OTA updates provide wireless firmware improvements directly to your vehicle, offering convenience without the need for physical connection, while OBD updates require a physical plug-in device to upload software via the On-Board Diagnostics port. Explore the rest of the article to understand which update method best suits your needs and enhances your vehicle's performance.
Table of Comparison
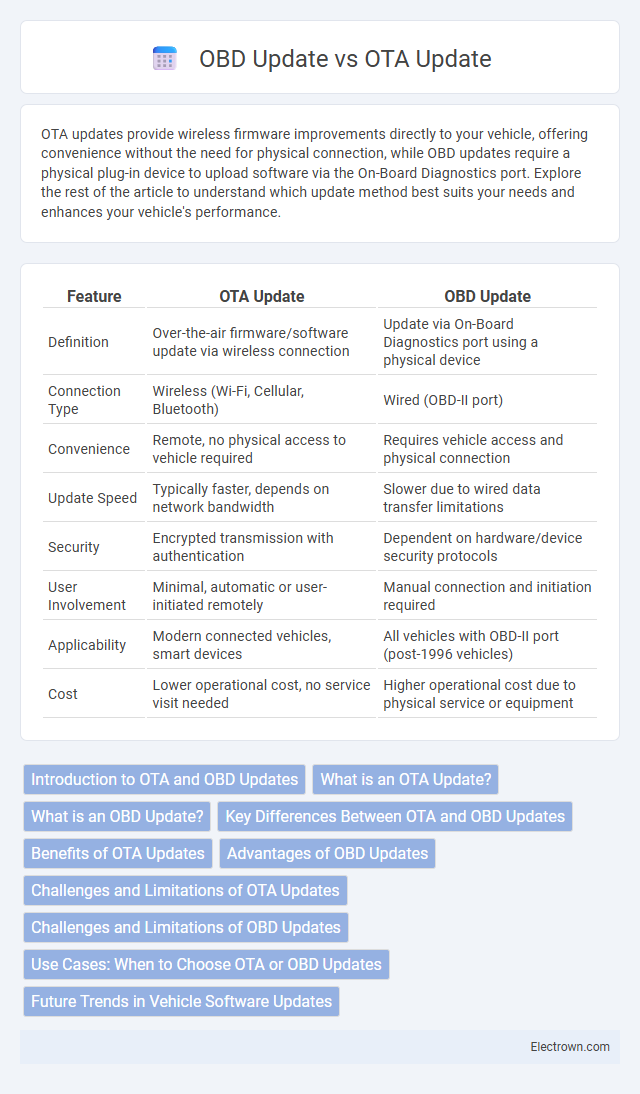
| Feature | OTA Update | OBD Update |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Over-the-air firmware/software update via wireless connection | Update via On-Board Diagnostics port using a physical device |
| Connection Type | Wireless (Wi-Fi, Cellular, Bluetooth) | Wired (OBD-II port) |
| Convenience | Remote, no physical access to vehicle required | Requires vehicle access and physical connection |
| Update Speed | Typically faster, depends on network bandwidth | Slower due to wired data transfer limitations |
| Security | Encrypted transmission with authentication | Dependent on hardware/device security protocols |
| User Involvement | Minimal, automatic or user-initiated remotely | Manual connection and initiation required |
| Applicability | Modern connected vehicles, smart devices | All vehicles with OBD-II port (post-1996 vehicles) |
| Cost | Lower operational cost, no service visit needed | Higher operational cost due to physical service or equipment |
Introduction to OTA and OBD Updates
OTA updates deliver software improvements wirelessly, allowing Your vehicle to receive the latest features and security patches without visiting a service center. OBD updates require physical connection through the On-Board Diagnostics port, typically necessitating a technician's intervention. Choosing between OTA and OBD updates depends on convenience, immediacy, and available infrastructure for seamless vehicle software maintenance.
What is an OTA Update?
An OTA (Over-The-Air) update delivers software enhancements, bug fixes, and feature upgrades directly to a vehicle's electronic control units via wireless internet connections, eliminating the need for physical access. This method enables manufacturers to efficiently deploy updates to millions of vehicles remotely, improving user experience and security without requiring dealership visits. OTA updates are crucial for modern connected cars, supporting continuous improvement and real-time software management.
What is an OBD Update?
An OBD update refers to updating a vehicle's software through the On-Board Diagnostics port using a physical device connected directly to your car. This method allows mechanics or car owners to access the vehicle's control modules to install firmware updates, configure settings, or diagnose issues without wireless connectivity. Compared to OTA updates, OBD updates often require a manual connection but provide a more controlled and secure way to manage your vehicle's software.
Key Differences Between OTA and OBD Updates
OTA updates deliver software improvements wirelessly through cellular or Wi-Fi connections, enabling seamless remote maintenance without physical vehicle access. OBD updates require a direct connection via the vehicle's On-Board Diagnostics port, often necessitating a technician's presence and specialized equipment. You benefit from OTA's convenience and speed, while OBD updates provide a controlled environment for critical diagnostics and firmware changes.
Benefits of OTA Updates
OTA updates enable seamless, wireless software enhancements, eliminating the need for physical connections or dealership visits associated with OBD updates. They provide faster deployment of critical patches and new features, improving vehicle performance and security in real-time. OTA updates also reduce maintenance costs and downtime by automating the update process remotely.
Advantages of OBD Updates
OBD updates offer direct and reliable communication with your vehicle's onboard systems, ensuring precise diagnostics and firmware improvements without relying on wireless connectivity. These updates provide enhanced security by avoiding vulnerabilities associated with over-the-air (OTA) transmissions. Your vehicle benefits from immediate, stable firmware application and troubleshooting capabilities that are often inaccessible through remote OTA processes.
Challenges and Limitations of OTA Updates
OTA updates face challenges such as ensuring secure data transmission to prevent cyberattacks and maintaining reliable connectivity in remote areas. The update process can strain vehicle hardware and software compatibility, leading to potential system malfunctions or incomplete installations. Limited bandwidth and varying vehicle models further complicate uniform distribution and timely updates.
Challenges and Limitations of OBD Updates
OBD updates face significant challenges including limited bandwidth and slower data transfer rates, which restrict the ability to deliver large or complex software patches efficiently. The requirement for physical access to the vehicle's diagnostic port also limits convenience and scalability, especially for fleet-wide or remote updates. Furthermore, compatibility issues arise due to diverse OBD standards and variations across vehicle models, complicating uniform software deployment.
Use Cases: When to Choose OTA or OBD Updates
OTA updates are ideal for vehicles requiring frequent, remote software improvements without user intervention, such as infotainment enhancements or security patches. OBD updates are preferred during vehicle servicing or diagnostics when direct access to the onboard computer is necessary, especially for critical firmware changes or when internet connectivity is unavailable. Your choice depends on convenience, update complexity, and whether real-time dealer interaction or remote deployment is more appropriate.
Future Trends in Vehicle Software Updates
OTA updates are rapidly becoming the standard for vehicle software enhancements due to their convenience, speed, and ability to deliver real-time security patches and feature upgrades without physical intervention. OBD updates, while still used for diagnostics and offline firmware installs, are gradually being supplemented by OTA systems that leverage cloud connectivity and edge computing for continuous improvement and predictive maintenance. Future trends indicate a rise in AI-driven OTA updates, enabling personalized driving experiences, seamless integration with smart city infrastructure, and robust cybersecurity protocols to protect against increasingly sophisticated threats.
OTA update vs OBD update Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com