Wireless power transfer offers seamless energy delivery without physical connectors, enhancing convenience and reducing wear on devices, while battery backup ensures uninterrupted power supply during outages, providing reliability and peace of mind. Explore the rest of the article to understand which solution best fits Your needs for efficient and dependable energy management.
Table of Comparison
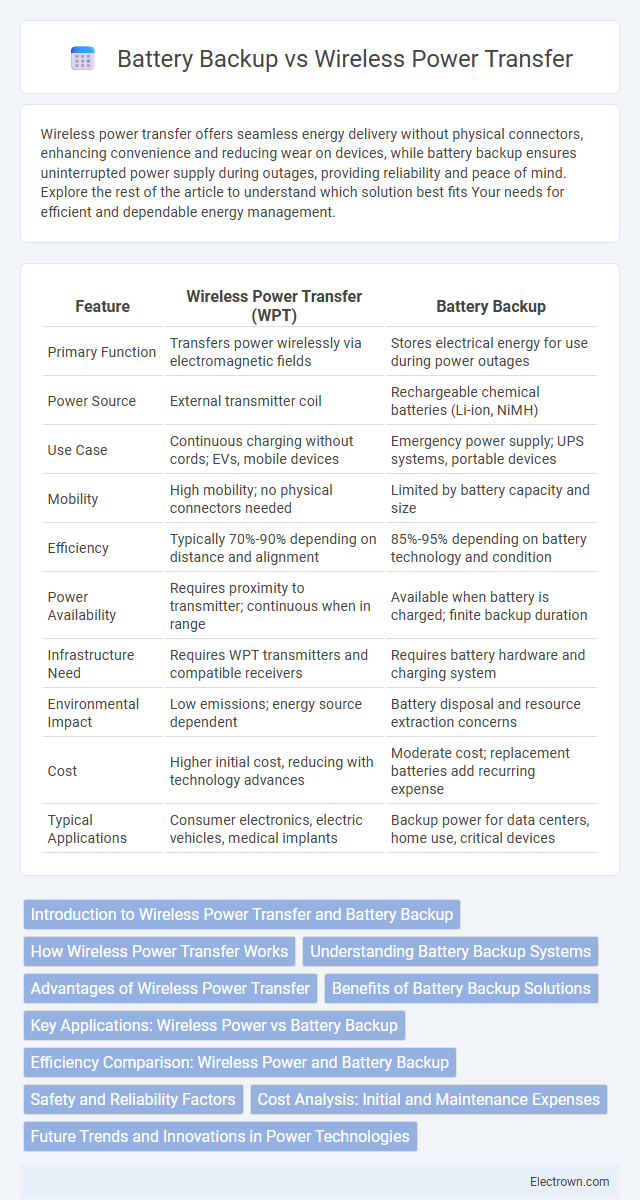
| Feature | Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) | Battery Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Transfers power wirelessly via electromagnetic fields | Stores electrical energy for use during power outages |
| Power Source | External transmitter coil | Rechargeable chemical batteries (Li-ion, NiMH) |
| Use Case | Continuous charging without cords; EVs, mobile devices | Emergency power supply; UPS systems, portable devices |
| Mobility | High mobility; no physical connectors needed | Limited by battery capacity and size |
| Efficiency | Typically 70%-90% depending on distance and alignment | 85%-95% depending on battery technology and condition |
| Power Availability | Requires proximity to transmitter; continuous when in range | Available when battery is charged; finite backup duration |
| Infrastructure Need | Requires WPT transmitters and compatible receivers | Requires battery hardware and charging system |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions; energy source dependent | Battery disposal and resource extraction concerns |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, reducing with technology advances | Moderate cost; replacement batteries add recurring expense |
| Typical Applications | Consumer electronics, electric vehicles, medical implants | Backup power for data centers, home use, critical devices |
Introduction to Wireless Power Transfer and Battery Backup
Wireless power transfer (WPT) enables energy to be transmitted without physical connectors, using electromagnetic fields or resonant inductive coupling to power devices remotely. Battery backup systems provide stored energy to maintain device functionality during power outages or interruptions, ensuring continuous operation. Understanding the differences between WPT's contactless energy delivery and battery backup's stored power is crucial for optimizing power solutions in various applications.
How Wireless Power Transfer Works
Wireless Power Transfer utilizes electromagnetic fields to transmit energy between a power source and a device without physical connections, often through inductive or resonant inductive coupling. This technology enables seamless charging by creating an oscillating magnetic field that induces a current in the receiver coil within your device. Unlike traditional battery backup systems, wireless power transfer eliminates the need for cables, providing continuous power delivery when within range of the transmitter.
Understanding Battery Backup Systems
Battery backup systems provide reliable power continuity during outages by storing energy from the grid or renewable sources in batteries. Unlike wireless power transfer, which delivers energy without physical connectors, battery backup ensures your critical devices remain operational by supplying stored electricity when primary power fails. Understanding battery capacity, recharge time, and compatibility with your devices is essential to maximizing uninterrupted power availability.
Advantages of Wireless Power Transfer
Wireless Power Transfer offers the advantage of eliminating physical cables, providing seamless and convenient charging for devices without the need for plug-in connections. It reduces wear and tear on charging ports and enhances safety by minimizing electrical contacts exposed to the environment. Your electronic devices benefit from continuous power delivery in applications where battery replacement or wired connections are impractical or inconvenient.
Benefits of Battery Backup Solutions
Battery backup solutions provide reliable power during outages, ensuring uninterrupted operation of critical devices and systems. They store energy efficiently, allowing you to maintain functionality without reliance on wireless power transfer or external power sources. This reliability and independence make battery backups essential for emergency preparedness and continuous device support.
Key Applications: Wireless Power vs Battery Backup
Wireless power transfer is key in applications requiring convenience and continuous charging without physical connectors, such as wearable devices, electric vehicle charging pads, and medical implants. Battery backup systems are essential in scenarios demanding reliable power during outages, including uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for data centers, emergency lighting, and critical healthcare equipment. Each technology optimizes power solutions based on mobility, reliability, and usage context.
Efficiency Comparison: Wireless Power and Battery Backup
Wireless power transfer systems often experience efficiency losses due to energy dissipation during transmission, typically ranging from 60% to 85%, depending on distance and technology used. Battery backup systems generally offer higher overall efficiency, with charge and discharge efficiencies often exceeding 90%, ensuring more reliable energy storage and supply. Your choice between these technologies should consider the specific application's power demands and location constraints to optimize energy utilization and system reliability.
Safety and Reliability Factors
Wireless Power Transfer offers enhanced safety by eliminating exposed connectors and reducing the risk of electric shock or short circuits, making it ideal for environments where safety is critical. Battery Backup systems provide reliable power continuity during outages but require regular maintenance to prevent degradation and potential hazards like overheating or leakage. Your choice should consider the specific reliability needs and safety protocols of your application to ensure optimal performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Maintenance Expenses
Wireless power transfer systems have higher initial costs due to advanced technology and installation requirements, while battery backup solutions typically offer lower upfront expenses but may require frequent replacements. Maintenance expenses for wireless power transfer are generally lower because of fewer moving parts and longer system lifespan, whereas battery backups incur ongoing costs linked to battery degradation and environmental disposal. Your choice depends on balancing initial investment against long-term operational savings and reliability needs.
Future Trends and Innovations in Power Technologies
Wireless power transfer technologies are advancing rapidly with innovations in resonant inductive coupling and microwave power transmission, promising seamless and efficient energy delivery without physical connectors. Battery backup systems are evolving through solid-state batteries and enhanced energy density materials, enabling longer-lasting, safer, and faster-charging storage solutions. Your choice between these technologies will increasingly depend on application-specific needs, as hybrid systems integrating wireless charging and advanced battery backup become more prevalent in future power networks.
Wireless Power Transfer vs Battery Backup Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com