filtering, decoupling | Precision timing, RF circuits, sensor applications |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Higher ESR | Lower ESR |
Introduction to C4 and C0G Capacitors
C4 and C0G capacitors differ primarily in their dielectric materials and performance characteristics. C0G capacitors use a stable ceramic dielectric with minimal temperature and voltage dependency, making them ideal for precise and high-frequency applications. You should consider C4 capacitors when requiring different voltage ratings and specific capacitance values, but they generally offer less stability compared to C0G types.
Material Composition and Dielectric Types
C4 capacitors typically use high-k ceramic dielectric materials like X7R or X5R, which provide greater capacitance but exhibit higher losses and temperature sensitivity. C0G capacitors, also known as NP0, utilize a stable Class 1 ceramic dielectric composed of titanium dioxide and other oxides, ensuring minimal temperature coefficient and low dielectric loss. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize capacitance stability and low loss (C0G) or higher capacitance density with some variability (C4).
Electrical Performance Comparison
C4 capacitors exhibit higher dielectric constants leading to greater capacitance per volume but suffer from higher dielectric losses and temperature dependence compared to C0G capacitors. C0G capacitors, classified as Class 1 ceramics, provide excellent electrical stability with near-zero temperature coefficient and minimal voltage dependence, making them ideal for precision applications. The superior low dissipation factor and high insulation resistance of C0G capacitors result in lower signal distortion and improved overall electrical performance compared to C4 types.
Temperature Stability and Tolerance
C0G capacitors exhibit exceptional temperature stability with minimal capacitance change, typically within +-30 ppm/degC, making them ideal for precision applications requiring consistent performance across wide temperature ranges. In contrast, C4 capacitors, designed primarily for high voltage applications, have a wider tolerance range and less stable capacitance over temperature variations, often deviating more significantly compared to C0G types. The superior tolerance and thermal stability of C0G capacitors ensure reliable operation in critical electronic circuits, whereas C4 capacitors prioritize voltage handling over temperature-sensitive performance.
Frequency Response and Distortion
C0G capacitors exhibit superior frequency response and minimal distortion due to their stable capacitance and low dissipation factor across a wide frequency range, making them ideal for high-frequency and precision applications. C4 capacitors, typically used in less critical circuits, may experience greater capacitance variation and higher distortion at elevated frequencies, impacting signal integrity. Your choice between C4 and C0G capacitors should prioritize low distortion and consistent frequency response, especially in RF and audio circuits.
Applications and Use Cases
C4 capacitors, known for their high capacitance stability over temperature, are ideal for applications requiring precision timing and filtering in RF circuits and oscillators. C0G capacitors excel in high-frequency and high-voltage environments, making them suitable for signal processing, resonant circuits, and sensor interfaces where low loss and minimal distortion are critical. Your choice depends on the need for either thermal stability with moderate capacitance (C4) or ultra-stable performance with minimal dielectric absorption (C0G).
Advantages of C4 Capacitors
C4 capacitors offer superior energy density and higher capacitance values compared to C0G capacitors, making them ideal for applications requiring compact size with substantial charge storage. They exhibit enhanced voltage handling and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), which improves overall circuit efficiency and performance in high-frequency environments. Furthermore, C4 capacitors provide better mechanical robustness and stability under thermal stress, extending device lifespan in demanding conditions.
Benefits of C0G Capacitors
C0G capacitors offer superior stability and low dielectric loss, making them ideal for precision applications requiring consistent capacitance over wide temperature ranges. Their minimal variation in capacitance under voltage stress and aging ensures reliable performance in RF circuits and timing devices. Unlike C4 capacitors, C0G capacitors provide low noise and excellent insulation resistance, enhancing overall circuit accuracy and longevity.
Limitations and Drawbacks
C4 capacitors suffer from high dielectric losses and significant capacitance variation with temperature, limiting their stability and precision in sensitive circuits. C0G capacitors offer exceptional stability and low loss but are generally limited in capacitance range and size, affecting their suitability for high-capacitance applications. When selecting a capacitor for your design, consider that C4 types may introduce noise and drift, while C0G capacitors might not meet requirements for large energy storage.
Choosing Between C4 and C0G Capacitors
Selecting between C4 and C0G capacitors depends on the application's frequency stability and dielectric losses requirements. C0G capacitors offer superior temperature stability and low dielectric absorption, making them ideal for precision circuits and RF applications. In contrast, C4 capacitors typically provide higher capacitance in smaller packages but with increased dielectric losses and less stability, suitable for general-purpose filtering where performance consistency is less critical.
C4 capacitor vs C0G capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com