LC filters utilize inductors and capacitors to achieve sharp frequency selectivity and high efficiency in signal filtering, making them ideal for radio frequency applications. Understanding the differences between LC and RC filters can help You choose the best option for your specific electronic circuit needs; continue reading to explore their characteristics and applications in detail.
Table of Comparison
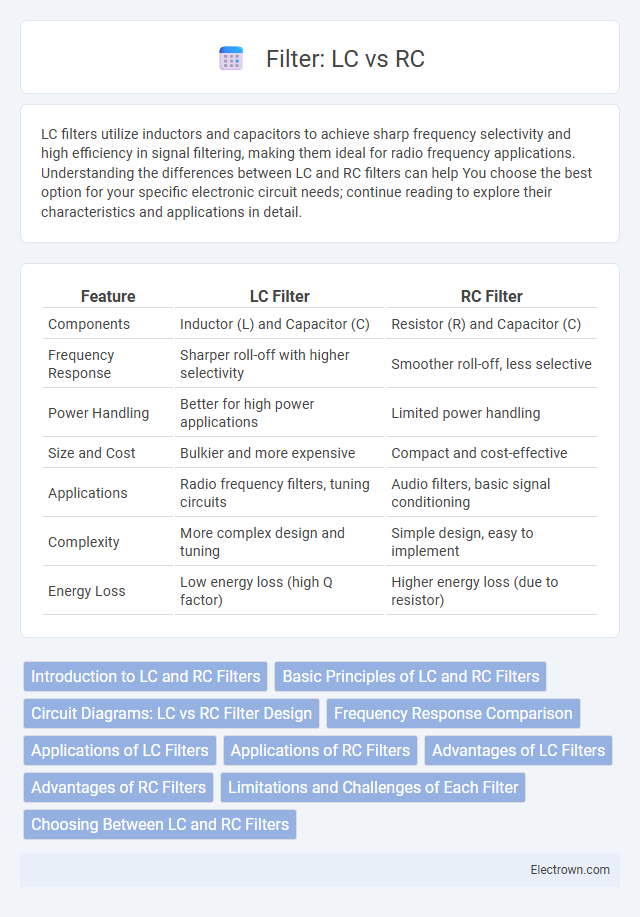
| Feature | LC Filter | RC Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Components | Inductor (L) and Capacitor (C) | Resistor (R) and Capacitor (C) |
| Frequency Response | Sharper roll-off with higher selectivity | Smoother roll-off, less selective |
| Power Handling | Better for high power applications | Limited power handling |
| Size and Cost | Bulkier and more expensive | Compact and cost-effective |
| Applications | Radio frequency filters, tuning circuits | Audio filters, basic signal conditioning |
| Complexity | More complex design and tuning | Simple design, easy to implement |
| Energy Loss | Low energy loss (high Q factor) | Higher energy loss (due to resistor) |
Introduction to LC and RC Filters
LC filters consist of inductors (L) and capacitors (C) that work together to block or pass specific frequency ranges, offering high selectivity and low signal loss in radio frequency applications. RC filters, made of resistors (R) and capacitors (C), provide simpler, cost-effective frequency filtering with moderate performance, commonly used in audio processing and basic signal conditioning. Understanding the differences in design and frequency response helps you select the appropriate filter type for your circuit's needs.
Basic Principles of LC and RC Filters
LC filters utilize inductors (L) and capacitors (C) to achieve frequency-selective impedance, leveraging resonance between inductive and capacitive reactances to pass or block specific frequency ranges with minimal energy loss. RC filters consist of resistors (R) and capacitors (C) that rely on the frequency-dependent voltage drop across the capacitor and resistor, creating a simple and cost-effective solution for attenuating undesired frequencies but with higher signal dissipation. The fundamental difference lies in LC filters' ability to provide sharper cutoff frequencies and higher quality factors (Q), making them ideal for applications requiring precise frequency discrimination, whereas RC filters are suited for less critical, low-cost filtering needs.
Circuit Diagrams: LC vs RC Filter Design
LC filters use inductors (L) and capacitors (C) arranged in series or parallel configurations to create resonant circuits that effectively block or pass specific frequency ranges, often depicted with a series inductor followed by a shunt capacitor in low-pass designs. RC filters employ resistors (R) and capacitors (C) in simpler circuit diagrams, typically with a resistor feeding into a capacitor connected to ground for low-pass filtering, providing easier implementation but lower selectivity. The LC design is favored for higher quality factors (Q) and sharper frequency cutoffs, whereas the RC design is more compact and cost-effective for less demanding applications.
Frequency Response Comparison
LC filters exhibit sharper frequency response with steep roll-off characteristics due to the resonant behavior of inductors and capacitors, enabling precise signal selection and rejection. RC filters have gentler slopes in their frequency response, typically 20 dB/decade per pole, resulting in less aggressive attenuation outside the passband. The LC filter's higher Q factor allows it to achieve better selectivity and lower insertion loss compared to RC filters, which are simpler but usually less efficient at isolating narrow frequency bands.
Applications of LC Filters
LC filters are widely used in radio frequency (RF) circuits, wireless communication systems, and audio electronics due to their ability to provide sharp frequency selectivity and low insertion loss. Your applications often include signal tuning, noise reduction, and impedance matching in transmitters and receivers. These filters are essential in designing devices like TV tuners, radio receivers, and RF power amplifiers, where precise filtering is critical.
Applications of RC Filters
RC filters are widely used in audio electronics for signal conditioning and noise reduction due to their simple design and effective low-pass or high-pass filtering capabilities. They are integral in smoothing voltage signals in power supplies and shaping frequency response in analog circuits. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of integration make them ideal for applications like tone control in audio equipment and basic signal processing tasks.
Advantages of LC Filters
LC filters provide superior frequency selectivity and lower insertion loss compared to RC filters, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. Their inductors and capacitors offer better energy storage and signal integrity, improving overall circuit performance. You benefit from enhanced efficiency and reduced signal distortion when using LC filters in your electronic designs.
Advantages of RC Filters
RC filters offer simple design and cost-effectiveness due to readily available resistors and capacitors, making them ideal for low-frequency applications. They provide stable performance with minimal inductive effects, ensuring accurate signal processing in audio and analog circuits. Your projects benefit from RC filters' ease of implementation and compact size, enhancing overall circuit efficiency.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Filter
LC filters face limitations such as bulky inductors and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, impacting performance in high-frequency applications. RC filters struggle with signal attenuation and limited selectivity, making them less ideal for precise frequency filtering. Understanding these challenges helps you choose the appropriate filter for your specific electronic circuit needs.
Choosing Between LC and RC Filters
Choosing between LC and RC filters depends on frequency range, component size, and signal integrity requirements. LC filters provide superior performance at high frequencies due to low loss and sharper cutoff, making them ideal for RF and communication systems. RC filters offer simpler design and cost-effectiveness for low-frequency applications, with easier implementation in integrated circuits.
LC vs RC Filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com