Chopper control and PWM control both regulate power delivery in electrical systems, with chopper control switching the voltage on and off to adjust motor speed, while PWM control varies the duty cycle of a constant voltage to fine-tune output. Understanding the differences and applications of these methods can help you optimize your electronic devices--explore the full article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
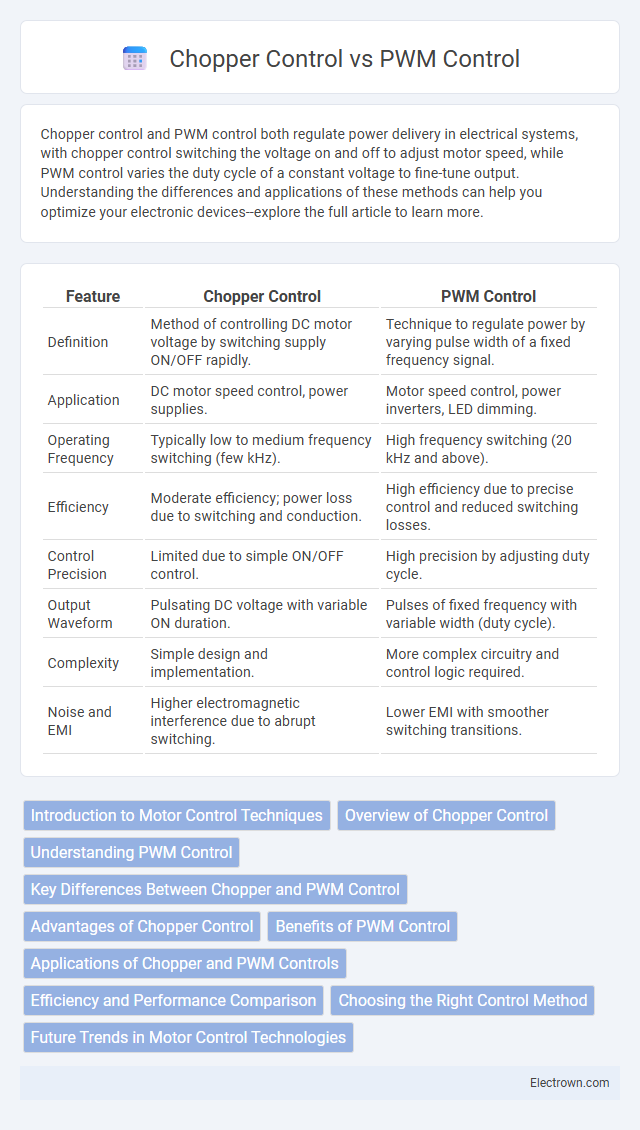
| Feature | Chopper Control | PWM Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Method of controlling DC motor voltage by switching supply ON/OFF rapidly. | Technique to regulate power by varying pulse width of a fixed frequency signal. |
| Application | DC motor speed control, power supplies. | Motor speed control, power inverters, LED dimming. |
| Operating Frequency | Typically low to medium frequency switching (few kHz). | High frequency switching (20 kHz and above). |
| Efficiency | Moderate efficiency; power loss due to switching and conduction. | High efficiency due to precise control and reduced switching losses. |
| Control Precision | Limited due to simple ON/OFF control. | High precision by adjusting duty cycle. |
| Output Waveform | Pulsating DC voltage with variable ON duration. | Pulses of fixed frequency with variable width (duty cycle). |
| Complexity | Simple design and implementation. | More complex circuitry and control logic required. |
| Noise and EMI | Higher electromagnetic interference due to abrupt switching. | Lower EMI with smoother switching transitions. |
Introduction to Motor Control Techniques
Chopper control and PWM control are essential motor control techniques used to regulate speed and torque efficiently in DC motors. Chopper control modulates voltage by rapidly switching the supply on and off, offering precise control with minimal energy loss. Your choice between these methods depends on the specific application requirements, such as motor type, efficiency, and desired performance characteristics.
Overview of Chopper Control
Chopper control is a method used in power electronics to regulate DC motor speed by rapidly switching the supply voltage on and off, effectively adjusting the average voltage applied to the motor. This technique enhances energy efficiency and offers precise control over motor torque and speed without the power losses associated with traditional resistive methods. Chopper control is widely used in applications requiring smooth speed variation and energy-saving operation, such as electric vehicles and industrial drives.
Understanding PWM Control
PWM control regulates power by rapidly switching a device on and off, adjusting the duty cycle to control the average voltage supplied to the load. This method improves efficiency and precision in motor speed and brightness control compared to chopper control, which modulates power by varying the on-time in fixed frequency. Understanding PWM control helps you achieve smoother operation and finer adjustments in various electronic and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Chopper and PWM Control
Chopper control regulates DC motor speed by varying the average voltage through rapid switching of the supply voltage, while PWM control modulates motor speed by adjusting the duty cycle of a fixed-frequency pulse signal. Chopper control typically operates on a variable frequency basis and is mainly applied to DC motors, whereas PWM control is widely used for both AC and DC motors with a fixed switching frequency. The key differences lie in their switching methods, control precision, and application scope, with PWM offering finer speed regulation and efficiency compared to traditional chopper control techniques.
Advantages of Chopper Control
Chopper control offers precise voltage regulation and high efficiency by rapidly switching the supply voltage on and off, minimizing energy loss in DC motor applications. It enables smooth speed control with reduced harmonic distortion compared to PWM control, improving motor performance and extending equipment lifespan. The simplicity of chopper circuits also results in lower cost and easier implementation for low-voltage DC drives.
Benefits of PWM Control
PWM control offers precise regulation of motor speed and torque by adjusting the duty cycle of voltage applied, resulting in higher energy efficiency and reduced heat generation compared to chopper control. It enhances performance in applications requiring fine speed control and smooth operation, minimizing electromagnetic interference and mechanical stress on components. Your system benefits from improved reliability and longer lifespan with PWM due to its effective management of power delivery and thermal conditions.
Applications of Chopper and PWM Controls
Chopper control is widely used in DC motor speed regulation, electric vehicles, and battery-powered devices due to its efficient voltage control and energy savings. PWM control finds applications in LED dimming, power inverters, and switching power supplies, offering precise output voltage and current control. You can optimize power efficiency and performance by selecting the suitable control method based on your application's voltage and current characteristics.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Chopper control offers higher efficiency in DC motor applications by minimizing power loss through rapid switches that regulate voltage with minimal heat dissipation. PWM control enhances performance by delivering precise voltage and current regulation, which improves torque response and speed control while maintaining lower harmonic distortion. Both methods optimize motor operation; chopper control excels in energy savings, whereas PWM control provides superior accuracy and smoother motor dynamics.
Choosing the Right Control Method
Choosing the right control method between chopper control and PWM control depends on your specific application requirements such as efficiency, speed regulation, and complexity. Chopper control is ideal for DC motor speed regulation with simpler circuitry and cost-effectiveness, while PWM control offers finer control, higher efficiency, and is more suitable for AC motors and variable frequency drives. Evaluate your system's power rating, desired precision, and thermal management needs to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Future Trends in Motor Control Technologies
Chopper control and PWM control represent foundational approaches in motor speed regulation, with PWM increasingly favored for its precision and efficiency in modern electric drives. Future trends indicate a shift towards advanced PWM techniques integrated with AI algorithms and IoT connectivity to optimize motor performance and energy consumption in real time. Your adoption of these evolving technologies can significantly enhance control accuracy and system responsiveness in emerging smart motor applications.
Chopper control vs PWM control Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com