Video encoders compress raw footage from automotive cameras into efficient formats for storage and transmission, while video decoders decompress these signals to display clear, real-time images crucial for driver assistance systems. Discover how understanding the differences between video encoders and decoders can enhance Your automotive camera setup by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
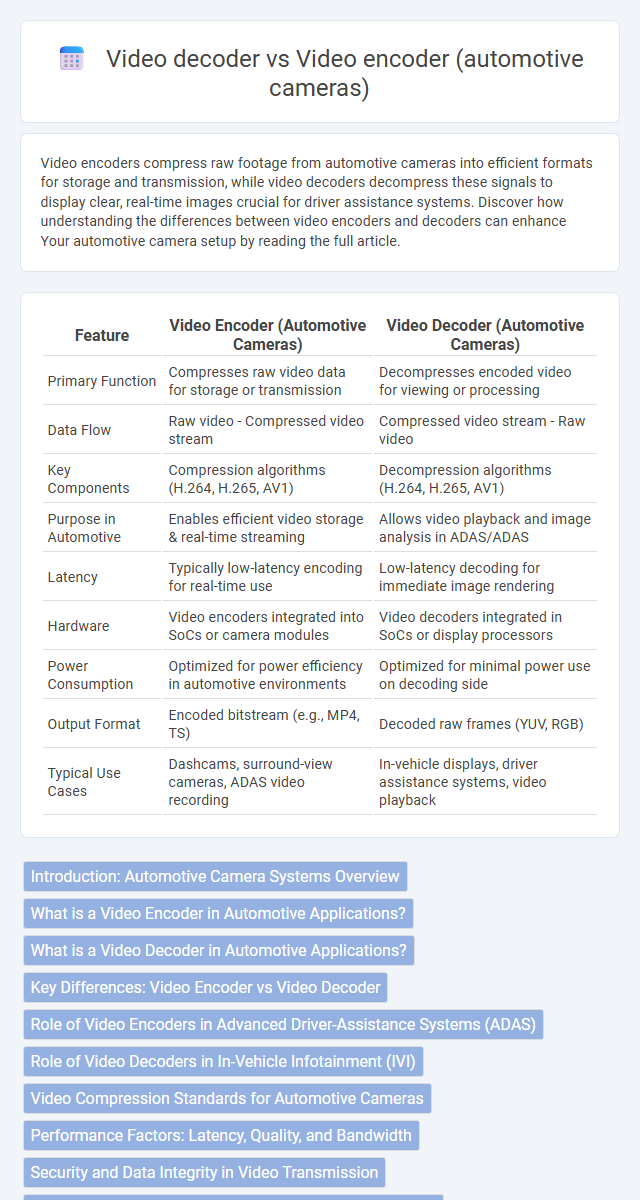
| Feature | Video Encoder (Automotive Cameras) | Video Decoder (Automotive Cameras) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Compresses raw video data for storage or transmission | Decompresses encoded video for viewing or processing |
| Data Flow | Raw video - Compressed video stream | Compressed video stream - Raw video |
| Key Components | Compression algorithms (H.264, H.265, AV1) | Decompression algorithms (H.264, H.265, AV1) |
| Purpose in Automotive | Enables efficient video storage & real-time streaming | Allows video playback and image analysis in ADAS/ADAS |
| Latency | Typically low-latency encoding for real-time use | Low-latency decoding for immediate image rendering |
| Hardware | Video encoders integrated into SoCs or camera modules | Video decoders integrated in SoCs or display processors |
| Power Consumption | Optimized for power efficiency in automotive environments | Optimized for minimal power use on decoding side |
| Output Format | Encoded bitstream (e.g., MP4, TS) | Decoded raw frames (YUV, RGB) |
| Typical Use Cases | Dashcams, surround-view cameras, ADAS video recording | In-vehicle displays, driver assistance systems, video playback |
Introduction: Automotive Camera Systems Overview
Automotive camera systems rely on video encoders to compress raw footage from cameras into efficient data streams for transmission or storage, while video decoders decompress this data for display or processing. Effective encoding ensures minimal latency and high-quality images critical for real-time driver assistance and autonomous driving features. Your vehicle's safety and performance depend on the seamless interaction between these video encoders and decoders within the camera system.
What is a Video Encoder in Automotive Applications?
A video encoder in automotive applications converts raw camera footage into a compressed digital format, enabling efficient storage and real-time transmission. It ensures high-quality video streaming for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving by minimizing latency and bandwidth usage. Understanding your vehicle's video encoder capabilities helps optimize performance and enhances safety through clearer, faster image processing.
What is a Video Decoder in Automotive Applications?
A video decoder in automotive applications converts compressed video signals from vehicle cameras into uncompressed formats for real-time processing and display. It plays a crucial role in Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) by enabling accurate image recognition and object detection through efficient video data handling. Your vehicle relies on video decoders to ensure high-quality visuals for enhanced safety and navigation accuracy.
Key Differences: Video Encoder vs Video Decoder
Video encoders in automotive cameras convert raw video signals into compressed digital formats, optimizing bandwidth and storage efficiency for transmission or recording. Video decoders perform the reverse, decompressing encoded video streams to render real-time visuals for driver assistance systems or display units. Key differences include encoding focused on compression algorithms like H.264 or H.265 for efficient data handling, whereas decoding emphasizes low-latency, error-resilient playback to ensure timely and accurate video rendering in critical automotive applications.
Role of Video Encoders in Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Video encoders in automotive cameras compress raw video data into efficient formats such as H.264 or H.265, essential for real-time transmission within Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS). These encoders minimize latency and bandwidth usage, enabling faster processing by ECUs for features like object detection, lane departure warning, and collision avoidance. Optimized video encoding ensures high-quality image streams critical for accurate analysis and reliable ADAS performance.
Role of Video Decoders in In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI)
Video decoders in automotive cameras play a crucial role in In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) systems by transforming compressed video streams into raw, display-ready images, ensuring seamless real-time video playback. They facilitate efficient processing of multiple camera feeds for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), navigation, and entertainment interfaces. High-performance video decoders reduce latency and improve image quality, enhancing the overall user experience in modern connected vehicles.
Video Compression Standards for Automotive Cameras
Video encoders in automotive cameras utilize advanced video compression standards such as H.264, H.265 (HEVC), and AV1 to efficiently compress raw footage for transmission or storage, minimizing bandwidth and storage requirements. Video decoders then decode these compressed streams in real-time, ensuring seamless playback and analysis for automotive safety systems like ADAS and autonomous driving. The choice of compression standards directly impacts latency, image quality, and computational load critical for effective real-time processing in automotive environments.
Performance Factors: Latency, Quality, and Bandwidth
Latency in automotive camera systems hinges on the efficiency of video encoders and decoders, with encoders compressing raw footage and decoders reconstructing the image for real-time analysis. Quality depends on the codec algorithms employed, impacting the clarity and accuracy of vehicle recognition and obstacle detection. Your camera system's bandwidth usage is optimized by balancing compression rates, ensuring swift data transmission without compromising critical visual information for safe autonomous driving.
Security and Data Integrity in Video Transmission
Video encoders in automotive cameras convert raw footage into compressed digital formats, ensuring efficient transmission while implementing encryption protocols to maintain data security. Video decoders decode the compressed streams at the receiver end, verifying the integrity of the video data through error detection and correction mechanisms. Your vehicle's safety relies on seamless coordination between encoders and decoders to prevent tampering and maintain secure, reliable video transmission.
Future Trends: Video Processing in Autonomous Vehicles
Future trends in video processing for autonomous vehicles emphasize enhanced video encoder and decoder technologies that support real-time high-resolution data transmission from automotive cameras. Advanced video codecs like H.265 and AV1 improve compression efficiency, reducing bandwidth requirements while maintaining image quality essential for object detection and environmental mapping. Integration of AI-driven video encoding and decoding accelerates processing speed and accuracy, enabling safer and more reliable autonomous navigation systems.
Video encoder vs Video decoder (automotive cameras) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com