ECU (Engine Control Unit) and ECM (Engine Control Module) both regulate engine performance, but the ECU primarily focuses on controlling engine functions, while the ECM manages a broader range of vehicle systems including emissions and fuel efficiency. Understanding their differences can help you optimize your vehicle's performance and maintenance--read on to explore the detailed distinctions and benefits.
Table of Comparison
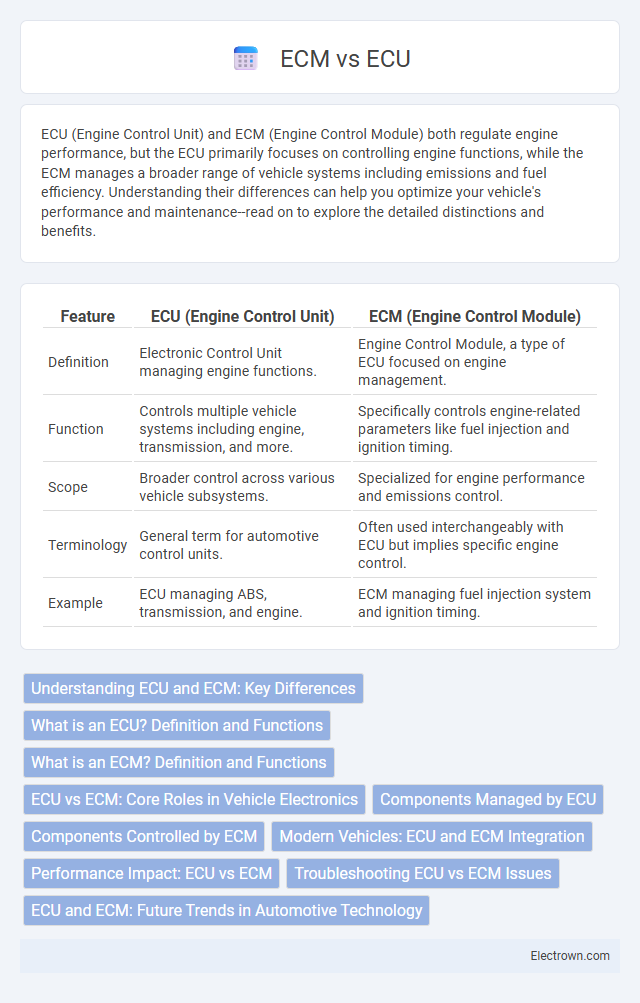
| Feature | ECU (Engine Control Unit) | ECM (Engine Control Module) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic Control Unit managing engine functions. | Engine Control Module, a type of ECU focused on engine management. |
| Function | Controls multiple vehicle systems including engine, transmission, and more. | Specifically controls engine-related parameters like fuel injection and ignition timing. |
| Scope | Broader control across various vehicle subsystems. | Specialized for engine performance and emissions control. |
| Terminology | General term for automotive control units. | Often used interchangeably with ECU but implies specific engine control. |
| Example | ECU managing ABS, transmission, and engine. | ECM managing fuel injection system and ignition timing. |
Understanding ECU and ECM: Key Differences
ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and ECM (Engine Control Module) are essential components in vehicle electronics, with the ECU serving as a broad term for various control units managing systems like transmission, brakes, and engine functions, whereas the ECM specifically controls engine performance parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emission controls. The ECU communicates with multiple sensors and actuators across different vehicle systems to optimize overall functionality, while the ECM focuses on processing engine data to ensure efficient power delivery and compliance with environmental standards. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for diagnosing automotive issues and enhancing vehicle performance through targeted electronic management.
What is an ECU? Definition and Functions
An Engine Control Unit (ECU) is a crucial electronic control module in modern vehicles responsible for managing engine performance by processing data from various sensors and adjusting fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture. It ensures optimal engine efficiency, emission control, and overall vehicle performance. The ECU interprets real-time information to regulate the engine's operation, enhancing fuel economy and reducing harmful exhaust emissions.
What is an ECM? Definition and Functions
An Engine Control Module (ECM) is a critical automotive component responsible for managing engine performance by monitoring and controlling various parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions. It uses input from sensors to optimize engine efficiency, reduce emissions, and ensure smooth operation under different driving conditions. Your vehicle relies on the ECM to maintain optimal engine functionality and comply with environmental regulations.
ECU vs ECM: Core Roles in Vehicle Electronics
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) primarily manages engine functions such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emission control to optimize performance and efficiency. The Engine Control Module (ECM) often combines the ECU's tasks with additional control systems, including transmission management and onboard diagnostics. Both units are crucial for vehicle electronics, but the ECM provides a more integrated approach to overall engine and system management.
Components Managed by ECU
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) manages crucial components such as fuel injectors, ignition coils, and the throttle position sensor to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency. It continuously monitors inputs from oxygen sensors, crankshaft position sensors, and airflow meters to adjust the air-fuel mixture and ignition timing precisely. Your vehicle's smooth operation and emission control rely heavily on the ECU's management of these critical engine components.
Components Controlled by ECM
The Engine Control Module (ECM) manages critical components such as fuel injectors, ignition coils, sensors (oxygen, temperature, and mass airflow), and the throttle body to optimize engine performance and emissions. Unlike the ECU, which is a broader term for vehicle control units, the ECM specifically focuses on engine-related systems to ensure efficient combustion and adherence to environmental standards. Its precise control over these components enhances fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, and maintains engine reliability.
Modern Vehicles: ECU and ECM Integration
Modern vehicles integrate Electronic Control Units (ECUs) and Engine Control Modules (ECMs) to optimize various automotive functions, from engine management to safety systems. The ECM acts as a specialized ECU focused on engine performance, controlling fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions. Advanced automotive systems rely on seamless communication between multiple ECUs and ECMs to enhance efficiency, diagnostics, and vehicle responsiveness.
Performance Impact: ECU vs ECM
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) directly influences vehicle performance by managing fuel injection, ignition timing, and engine parameters for optimal power and efficiency. The Engine Control Module (ECM), often synonymous with ECU, sometimes encompasses broader functions including transmission control and emissions management, impacting overall drivability and engine responsiveness. Advanced ECU systems enable real-time adjustments that enhance acceleration, fuel economy, and emissions compliance compared to more basic ECM setups.
Troubleshooting ECU vs ECM Issues
Troubleshooting ECU vs ECM issues requires understanding their distinct functions: the ECU (Engine Control Unit) manages engine parameters, while the ECM (Engine Control Module) often integrates additional systems like transmission control. Diagnosing ECU problems involves checking sensor inputs, wiring integrity, and software updates, whereas ECM troubleshooting includes examining communication with other modules and assessing both engine and drivetrain data. Your approach should prioritize scanning for error codes, performing live data analysis, and inspecting connectors to efficiently isolate faults in either control system.
ECU and ECM: Future Trends in Automotive Technology
The future of automotive technology sees ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and ECM (Engine Control Module) evolving with enhanced integration of AI and IoT for predictive maintenance and real-time diagnostics. Advanced ECUs and ECMs will enable improved fuel efficiency, emissions control, and autonomous driving capabilities through increased processing power and connectivity. Industry trends highlight the shift towards modular, software-defined control units that support over-the-air updates and adaptive vehicle performance.
ECU vs ECM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com