HVAC controllers primarily regulate heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to maintain indoor comfort by adjusting temperature and airflow, whereas climate control modules offer more advanced, integrated management of multiple environmental factors such as humidity, air quality, and zone-specific settings. Explore the rest of this article to understand how your choice between these systems can impact overall building efficiency and comfort.
Table of Comparison
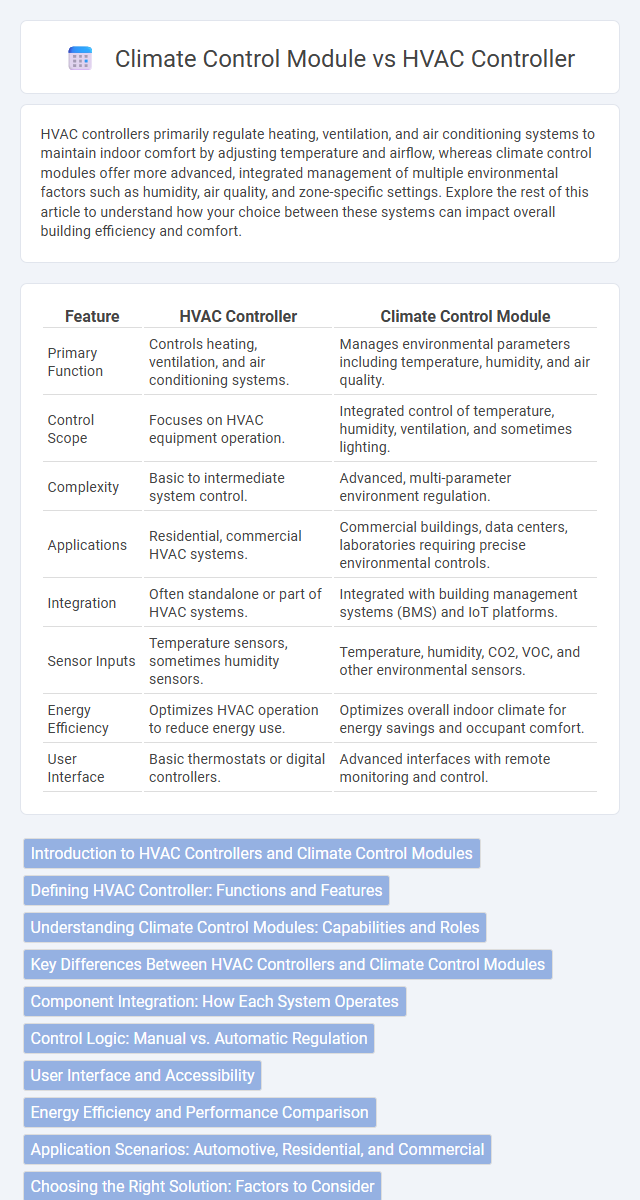
| Feature | HVAC Controller | Climate Control Module |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Controls heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. | Manages environmental parameters including temperature, humidity, and air quality. |
| Control Scope | Focuses on HVAC equipment operation. | Integrated control of temperature, humidity, ventilation, and sometimes lighting. |
| Complexity | Basic to intermediate system control. | Advanced, multi-parameter environment regulation. |
| Applications | Residential, commercial HVAC systems. | Commercial buildings, data centers, laboratories requiring precise environmental controls. |
| Integration | Often standalone or part of HVAC systems. | Integrated with building management systems (BMS) and IoT platforms. |
| Sensor Inputs | Temperature sensors, sometimes humidity sensors. | Temperature, humidity, CO2, VOC, and other environmental sensors. |
| Energy Efficiency | Optimizes HVAC operation to reduce energy use. | Optimizes overall indoor climate for energy savings and occupant comfort. |
| User Interface | Basic thermostats or digital controllers. | Advanced interfaces with remote monitoring and control. |
Introduction to HVAC Controllers and Climate Control Modules
HVAC controllers manage heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems by regulating temperature, airflow, and humidity for optimal indoor comfort and energy efficiency. Climate control modules integrate sensors and control algorithms to adjust environmental conditions based on real-time data, enhancing precision and responsiveness. Your choice between an HVAC controller and a climate control module depends on the complexity of the system and specific climate management needs.
Defining HVAC Controller: Functions and Features
An HVAC controller regulates heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems by managing temperature, humidity, and airflow to maintain indoor comfort. It features programmable settings, sensors, and real-time monitoring to optimize energy efficiency and system performance. Your ability to customize these controls ensures precise climate management tailored to specific environmental needs.
Understanding Climate Control Modules: Capabilities and Roles
Climate control modules integrate temperature, humidity, and air quality sensors to maintain optimal indoor environments, surpassing basic HVAC controllers by offering precise, automated adjustments. These modules manage multiple zones and adapt settings based on occupancy patterns and external weather data, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Their advanced algorithms facilitate seamless coordination between heating, ventilation, and air conditioning components for comprehensive climate regulation.
Key Differences Between HVAC Controllers and Climate Control Modules
HVAC controllers primarily manage heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems using sensors and user inputs to regulate temperature and airflow in a building. Climate control modules integrate advanced features such as humidity control, air quality monitoring, and multi-zone management for comprehensive environmental regulation. Your choice between these systems depends on the complexity of your needs, with HVAC controllers suited for basic temperature control and climate control modules offering enhanced, precise environmental management.
Component Integration: How Each System Operates
HVAC controllers primarily manage heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functions through dedicated sensors and actuators that regulate temperature and airflow within a building. Climate control modules integrate multiple environmental parameters, including humidity, CO2 levels, and air quality, using advanced algorithms to optimize overall indoor climate conditions. The integration in climate control modules allows for more comprehensive system operation by coordinating HVAC components with additional sensory inputs for enhanced comfort and energy efficiency.
Control Logic: Manual vs. Automatic Regulation
HVAC controllers typically rely on manual regulation, allowing users to adjust settings such as temperature, fan speed, and airflow based on preference, providing direct control over the comfort environment. Climate control modules operate with advanced automatic regulation, using sensors and algorithms to continuously monitor and adjust temperature, humidity, and air quality for optimal indoor conditions. Your choice between these options depends on the desired balance between hands-on control and seamless, automated climate management.
User Interface and Accessibility
HVAC controllers typically feature straightforward user interfaces with physical buttons and knobs, enabling quick manual adjustments of temperature settings. Climate control modules offer advanced digital touchscreens and smartphone app integration, providing enhanced accessibility and remote control capabilities. The choice between the two depends on the desired balance between simplicity and technological convenience for user interaction.
Energy Efficiency and Performance Comparison
HVAC controllers optimize energy consumption by precisely regulating heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems based on real-time data, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced utility costs. Climate control modules integrate multiple environmental sensors and adaptive algorithms, enhancing overall system performance by maintaining consistent indoor comfort with minimal energy waste. Your choice between these technologies should consider the specific energy savings and performance needs of your building's HVAC infrastructure.
Application Scenarios: Automotive, Residential, and Commercial
HVAC controllers are widely used in automotive settings to manage air distribution and temperature for passenger comfort, while climate control modules offer enhanced features like humidity regulation and air quality monitoring, making them ideal for commercial buildings requiring precise environmental management. In residential applications, HVAC controllers typically handle basic heating and cooling functions, whereas climate control modules integrate smart technology for optimized energy efficiency and personalized comfort. Your choice depends on the complexity of control needed and the specific environmental demands of the automotive, residential, or commercial scenario.
Choosing the Right Solution: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right solution between an HVAC controller and a climate control module depends on factors like system complexity, integration needs, and user control preferences. HVAC controllers typically offer robust management of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functions, ideal for large or commercial setups. Your decision should consider energy efficiency goals, compatibility with existing infrastructure, and the level of automation required for optimal indoor environmental comfort.
HVAC controller vs Climate control module Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com