Patient ground is a safety measure connecting the patient to earth ground to prevent electrical shock during medical procedures, while chassis ground refers to the common reference point in electronic equipment, typically the metal frame linked to earth ground. Understanding the differences between patient ground and chassis ground is crucial for ensuring your safety and the correct operation of medical devices, so continue reading to explore their specific functions and applications.
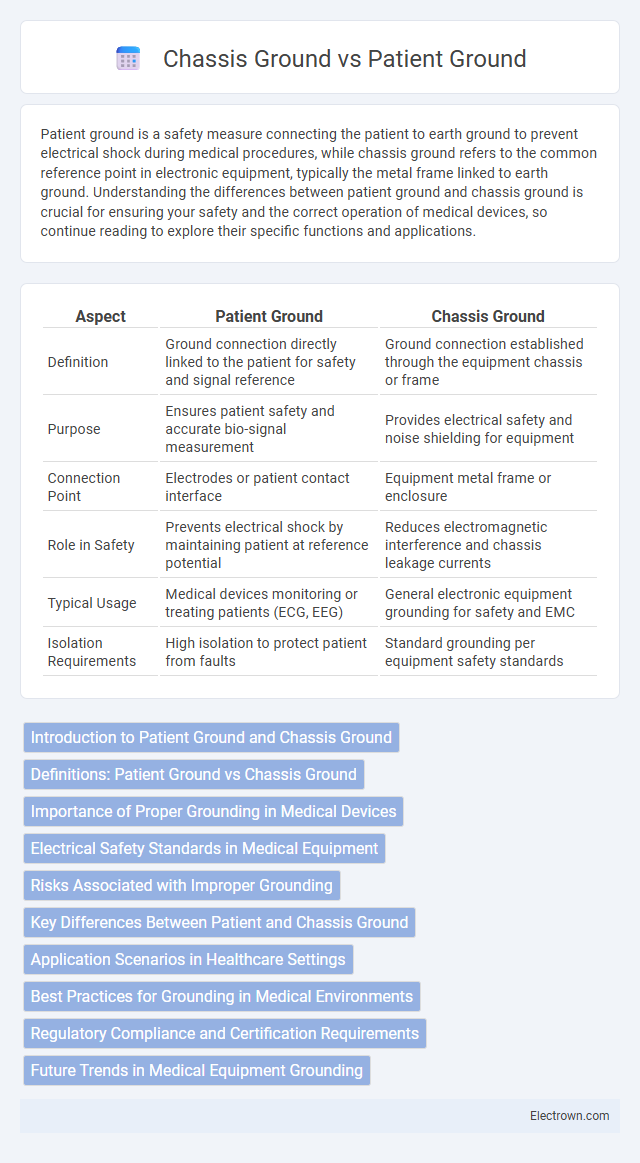
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Patient Ground | Chassis Ground |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ground connection directly linked to the patient for safety and signal reference | Ground connection established through the equipment chassis or frame |
| Purpose | Ensures patient safety and accurate bio-signal measurement | Provides electrical safety and noise shielding for equipment |
| Connection Point | Electrodes or patient contact interface | Equipment metal frame or enclosure |
| Role in Safety | Prevents electrical shock by maintaining patient at reference potential | Reduces electromagnetic interference and chassis leakage currents |
| Typical Usage | Medical devices monitoring or treating patients (ECG, EEG) | General electronic equipment grounding for safety and EMC |
| Isolation Requirements | High isolation to protect patient from faults | Standard grounding per equipment safety standards |
Introduction to Patient Ground and Chassis Ground
Patient ground refers to the conductive pathway designed to safely divert electrical current away from a patient during medical device operation, minimizing the risk of electric shock. Chassis ground is the connection from electrical equipment parts to the equipment frame, ensuring overall device safety by preventing electrical faults. Both grounds serve critical roles in medical device safety but target different aspects of electrical protection.
Definitions: Patient Ground vs Chassis Ground
Patient ground refers to the electrical connection designed to protect patients from electrical shock by providing a safe path for stray currents in medical devices. Chassis ground is the connection of the device's metal frame or enclosure to earth ground, preventing electrical hazards by stabilizing voltage levels and reducing electrical noise. Understanding the distinction ensures your medical equipment meets safety standards and minimizes the risk of electrical injury to patients.
Importance of Proper Grounding in Medical Devices
Proper grounding in medical devices ensures patient safety by preventing electrical shocks and minimizing electromagnetic interference that can disrupt device functionality. Patient ground is directly connected to the patient to provide a reference potential, while chassis ground is the equipment's protective grounding to avoid leakage currents. Ensuring your medical device has both correctly implemented patient and chassis grounds is crucial for accurate measurements and reliable operation in clinical environments.
Electrical Safety Standards in Medical Equipment
Patient ground and chassis ground serve distinct purposes in medical equipment to meet rigorous electrical safety standards; patient grounds ensure direct protection from leakage currents by providing a safe low-resistance path, while chassis grounds prevent electrical shock by connecting exposed metal parts to earth ground. Compliance with IEC 60601-1 standards mandates precise separation and performance criteria for both grounding systems to minimize risks of electric shock and interference. Your medical devices must integrate these grounding configurations effectively to protect patients and operators under all operating conditions.
Risks Associated with Improper Grounding
Improper grounding between patient ground and chassis ground risks electrical shock and interference with medical device operation, potentially leading to inaccurate diagnostics or treatment errors. Faulty grounding can cause current leakage, increasing the chance of patient injury or equipment malfunction during critical procedures. Ensuring proper isolation and grounding protocols minimizes these risks and maintains patient safety and device reliability.
Key Differences Between Patient and Chassis Ground
Patient ground provides a direct low-resistance path to protect the patient from electrical shocks by safely diverting fault currents away from the body. Chassis ground connects the equipment frame to earth to prevent electrical hazards from leakage currents, ensuring user safety and equipment reliability. Understanding these key differences helps you maintain proper medical device grounding and enhances overall patient safety in clinical environments.
Application Scenarios in Healthcare Settings
Patient ground and chassis ground serve distinct applications in healthcare settings to ensure safety and operational integrity. Patient ground is directly connected to the patient to prevent electrical shock during diagnostic or therapeutic procedures, commonly used with devices like ECG machines and defibrillators. Chassis ground provides a return path for electrical current and protects equipment from electrical faults, maintaining system stability in medical devices such as imaging systems and monitors.
Best Practices for Grounding in Medical Environments
Ensuring effective Patient Ground vs Chassis Ground separation in medical environments is crucial to prevent electrical interference and enhance patient safety. Best practices include using isolated, low-resistance patient grounding systems that are independent from chassis ground to avoid ground loops and reduce the risk of electrical shock. Implementation of dedicated patient ground electrodes and routine verification of grounding integrity help maintain signal accuracy and compliance with medical safety standards.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification Requirements
Patient ground and chassis ground fulfill distinct roles in medical device safety standards to meet regulatory compliance and certification requirements. Patient ground ensures direct electrical connection to minimize leakage current, critical for IEC 60601-1 compliance, which mandates strict limits on patient leakage currents to prevent electrical hazards during medical procedures. Your device must also implement chassis grounding to provide electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and reduce interference, aligning with regulatory frameworks like UL and CE certifications for safe medical equipment operation.
Future Trends in Medical Equipment Grounding
Future trends in medical equipment grounding emphasize enhanced patient safety through advanced isolation techniques that distinguish patient ground from chassis ground more effectively. Innovations include smart grounding systems with real-time monitoring to detect faults instantly, minimizing electrical hazards in sensitive medical environments. Your healthcare facility can benefit from integrating these intelligent grounding solutions to ensure compliance with evolving international safety standards.
Patient Ground vs Chassis Ground Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com