Digital potentiometers offer precise, programmable resistance adjustments with enhanced durability and integration capabilities compared to traditional mechanical potentiometers, which rely on physical movement and manual control. Discover how choosing the right potentiometer can impact your project's performance and longevity by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
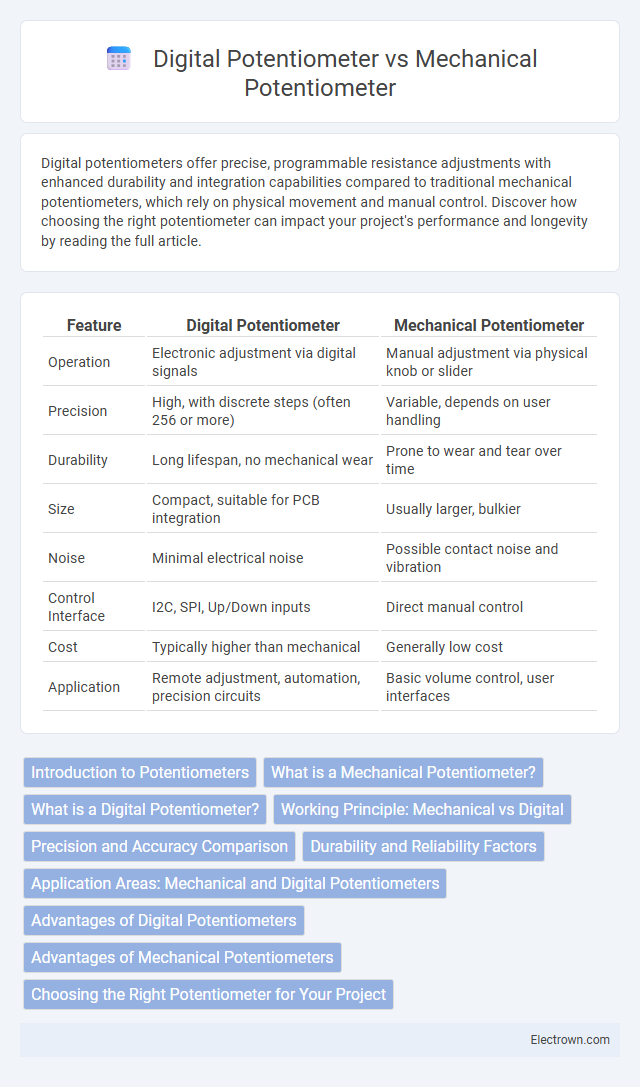
| Feature | Digital Potentiometer | Mechanical Potentiometer |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Electronic adjustment via digital signals | Manual adjustment via physical knob or slider |
| Precision | High, with discrete steps (often 256 or more) | Variable, depends on user handling |
| Durability | Long lifespan, no mechanical wear | Prone to wear and tear over time |
| Size | Compact, suitable for PCB integration | Usually larger, bulkier |
| Noise | Minimal electrical noise | Possible contact noise and vibration |
| Control Interface | I2C, SPI, Up/Down inputs | Direct manual control |
| Cost | Typically higher than mechanical | Generally low cost |
| Application | Remote adjustment, automation, precision circuits | Basic volume control, user interfaces |
Introduction to Potentiometers
Potentiometers control electrical voltage by varying resistance within a circuit, essential for adjusting signal levels, volume, and sensors. Mechanical potentiometers use a physical wiper moving along a resistive track, while digital potentiometers, controlled electronically, offer precise, repeatable adjustments without mechanical wear. Your choice between digital and mechanical potentiometers depends on factors like durability, resolution, and interface requirements for your application.
What is a Mechanical Potentiometer?
A mechanical potentiometer is an analog device that adjusts voltage by physically rotating a wiper over a resistive element, enabling variable resistance control. It consists of a shaft connected to a resistive track and requires manual operation for tuning circuit parameters. Mechanical potentiometers offer simplicity and tactile feedback but are prone to wear and noise compared to digital counterparts.
What is a Digital Potentiometer?
A digital potentiometer is an electronic device that mimics the function of a mechanical potentiometer by providing variable resistance controlled through digital signals rather than manual adjustment. It offers precise resistance settings via microcontrollers or digital interfaces, enabling automated tuning and improved reliability in circuits. Your applications benefit from enhanced accuracy, repeatability, and integration capabilities compared to traditional mechanical potentiometers.
Working Principle: Mechanical vs Digital
Mechanical potentiometers operate by physically sliding a wiper over a resistive element to vary resistance, providing analog control through manual adjustment. Digital potentiometers use electronic switches and resistors controlled by digital signals, allowing precise, programmable resistance changes without mechanical wear. Your choice depends on whether manual control or automated, repeatable adjustment is essential for the application.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Digital potentiometers offer higher precision and consistency due to their programmable resistance values and immunity to mechanical wear, achieving resolution as fine as 256 to 1024 steps. Mechanical potentiometers rely on manual adjustment with a physical wiper, which can introduce variability and lower accuracy over time because of contact resistance and component wear. Consequently, digital potentiometers are preferred in applications demanding stable and repeatable resistance settings, while mechanical types may suit simpler, less precise tasks.
Durability and Reliability Factors
Digital potentiometers offer superior durability compared to mechanical potentiometers due to the absence of physical wiper contacts, reducing wear and extending lifespan. Mechanical potentiometers experience degradation from repeated mechanical movements and environmental factors like dust and moisture, which can cause signal noise and failure. In high-reliability applications, digital potentiometers provide more consistent performance and longer mean time between failures (MTBF).
Application Areas: Mechanical and Digital Potentiometers
Mechanical potentiometers are widely used in audio equipment, volume controls, and analog signal adjustments due to their tactile feedback and simplicity. Digital potentiometers excel in embedded systems, microcontroller interfaces, and automated calibration, offering precise electronic control without mechanical wear. Your choice depends on the application's demand for resolution, durability, and ease of integration in industrial automation, consumer electronics, or instrumentation.
Advantages of Digital Potentiometers
Digital potentiometers offer precise, consistent adjustments without the wear and tear associated with mechanical components, ensuring longer device lifespan and reliability. They enable remote control and automation, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent or complex resistance changes. Your design benefits from reduced noise, improved accuracy, and seamless integration with microcontrollers or digital systems.
Advantages of Mechanical Potentiometers
Mechanical potentiometers offer precise tactile feedback and intuitive manual adjustment, enhancing user control in various applications. They provide reliable analog input without requiring power, making them ideal for low-power or offline environments. Your projects benefit from their durability and simplicity, ensuring consistent performance over time.
Choosing the Right Potentiometer for Your Project
Digital potentiometers offer precise, programmable resistance control ideal for automated systems and microcontroller interfaces, whereas mechanical potentiometers provide tactile feedback and variable resistance through manual adjustment. For projects requiring high accuracy, repeatability, and remote operation, digital potentiometers are preferred, while mechanical potentiometers suit applications needing simple, direct user interaction. Consider factors such as resolution, noise, size, and environmental conditions when selecting the appropriate type to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Digital potentiometer vs Mechanical potentiometer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com