Single CAN systems streamline communication by using one Controller Area Network bus, reducing complexity and costs, while Dual CAN systems offer redundancy and enhanced reliability through two separate buses for critical automotive or industrial applications. Discover how each system impacts your vehicle's performance and safety by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
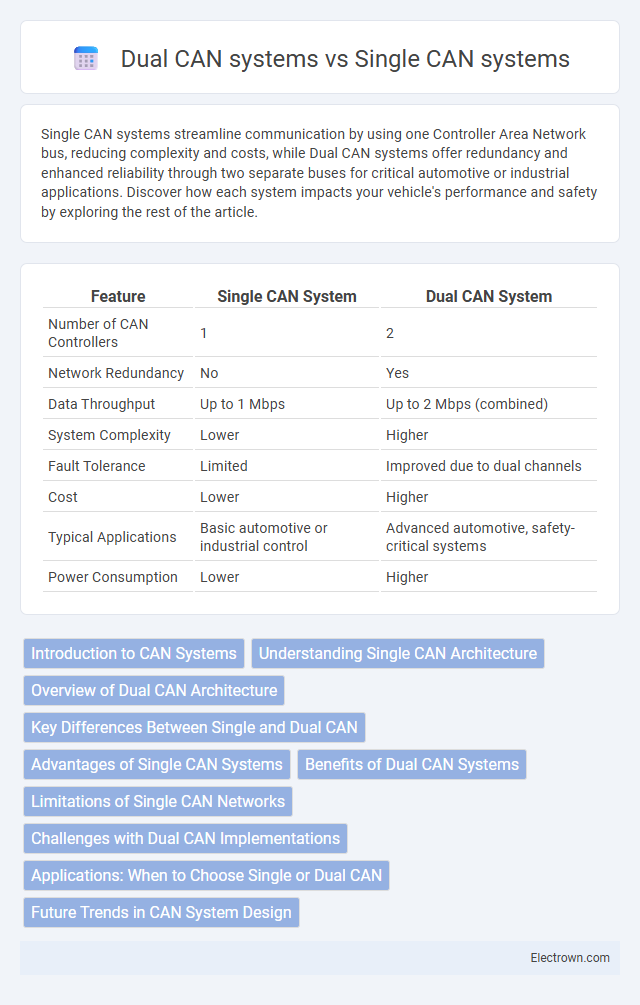
| Feature | Single CAN System | Dual CAN System |
|---|---|---|
| Number of CAN Controllers | 1 | 2 |
| Network Redundancy | No | Yes |
| Data Throughput | Up to 1 Mbps | Up to 2 Mbps (combined) |
| System Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Fault Tolerance | Limited | Improved due to dual channels |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Basic automotive or industrial control | Advanced automotive, safety-critical systems |
| Power Consumption | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to CAN Systems
Controller Area Network (CAN) systems enable robust communication between microcontrollers and devices without a host computer, commonly used in automotive and industrial applications. Single CAN systems utilize one communication bus for data transmission, simplifying design but limiting bandwidth and fault tolerance. Dual CAN systems incorporate two independent CAN buses, enhancing network reliability, fault isolation, and supporting higher data loads for complex vehicle architectures.
Understanding Single CAN Architecture
Single CAN architecture features a single Controller Area Network bus that facilitates communication between multiple electronic control units (ECUs) in a vehicle. This system reduces complexity and cost while providing reliable data transfer at moderate speeds, typically up to 1 Mbps. Your choice of Single CAN suits applications where network traffic is limited and real-time data exchange demands are not extremely high.
Overview of Dual CAN Architecture
Dual CAN architecture features two independent Controller Area Network (CAN) buses, providing enhanced communication redundancy and increased data throughput in automotive and industrial applications. By separating critical control signals and less critical data across two CAN channels, Dual CAN systems improve fault tolerance and system reliability compared to Single CAN setups. Your vehicle or device benefits from uninterrupted data exchange, even if one CAN bus encounters an error or failure.
Key Differences Between Single and Dual CAN
Single CAN systems utilize one Controller Area Network bus for communication, offering simplicity and lower cost but limited bandwidth and redundancy. Dual CAN systems incorporate two separate CAN buses, enhancing communication reliability, fault tolerance, and increased data throughput for complex automotive or industrial applications. Your choice depends on system requirements for performance, safety, and budget constraints.
Advantages of Single CAN Systems
Single CAN systems offer simplicity and cost-efficiency by requiring fewer components and less wiring, making them ideal for basic vehicle applications. Their streamlined architecture reduces the risk of communication errors and simplifies diagnostic processes, enhancing reliability. If your vehicle's data exchange needs are moderate, a Single CAN system provides an effective solution without the complexity of Dual CAN networks.
Benefits of Dual CAN Systems
Dual CAN systems offer enhanced data transmission capacity and improved fault tolerance by utilizing two independent communication channels. This redundancy increases system reliability in automotive networks, allowing for continuous operation even if one CAN bus fails. Additionally, Dual CAN enables simultaneous communication for multiple subsystems, optimizing real-time data exchange and overall vehicle performance.
Limitations of Single CAN Networks
Single CAN networks face limitations such as restricted bandwidth and network length, which can hinder the communication efficiency in complex automotive systems. These constraints reduce data transmission speeds and increase latency, impacting real-time control applications critical to vehicle safety. Your system's scalability may be compromised due to the limited number of nodes supported, making Dual CAN systems a preferred choice for advanced vehicle architectures requiring higher performance and reliability.
Challenges with Dual CAN Implementations
Dual CAN systems present challenges such as increased complexity in hardware design and communication synchronization, leading to higher development costs and potential latency issues. Managing message arbitration and ensuring fault tolerance across both CAN buses require advanced diagnostic tools and meticulous software integration. Your system's reliability may be compromised if these challenges are not properly addressed, impacting overall vehicle network performance.
Applications: When to Choose Single or Dual CAN
Single CAN systems are ideal for basic automotive applications such as engine management and simple body control modules where communication requirements are minimal. Dual CAN systems are preferred in complex vehicles requiring extensive data exchange, such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and body control with multiple electronic control units (ECUs) needing redundancy and higher network bandwidth. Choosing between Single and Dual CAN depends on factors like system complexity, safety requirements, and the need for fault tolerance.
Future Trends in CAN System Design
Future trends in CAN system design emphasize increased data rates and enhanced fault tolerance, shifting from Single CAN to Dual CAN architectures to meet growing demands for automotive and industrial applications. Dual CAN systems provide improved redundancy and reliability, supporting simultaneous communication paths essential for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. Integrating higher-layer protocols and time-sensitive networking in your Dual CAN setup ensures robust, scalable communication for next-generation smart systems.
Single CAN vs Dual CAN systems Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com