Macro-scale sensors detect changes over large areas and are ideal for monitoring environmental or structural conditions, while micro-scale sensors operate at a much smaller scale for precise measurements in applications like medical diagnostics or electronics. Explore the differences in technology and applications to understand which sensor suits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
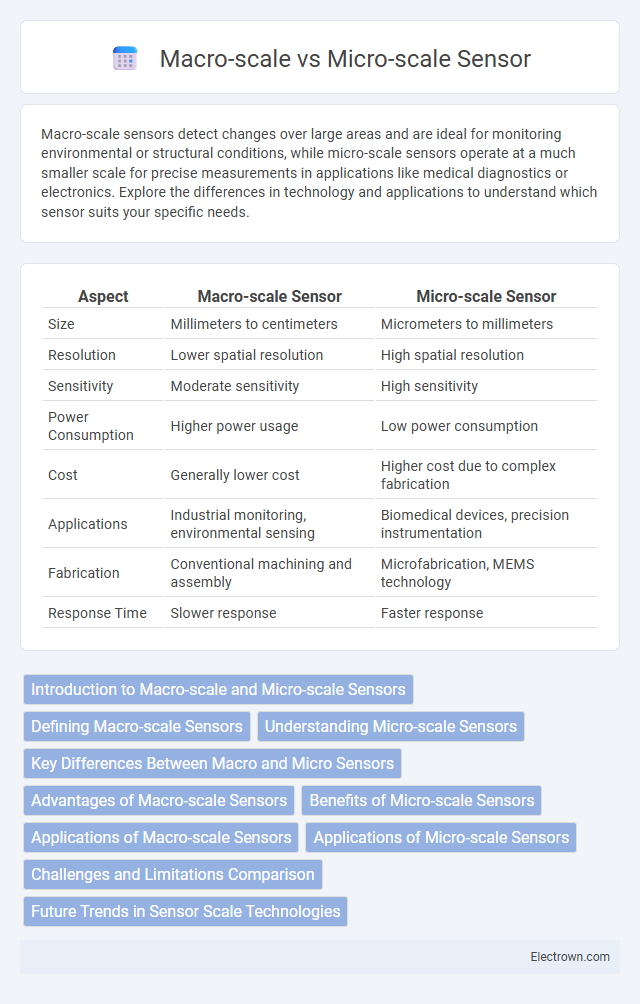
| Aspect | Macro-scale Sensor | Micro-scale Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Millimeters to centimeters | Micrometers to millimeters |
| Resolution | Lower spatial resolution | High spatial resolution |
| Sensitivity | Moderate sensitivity | High sensitivity |
| Power Consumption | Higher power usage | Low power consumption |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex fabrication |
| Applications | Industrial monitoring, environmental sensing | Biomedical devices, precision instrumentation |
| Fabrication | Conventional machining and assembly | Microfabrication, MEMS technology |
| Response Time | Slower response | Faster response |
Introduction to Macro-scale and Micro-scale Sensors
Macro-scale sensors detect physical phenomena on a larger scale, often used in industrial applications for monitoring temperature, pressure, and motion, leveraging established technologies for robust and reliable measurements. Micro-scale sensors, including MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems), operate at microscopic levels, enabling high sensitivity and precision in compact forms, crucial for applications like medical diagnostics and wearable devices. Your choice between macro-scale and micro-scale sensors depends on the required sensitivity, size constraints, and application environment.
Defining Macro-scale Sensors
Macro-scale sensors are devices designed to detect and measure physical phenomena at a larger scale, typically visible and measurable without specialized microscopy. These sensors are commonly used in industrial applications, environmental monitoring, and structural health assessments where broad area coverage or bulk property detection is essential. Unlike micro-scale sensors that operate at microscopic dimensions, macro-scale sensors prioritize durability, sensitivity over large regions, and ease of integration into existing systems.
Understanding Micro-scale Sensors
Micro-scale sensors measure physical, chemical, or biological parameters at a microscopic level, enabling high precision and sensitivity in applications like medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and wearable technology. These sensors utilize microscale components such as MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) to detect subtle changes in temperature, pressure, humidity, or chemical composition with minimal power consumption. Their compact size and enhanced resolution distinguish them from macro-scale sensors, which are designed for larger-scale measurements and often lack the detailed responsiveness required in advanced technological applications.
Key Differences Between Macro and Micro Sensors
Macro-scale sensors typically measure physical quantities over larger areas or volumes, offering high durability but often lower sensitivity and slower response times compared to micro-scale sensors. Micro-scale sensors, such as MEMS devices, are designed to detect minute changes at the microscale with greater precision, faster response, and lower power consumption, making them ideal for applications requiring detailed monitoring. Your choice between macro and micro sensors depends on the specific requirements for accuracy, size constraints, and environmental conditions.
Advantages of Macro-scale Sensors
Macro-scale sensors offer enhanced durability and robustness, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments and extended operational lifespans. Their larger size allows for easier integration with conventional measurement systems and greater sensitivity to physical changes, leading to accurate and stable readings. These sensors typically require less complex fabrication processes, resulting in lower manufacturing costs and simplified maintenance.
Benefits of Micro-scale Sensors
Micro-scale sensors offer exceptional sensitivity and precision due to their small size, enabling accurate detection of minute physical, chemical, or biological changes. Their compact form allows integration into portable and wearable devices, enhancing real-time monitoring and personalized applications. You benefit from faster response times and reduced power consumption, making micro-scale sensors ideal for advanced healthcare, environmental monitoring, and industrial automation.
Applications of Macro-scale Sensors
Macro-scale sensors are widely employed in industrial automation, environmental monitoring, and structural health diagnostics due to their robust design and ability to measure large-scale phenomena such as pressure, temperature, and strain over extensive areas. These sensors excel in infrastructure applications like bridge monitoring and machinery condition assessment, where durability and long-range signal transmission are critical. Their scalability and integration with control systems make them essential for real-time process optimization in manufacturing and energy production.
Applications of Micro-scale Sensors
Micro-scale sensors are extensively applied in medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and industrial automation due to their high sensitivity and compact size. These sensors enable precise detection of chemical, biological, and physical parameters at a microscopic level, making them essential for wearable health devices and real-time pollution analysis. Your ability to incorporate micro-scale sensors can significantly enhance system performance by providing detailed data in confined spaces.
Challenges and Limitations Comparison
Macro-scale sensors face challenges such as limited sensitivity and slower response times due to their larger physical dimensions, which can hinder precise detection in complex environments. Micro-scale sensors, while offering higher sensitivity and faster response, encounter limitations including fabrication complexity, higher production costs, and susceptibility to environmental noise. Your choice between these sensor scales depends on the application's sensitivity requirements and budget constraints.
Future Trends in Sensor Scale Technologies
Future trends in sensor scale technologies point towards increased integration of micro-scale sensors with advanced nano-scale materials to enhance sensitivity and reduce power consumption. Macro-scale sensors continue to evolve with improvements in durability and data processing capabilities for large-scale environmental monitoring. Your choice between macro-scale and micro-scale sensors will depend on application requirements such as precision, scalability, and energy efficiency in emerging IoT and smart device ecosystems.
Macro-scale vs Micro-scale Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com