Low-side drivers switch the load to ground, providing a simpler design and easier control but can cause ground reference issues in certain applications. High-side drivers connect the load to the positive supply, offering better safety and load protection while requiring more complex circuitry; discover which driver best suits your needs by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
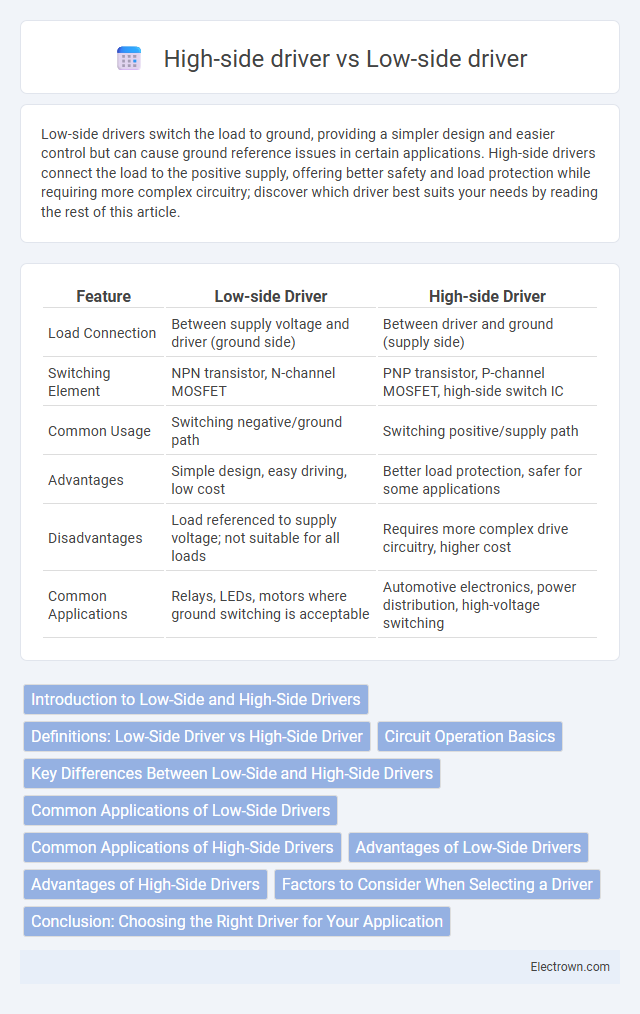
| Feature | Low-side Driver | High-side Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Load Connection | Between supply voltage and driver (ground side) | Between driver and ground (supply side) |
| Switching Element | NPN transistor, N-channel MOSFET | PNP transistor, P-channel MOSFET, high-side switch IC |
| Common Usage | Switching negative/ground path | Switching positive/supply path |
| Advantages | Simple design, easy driving, low cost | Better load protection, safer for some applications |
| Disadvantages | Load referenced to supply voltage; not suitable for all loads | Requires more complex drive circuitry, higher cost |
| Common Applications | Relays, LEDs, motors where ground switching is acceptable | Automotive electronics, power distribution, high-voltage switching |
Introduction to Low-Side and High-Side Drivers
Low-side drivers switch the load connection to ground, controlling the current flow by connecting the load's negative terminal to the ground, commonly used in applications where the load is connected to a positive voltage supply. High-side drivers switch the load connection to the power supply, providing current by connecting the load's positive terminal to the voltage source, often employed for better safety and noise immunity in automotive and industrial circuits. Both driver types optimize transistor switching configurations, such as using NPN transistors or N-channel MOSFETs for low-side and PNP transistors or P-channel MOSFETs for high-side driving.
Definitions: Low-Side Driver vs High-Side Driver
A low-side driver switches the load connection to ground, allowing current to flow from the positive supply through the load to the driver, commonly used in switching power devices or controlling LEDs. A high-side driver switches the positive supply connection to the load, providing current from the power source while the load is connected to ground, typically used in applications requiring positive voltage control such as motor drives. Understanding the placement of the switch relative to the load is critical for proper circuit design and ensuring correct voltage levels and protection mechanisms.
Circuit Operation Basics
Low-side drivers switch the load by connecting it to ground, allowing current to flow through the load to the driver when activated. High-side drivers connect the load to the positive supply voltage, enabling current to flow from the supply through the load to ground. Your choice between low-side and high-side drivers depends on the control logic and voltage requirements of your specific circuit application.
Key Differences Between Low-Side and High-Side Drivers
Low-side drivers control the connection of the load to ground, switching the negative side, while high-side drivers switch the positive supply voltage to the load. Low-side drivers typically offer simpler designs and cost efficiency but may introduce grounding issues, whereas high-side drivers provide better load isolation and are safer for controlling high-voltage or inductive loads. Your choice depends on the application's voltage level, load type, and safety requirements to ensure optimal performance and protection.
Common Applications of Low-Side Drivers
Low-side drivers are commonly used in applications like switching loads to ground in automotive lighting, motor control circuits, and LED arrays where controlling the negative side simplifies wiring and reduces cost. These drivers are favored for their ease of implementation in microcontroller output stages when driving resistive or inductive loads at lower voltages. Understanding your system's voltage reference and load requirements helps determine if a low-side driver is the optimal choice for efficient and reliable control.
Common Applications of High-Side Drivers
High-side drivers are widely used in automotive systems for controlling power to actuators and sensors, providing safe switching between the supply voltage and the load. Industrial automation frequently employs high-side drivers for driving inductive loads such as relays and solenoids, benefiting from their ability to handle higher voltages and protect against short circuits. In battery-powered devices, high-side drivers manage power distribution efficiently, ensuring stable operation of connected components without direct grounding.
Advantages of Low-Side Drivers
Low-side drivers offer advantages such as simpler circuit design, lower cost, and easier implementation due to their common ground reference. They provide effective switching for loads connected to the positive supply voltage, often resulting in improved thermal management and reduced electromagnetic interference. Your choice of a low-side driver can enhance efficiency in applications with grounded load configurations and straightforward control requirements.
Advantages of High-Side Drivers
High-side drivers provide superior safety by connecting the load to the positive supply voltage, preventing ground faults and reducing the risk of short circuits. They enable easier switching of the supply voltage, which is essential for controlling loads in automotive and industrial applications. High-side drivers also offer better protection for sensitive components by isolating the load from ground and minimizing potential voltage spikes.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Driver
When selecting between a low-side driver and a high-side driver, key factors include the load type, voltage requirements, and thermal management. Low-side drivers are often preferred for switching the ground path in resistive or inductive loads, offering simpler control but limited protection against short circuits. High-side drivers are essential for connecting loads to the power supply, providing better safety features and compatibility with positive voltage loads, especially in automotive and industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Driver for Your Application
Choosing the right driver depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as load type, voltage levels, and safety considerations. Low-side drivers are ideal for switching grounded loads and offer simpler design and cost advantages, while high-side drivers are better suited for switching positive voltage rails and provide better isolation and protection. Evaluating factors like control signal availability, current capacity, and switching speed ensures optimal performance and reliability in your circuit design.
Low-side driver vs High-side driver Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com