E-axis encoders provide precise rotational position data critical for accurate motor control, while H-axis sensors detect magnetic field orientation to optimize angular positioning in various applications. Explore the differences and benefits of each technology to determine which best suits Your specific needs in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
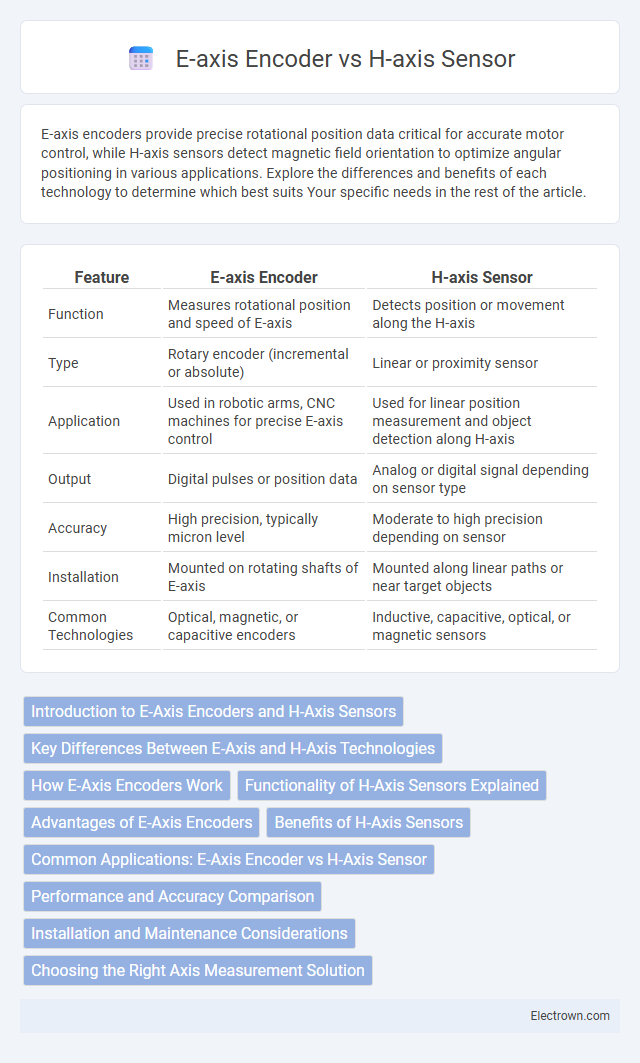
| Feature | E-axis Encoder | H-axis Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures rotational position and speed of E-axis | Detects position or movement along the H-axis |
| Type | Rotary encoder (incremental or absolute) | Linear or proximity sensor |
| Application | Used in robotic arms, CNC machines for precise E-axis control | Used for linear position measurement and object detection along H-axis |
| Output | Digital pulses or position data | Analog or digital signal depending on sensor type |
| Accuracy | High precision, typically micron level | Moderate to high precision depending on sensor |
| Installation | Mounted on rotating shafts of E-axis | Mounted along linear paths or near target objects |
| Common Technologies | Optical, magnetic, or capacitive encoders | Inductive, capacitive, optical, or magnetic sensors |
Introduction to E-Axis Encoders and H-Axis Sensors
E-axis encoders are precision devices that measure rotational position or displacement along the E-axis, widely used in CNC machines and robotics for accurate motion control. H-axis sensors detect linear or rotational movements on the H-axis, ensuring high-resolution feedback essential for industrial automation and machinery alignment. Understanding your choice between E-axis encoders and H-axis sensors is crucial for optimizing system performance and achieving precise motion monitoring in specialized applications.
Key Differences Between E-Axis and H-Axis Technologies
E-axis encoders primarily measure rotational position and angular displacement, offering high precision in motor control systems, while H-axis sensors detect horizontal or linear movement, catering to applications requiring positional accuracy along a single plane. The E-axis encoder often integrates with rotary systems for feedback in robotics and CNC machinery, whereas H-axis sensors are commonly employed in alignment and leveling tasks within industrial automation. Key differences lie in their operational focus--rotational versus linear positioning--and the specific sensor technologies optimized for each axis type, impacting application suitability and data resolution.
How E-Axis Encoders Work
E-axis encoders operate by detecting rotational position through optical or magnetic sensing elements, converting mechanical motion into precise electronic signals used for feedback in motion control systems. These encoders track angular displacement on the E-axis, providing real-time data that enhances the accuracy and repeatability of automated machinery. Your choice of an E-axis encoder over an H-axis sensor depends on application needs for resolution, environmental robustness, and integration complexity.
Functionality of H-Axis Sensors Explained
H-axis sensors accurately detect angular positions and rotational displacement, ensuring precise motion control in various industrial applications. Unlike E-axis encoders, which focus on linear position feedback, H-axis sensors specialize in capturing horizontal axis movements, enhancing system stability and performance. Your choice of H-axis sensor directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of automated machinery operations.
Advantages of E-Axis Encoders
E-axis encoders provide precise angular position feedback, enhancing the accuracy and stability of motion control systems. Their compact design and high resolution enable superior performance in applications requiring fine-tuned movements, such as robotics and CNC machines. You benefit from improved system reliability and reduced downtime due to the robust construction and advanced signal processing of E-axis encoders compared to H-axis sensors.
Benefits of H-Axis Sensors
H-axis sensors offer superior precision and faster response times compared to E-axis encoders, enhancing the accuracy of position and speed measurements. These sensors provide improved durability and resistance to environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and vibration, ensuring consistent performance in harsh industrial settings. Your system benefits from reduced maintenance requirements and extended operational lifespan when using H-axis sensors over traditional E-axis encoders.
Common Applications: E-Axis Encoder vs H-Axis Sensor
E-axis encoders are commonly used in precise rotary motion control applications such as robotics, CNC machines, and industrial automation where accurate position feedback is essential. H-axis sensors are typically employed in linear position sensing tasks including conveyor systems, material handling, and automotive applications requiring reliable displacement measurement. Both devices enhance system performance by providing critical feedback for motion control but target different mechanical axes and sensor technologies.
Performance and Accuracy Comparison
E-axis encoders typically offer higher resolution and greater precision due to their advanced optical or magnetic sensing technology, making them ideal for applications requiring exact position feedback. H-axis sensors provide robust performance with moderate accuracy, often favored for their durability and reliability in harsh environments. The performance difference is evident in motion control systems, where E-axis encoders excel in fine-tuned positioning, while H-axis sensors are preferred for steady, less precise measurements.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
E-axis encoders require precise alignment during installation to ensure accurate rotational position feedback, often involving mounting brackets and shaft coupling. H-axis sensors typically feature simpler installation due to their fixed position detection and less demanding alignment requirements. Maintenance for E-axis encoders involves periodic cleaning and calibration to prevent signal degradation, while H-axis sensors generally require less frequent maintenance, focusing mainly on environmental protection to avoid sensor damage.
Choosing the Right Axis Measurement Solution
Selecting the appropriate axis measurement solution depends on factors such as resolution, accuracy, and application requirements. E-axis encoders excel in providing high-resolution rotary position feedback for precise angular measurements, often used in motor control and robotics. H-axis sensors typically offer robust linear position sensing ideal for heavy machinery and industrial automation where detecting horizontal displacement is crucial.
E-axis encoder vs H-axis sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com