EGT sensors measure exhaust gas temperature to protect engine components and optimize performance, while O2 sensors monitor oxygen levels in the exhaust for precise fuel mixture control. Discover how understanding the differences between these sensors can enhance your vehicle's efficiency and longevity by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
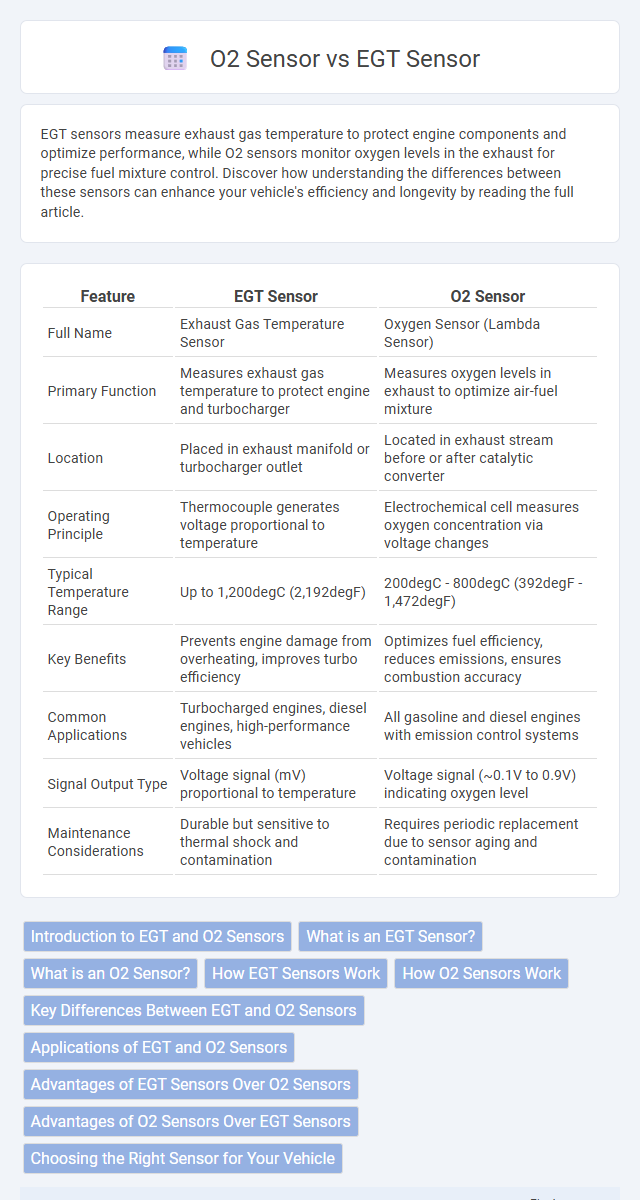
| Feature | EGT Sensor | O2 Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor | Oxygen Sensor (Lambda Sensor) |
| Primary Function | Measures exhaust gas temperature to protect engine and turbocharger | Measures oxygen levels in exhaust to optimize air-fuel mixture |
| Location | Placed in exhaust manifold or turbocharger outlet | Located in exhaust stream before or after catalytic converter |
| Operating Principle | Thermocouple generates voltage proportional to temperature | Electrochemical cell measures oxygen concentration via voltage changes |
| Typical Temperature Range | Up to 1,200degC (2,192degF) | 200degC - 800degC (392degF - 1,472degF) |
| Key Benefits | Prevents engine damage from overheating, improves turbo efficiency | Optimizes fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, ensures combustion accuracy |
| Common Applications | Turbocharged engines, diesel engines, high-performance vehicles | All gasoline and diesel engines with emission control systems |
| Signal Output Type | Voltage signal (mV) proportional to temperature | Voltage signal (~0.1V to 0.9V) indicating oxygen level |
| Maintenance Considerations | Durable but sensitive to thermal shock and contamination | Requires periodic replacement due to sensor aging and contamination |
Introduction to EGT and O2 Sensors
EGT sensors measure exhaust gas temperature to monitor engine performance and prevent overheating by detecting the heat level in the exhaust stream. O2 sensors analyze the oxygen concentration in exhaust gases, providing crucial feedback for optimizing air-fuel mixture and improving combustion efficiency. Both sensors are essential in modern vehicles for emissions control, engine diagnostics, and fuel economy enhancement.
What is an EGT Sensor?
An EGT sensor, or Exhaust Gas Temperature sensor, measures the temperature of exhaust gases emitted by the engine to monitor combustion efficiency and protect the engine from overheating. Unlike an O2 sensor that detects oxygen levels in the exhaust to optimize air-fuel mixture for better fuel economy and emissions control, the EGT sensor provides critical temperature data to prevent engine damage and improve performance. You can rely on the EGT sensor to ensure your vehicle's exhaust system operates within safe thermal limits, enhancing durability and overall engine reliability.
What is an O2 Sensor?
An O2 sensor, or oxygen sensor, measures the oxygen level in a vehicle's exhaust gases, providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) for optimal air-fuel mixture adjustment. This sensor helps improve fuel efficiency and reduce harmful emissions by ensuring complete combustion. Unlike the EGT sensor, which monitors exhaust gas temperature, the O2 sensor primarily focuses on air-fuel ratio accuracy.
How EGT Sensors Work
EGT sensors monitor exhaust gas temperature by using a thermocouple to generate voltage corresponding to temperature changes, providing critical data for engine tuning and performance optimization. Unlike O2 sensors that measure oxygen levels to adjust fuel mixture, EGT sensors directly track heat levels in the exhaust, protecting your engine from overheating and improving combustion efficiency. This precise temperature feedback helps maintain optimal engine conditions and prevent damage from excessive exhaust temperatures.
How O2 Sensors Work
O2 sensors measure the oxygen levels in your vehicle's exhaust gases to optimize fuel combustion and reduce emissions by sending voltage signals to the engine control unit (ECU). Unlike EGT sensors that monitor the exhaust gas temperature, O2 sensors detect the air-fuel mixture's stoichiometry, ensuring your engine operates efficiently. Accurate O2 sensor feedback helps maintain optimal engine performance and fuel economy.
Key Differences Between EGT and O2 Sensors
EGT sensors measure exhaust gas temperature to monitor engine performance and prevent overheating, while O2 sensors detect oxygen levels in the exhaust to optimize air-fuel mixture for fuel efficiency and emissions control. EGT sensors provide critical data for protecting engine components, whereas O2 sensors primarily help your vehicle's ECU adjust fuel injection for cleaner combustion. Understanding these key differences ensures your vehicle maintains optimal performance and complies with emission standards.
Applications of EGT and O2 Sensors
EGT sensors are primarily used in automotive and aerospace industries to monitor exhaust gas temperatures for optimizing engine performance and preventing overheating. O2 sensors are widely applied in internal combustion engines to measure oxygen levels in exhaust gases, enabling precise air-fuel ratio control for emissions reduction and fuel efficiency. Both sensors play critical roles in engine management systems, but EGT sensors focus on temperature monitoring while O2 sensors concentrate on combustion quality.
Advantages of EGT Sensors Over O2 Sensors
EGT sensors provide faster response times and more accurate temperature readings directly from the exhaust gas, enabling precise monitoring of combustion conditions to prevent engine damage. Unlike O2 sensors, which measure oxygen concentration to infer air-fuel ratios, EGT sensors directly track exhaust gas temperature for enhanced thermal management and engine tuning. This direct temperature measurement helps optimize performance and fuel efficiency while protecting components from overheating.
Advantages of O2 Sensors Over EGT Sensors
O2 sensors provide more precise real-time feedback on air-fuel mixture quality, enabling better engine tuning and improved fuel efficiency compared to EGT sensors, which primarily measure exhaust gas temperature. These sensors help prevent engine damage by detecting lean or rich conditions early, optimizing combustion and reducing emissions directly. Your vehicle benefits from enhanced performance and lower emissions due to the advanced monitoring capabilities of O2 sensors over EGT sensors.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right sensor for your vehicle depends on your specific needs: an EGT sensor (Exhaust Gas Temperature) provides critical data to protect engine components by monitoring exhaust heat, ideal for performance tuning and preventing overheating. In contrast, an O2 sensor (Oxygen sensor) measures the oxygen levels in exhaust gases to optimize air-fuel mixture, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Understanding whether you prioritize thermal protection or emissions control will help determine if the EGT sensor or O2 sensor best suits your vehicle's diagnostics and performance requirements.
EGT sensor vs O2 sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com