Paddle shifters use electronic sensors and actuators to send gear change signals directly to the transmission control unit, enabling faster and smoother shifts compared to traditional shifters, which mechanically link to the transmission via cables or rods. Discover how these electronic differences impact Your driving experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
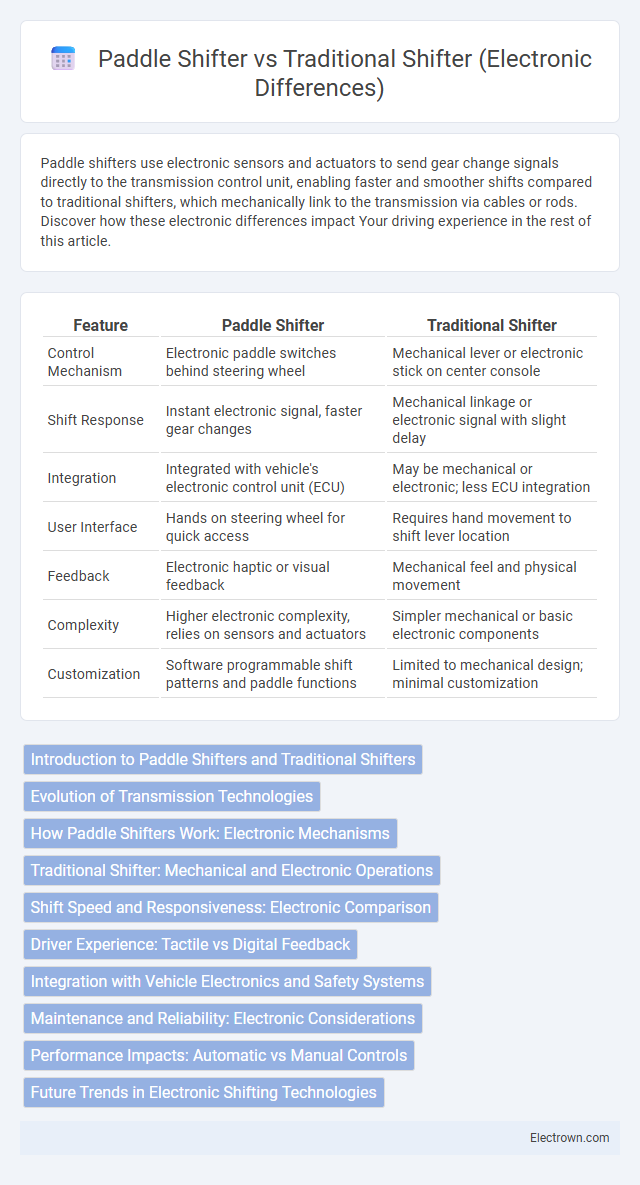
| Feature | Paddle Shifter | Traditional Shifter |
|---|---|---|
| Control Mechanism | Electronic paddle switches behind steering wheel | Mechanical lever or electronic stick on center console |
| Shift Response | Instant electronic signal, faster gear changes | Mechanical linkage or electronic signal with slight delay |
| Integration | Integrated with vehicle's electronic control unit (ECU) | May be mechanical or electronic; less ECU integration |
| User Interface | Hands on steering wheel for quick access | Requires hand movement to shift lever location |
| Feedback | Electronic haptic or visual feedback | Mechanical feel and physical movement |
| Complexity | Higher electronic complexity, relies on sensors and actuators | Simpler mechanical or basic electronic components |
| Customization | Software programmable shift patterns and paddle functions | Limited to mechanical design; minimal customization |
Introduction to Paddle Shifters and Traditional Shifters
Paddle shifters utilize electronic sensors to send shift commands to the transmission control unit, enabling quicker and more precise gear changes compared to the mechanical linkages found in traditional shifters. While traditional shifters rely on direct physical movement to engage gears, paddle shifters operate through electronic signals that enhance responsiveness and reduce shift lag. Your driving experience improves with paddle shifters due to their seamless integration with modern electronic transmission systems, offering greater control and efficiency.
Evolution of Transmission Technologies
Paddle shifters integrate electronic controls that send signals to the transmission's computer module, enabling quicker and more precise gear changes compared to traditional mechanical shifters, which rely on direct physical linkages. The evolution of transmission technologies has shifted from manual cables and hydraulic systems toward advanced electronic systems, improving responsiveness and fuel efficiency. Your driving experience benefits from paddle shifters' seamless integration with modern automated transmissions, enhancing control without manual clutch operation.
How Paddle Shifters Work: Electronic Mechanisms
Paddle shifters use electronic sensors to detect driver inputs, sending signals to the transmission control unit (TCU) that electronically commands gear changes without mechanical linkage. Traditional shifters rely on direct mechanical linkages or cable systems to physically engage gears, offering less precision and slower response compared to electronic paddle controls. The electronic mechanism in paddle shifters enables faster, smoother shifts by eliminating physical constraints and allowing integration with advanced transmission software.
Traditional Shifter: Mechanical and Electronic Operations
Traditional shifters operate through a combination of mechanical linkages and electronic sensors that translate the lever movement into gear changes, providing tactile feedback and precise control. Mechanical components physically connect the gear lever to the transmission, while electronic sensors send signals to the vehicle's control unit to activate gear shifts, ensuring smooth transitions. This hybrid operation contrasts with paddle shifters, which rely primarily on electronic signals without direct mechanical linkage, enabling quicker and more integrated gear changes within modern automatic transmissions.
Shift Speed and Responsiveness: Electronic Comparison
Paddle shifters utilize electronic sensors and actuators to instantaneously transmit shift commands to the transmission control unit, resulting in significantly faster shift speeds and improved responsiveness compared to traditional mechanical shifters that rely on physical linkages. The electronic interface in paddle shifters reduces input lag and allows for precise gear changes, enhancing driving performance and control. Traditional shifters often exhibit slower response times due to the mechanical nature of their operation, leading to less efficient gear changes.
Driver Experience: Tactile vs Digital Feedback
Paddle shifters deliver immediate tactile feedback through mechanical clicks, enhancing driver engagement by simulating manual gear changes. Traditional shifters rely on electronic signals with minimal physical resistance, offering a smoother but less interactive shifting experience. Your preference depends on whether you value sensory connection or seamless automation in your driving style.
Integration with Vehicle Electronics and Safety Systems
Paddle shifters integrate more seamlessly with vehicle electronics, enabling faster and more precise gear changes through electronic signals rather than mechanical linkages found in traditional shifters. This advanced integration allows paddle shifters to communicate directly with safety systems like traction control and engine management, enhancing overall vehicle performance and safety. Your driving experience benefits from this synergy, as electronic coordination improves shift timing and responsiveness in critical situations.
Maintenance and Reliability: Electronic Considerations
Paddle shifters rely on electronic sensors and actuators to send gear change signals to the transmission control unit, reducing mechanical wear and minimizing maintenance compared to traditional shifters that use direct mechanical linkages. The electronic components in paddle shifters demand attention to wiring integrity and software updates to prevent signal failures, while traditional shifters primarily require mechanical lubrication and cable adjustments. Your vehicle's electronic shifting system offers quicker response times and improved reliability but may incur higher diagnostic costs if electronic malfunctions occur.
Performance Impacts: Automatic vs Manual Controls
Paddle shifters utilize electronic signals to instantly communicate gear changes to the transmission control unit, enabling faster and more precise gear shifts compared to traditional mechanical shifters. This electronic interface reduces shift lag commonly found in manual transmissions, optimizing vehicle performance and responsiveness during acceleration and deceleration. Automatic control systems integrated with paddle shifters also enhance fuel efficiency by adapting shifts to driving conditions, unlike manual controls which rely on driver input and timing.
Future Trends in Electronic Shifting Technologies
Paddle shifters utilize electronic sensors and microprocessors to send shift commands instantly to the transmission control unit, enabling faster and more precise gear changes compared to traditional mechanical shifters that rely on physical linkage. Future trends in electronic shifting technologies emphasize integration with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), increased use of drive-by-wire technology, and enhanced customization through software updates, which offer adaptive shifting patterns tailored to driving conditions and driver preferences. Emerging innovations include AI-driven predictive shifting algorithms and seamless connectivity with vehicle telematics, leading to improved efficiency, performance, and user experience in next-generation transmission systems.
Paddle shifter vs Traditional shifter (electronic differences) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com