Microfluidic blood analyzers use tiny channels to process small blood samples rapidly and with high precision, contrasting with traditional analyzers that require larger volumes and longer times for results. Discover how your choice between these technologies can impact diagnostic speed, accuracy, and convenience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
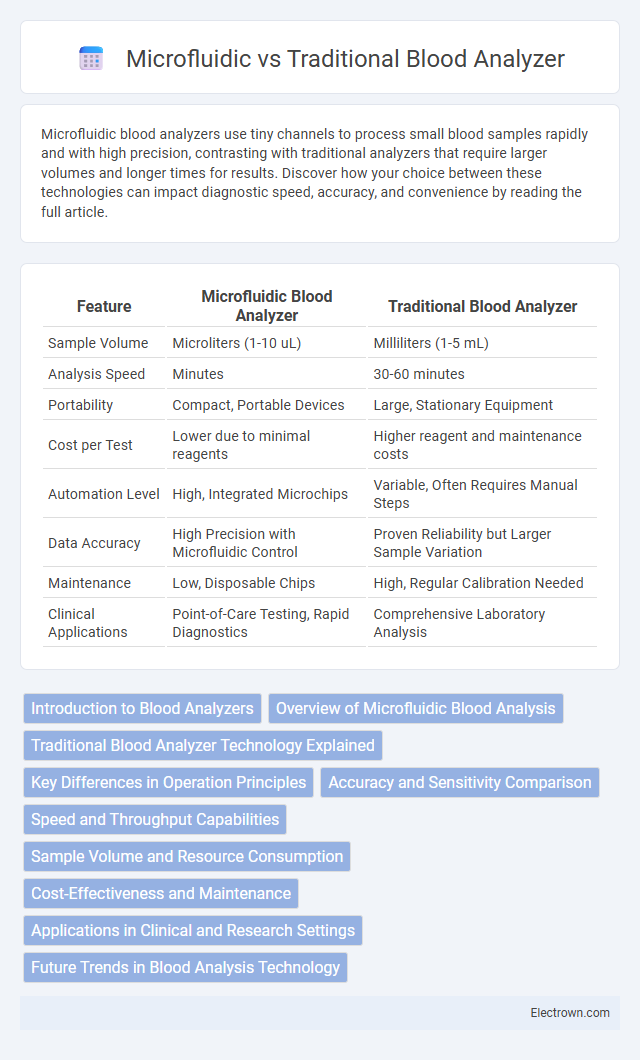
| Feature | Microfluidic Blood Analyzer | Traditional Blood Analyzer |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Volume | Microliters (1-10 uL) | Milliliters (1-5 mL) |
| Analysis Speed | Minutes | 30-60 minutes |
| Portability | Compact, Portable Devices | Large, Stationary Equipment |
| Cost per Test | Lower due to minimal reagents | Higher reagent and maintenance costs |
| Automation Level | High, Integrated Microchips | Variable, Often Requires Manual Steps |
| Data Accuracy | High Precision with Microfluidic Control | Proven Reliability but Larger Sample Variation |
| Maintenance | Low, Disposable Chips | High, Regular Calibration Needed |
| Clinical Applications | Point-of-Care Testing, Rapid Diagnostics | Comprehensive Laboratory Analysis |
Introduction to Blood Analyzers
Blood analyzers play a crucial role in medical diagnostics by measuring components such as glucose, cholesterol, and hemoglobin levels. Microfluidic blood analyzers use miniature channels and small sample volumes to provide rapid, accurate results with high sensitivity and portability. Traditional blood analyzers rely on larger sample volumes and more complex machinery, offering comprehensive testing but often requiring longer processing times and laboratory settings.
Overview of Microfluidic Blood Analysis
Microfluidic blood analysis utilizes miniaturized devices to process and analyze small blood samples rapidly, offering high precision and reduced reagent consumption compared to traditional blood analyzers. These systems integrate microchannels and sensors on a chip, enabling point-of-care testing with faster turnaround times and enhanced portability. Your ability to conduct real-time diagnostics is significantly improved, facilitating more timely and accurate clinical decisions.
Traditional Blood Analyzer Technology Explained
Traditional blood analyzer technology relies on large, bench-top instruments using optical and electrical impedance methods to measure blood cell counts and biochemical parameters. These analyzers require significant sample preparation, reagents, and maintenance, often leading to longer processing times and higher operational costs. Although highly accurate and widely used in clinical laboratories, traditional analyzers lack the portability and rapid processing capabilities seen in emerging microfluidic systems.
Key Differences in Operation Principles
Microfluidic blood analyzers use microscale channels to manipulate minute blood samples, enabling rapid analysis through precise fluid control and integration of multiple tests on a single chip. Traditional blood analyzers rely on larger sample volumes and separate processing steps, often involving centrifugation and chemical reagents for each test. You benefit from microfluidic systems' enhanced speed, reduced sample size, and potential for point-of-care diagnostics compared to conventional methods.
Accuracy and Sensitivity Comparison
Microfluidic blood analyzers offer higher accuracy and sensitivity compared to traditional blood analyzers due to their ability to process smaller sample volumes with precise control over fluid dynamics. These devices enable rapid detection of biomarkers and subtle changes in blood composition, improving diagnostic reliability for early disease detection. Your choice of a microfluidic analyzer can enhance testing efficiency and provide more detailed patient data than conventional methods.
Speed and Throughput Capabilities
Microfluidic blood analyzers offer significantly faster processing speeds and higher throughput capabilities compared to traditional blood analyzers, enabling rapid analysis of multiple samples simultaneously with minimal reagent volume. Traditional analyzers often require longer incubation times and larger sample volumes, limiting their efficiency in high-demand clinical settings. Your lab can enhance diagnostic turnaround times and increase sample processing capacity by integrating microfluidic technology.
Sample Volume and Resource Consumption
Microfluidic blood analyzers require significantly lower sample volumes, often just a few microliters, compared to traditional analyzers that need several milliliters of blood. This reduction in sample volume leads to decreased resource consumption, including reagents and energy, making microfluidic devices more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Your ability to perform rapid, point-of-care testing improves with microfluidic technology due to its minimal sample and resource requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness and Maintenance
Microfluidic blood analyzers offer significantly lower operational costs compared to traditional blood analyzers by using smaller sample volumes and reducing reagent consumption. Maintenance requirements for microfluidic devices are often simpler and less frequent due to integrated system designs and fewer mechanical parts, enhancing overall cost-effectiveness. Your choice of analyzer can impact long-term expenses, with microfluidic technology providing a more affordable and low-maintenance solution for routine blood testing.
Applications in Clinical and Research Settings
Microfluidic blood analyzers enable rapid, point-of-care testing with minimal sample volumes, making them ideal for decentralized clinical diagnostics and real-time monitoring in research. Traditional blood analyzers, while offering high throughput and broad parameter analysis, are generally confined to centralized laboratories due to their larger size and operational complexity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize portability and speed for personalized medicine or comprehensive data for extensive clinical studies.
Future Trends in Blood Analysis Technology
Microfluidic blood analyzers are driving the future of blood analysis technology with their ability to perform rapid, point-of-care diagnostics using minimal sample volumes and integrated lab-on-a-chip systems. Traditional blood analyzers, while reliable and high-throughput, face limitations in portability and speed compared to microfluidic devices that enable real-time monitoring and personalized medicine applications. Advances in AI integration, nanotechnology, and multifunctional microfluidic platforms are expected to revolutionize disease detection, treatment monitoring, and decentralized healthcare delivery.
Microfluidic vs Traditional Blood Analyzer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com