Overrun relays protect motors from overheating by extending power supply after the motor stops, while time delay relays control the timing of electrical circuits by activating or deactivating after a set delay. Understanding the differences between these relays can enhance your control system efficiency--read on to explore their distinct functions and applications.
Table of Comparison
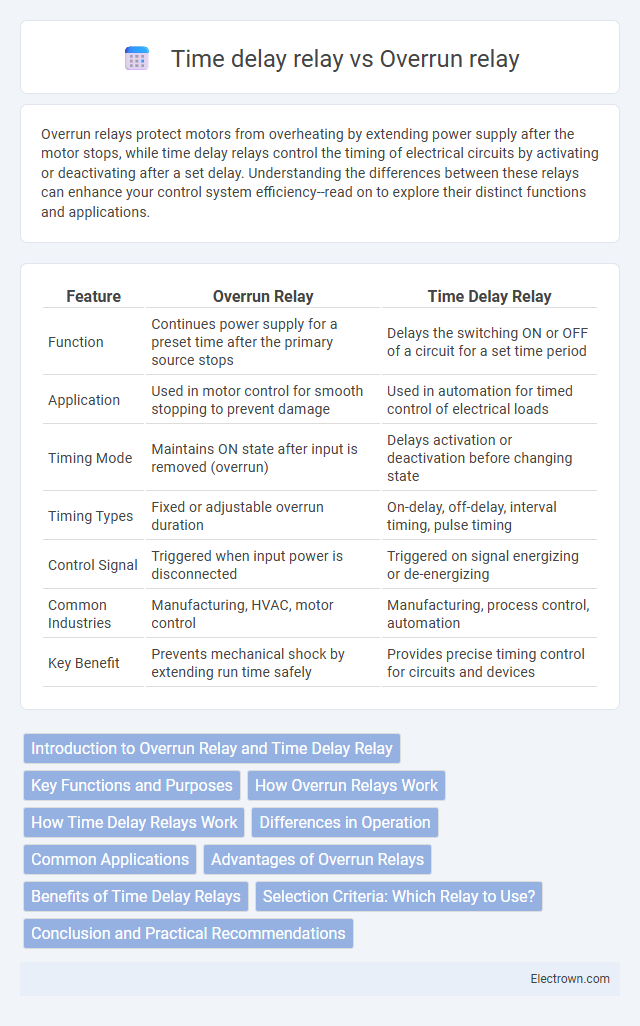
| Feature | Overrun Relay | Time Delay Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Continues power supply for a preset time after the primary source stops | Delays the switching ON or OFF of a circuit for a set time period |
| Application | Used in motor control for smooth stopping to prevent damage | Used in automation for timed control of electrical loads |
| Timing Mode | Maintains ON state after input is removed (overrun) | Delays activation or deactivation before changing state |
| Timing Types | Fixed or adjustable overrun duration | On-delay, off-delay, interval timing, pulse timing |
| Control Signal | Triggered when input power is disconnected | Triggered on signal energizing or de-energizing |
| Common Industries | Manufacturing, HVAC, motor control | Manufacturing, process control, automation |
| Key Benefit | Prevents mechanical shock by extending run time safely | Provides precise timing control for circuits and devices |
Introduction to Overrun Relay and Time Delay Relay
Overrun relays are specialized devices designed to keep an electrical circuit active for a set period after the input power is removed, primarily used in motor control applications to allow motors to coast to a stop. Time delay relays provide precise control over timing sequences by introducing delays in the activation or deactivation of electrical circuits, commonly found in automation and industrial processes. Both relays enhance operational efficiency and equipment protection by managing time-based control in electrical systems.
Key Functions and Purposes
Overrun relays are designed to maintain power to a load for a specific period after the control signal is removed, commonly used in motor cooling to prevent overheating by extending run time. Time delay relays provide controlled delays in switching operations, enabling precise control over the initiation or interruption of electrical circuits based on preset time intervals. Both devices optimize system protection and operational efficiency, with overrun relays focusing on post-operation energy application and time delay relays emphasizing timing control for start and stop functions.
How Overrun Relays Work
Overrun relays operate by maintaining current flow for a specified period after the controlling device stops, preventing abrupt shutdowns and protecting equipment like motors from damage due to sudden stops. Their mechanism typically relies on a mechanical or electronic timing element that extends the relay's activation beyond the initial signal. Your system benefits from smoother transitions and enhanced longevity by using overrun relays in applications requiring controlled deceleration or delayed power cut-off.
How Time Delay Relays Work
Time delay relays operate by activating or deactivating a circuit after a preset time interval, using internal timing mechanisms such as electronic or electromechanical components. They control the duration of current flow, ensuring precise timing in applications like motor control or lighting systems. Your choice of a time delay relay allows for automation and protection by accurately managing operational delays in electrical equipment.
Differences in Operation
Overrun relays maintain circuit operation for a set period after the initiating signal stops, ensuring equipment cool-down or safety processes. Time delay relays activate or deactivate circuits based on a preset time interval triggered by an input signal, controlling timing sequences precisely. The key operational difference lies in overrun relays extending the output after signal cessation, whereas time delay relays control timing from the moment of signal activation or deactivation.
Common Applications
Overrun relays are commonly used in motor control circuits to provide protection by shutting off power when an abnormal condition is detected, making them ideal for industrial machinery and HVAC systems. Time delay relays find frequent application in lighting control, conveyor systems, and automated equipment where precise time-based switching is essential. Your choice between the two depends on whether you need immediate protective action or controlled timing sequences in your electrical system.
Advantages of Overrun Relays
Overrun relays offer precise control by allowing equipment to continue running for a predetermined period after the initiating signal stops, which prevents abrupt operational halts and mechanical wear. These relays enhance system safety and reliability in applications such as fans, pumps, and conveyors by ensuring smooth shutdown sequences. Their robust design facilitates easy integration with various control circuits, improving overall equipment longevity and energy efficiency.
Benefits of Time Delay Relays
Time delay relays offer precise control over circuit operation by allowing a set delay before activation or deactivation, enhancing system safety and preventing equipment damage due to rapid switching. Your electrical systems benefit from improved timing accuracy, reducing wear on components and ensuring smoother operation in automation processes. These relays provide flexibility in controlling sequences, making them ideal for applications requiring timed intervals and delayed responses.
Selection Criteria: Which Relay to Use?
Selecting between an overrun relay and a time delay relay depends on the specific application requirements and operational goals. Overrun relays are ideal for extending equipment operation beyond a normal shutdown, useful in motor cooling or sequencing tasks, while time delay relays provide precise control by activating or deactivating circuits after a preset delay. Your choice should consider load characteristics, desired timing accuracy, and the necessity for protection versus timing functions to optimize system performance.
Conclusion and Practical Recommendations
Overrun relays provide protection by allowing motors to decelerate safely, making them ideal for applications requiring controlled stop times. Time delay relays offer precise control over activation intervals, suitable for sequential switching and timing control in automation systems. For your choice, prioritize overrun relays in motor braking scenarios and time delay relays when accurate timing sequences are critical.
Overrun relay vs Time delay relay Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com