Heatsinks provide efficient heat dissipation through metal fins that increase surface area, while thermal pads offer a convenient, flexible solution for filling gaps between components and heat sinks. Learn more about how these cooling solutions impact your device's performance in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
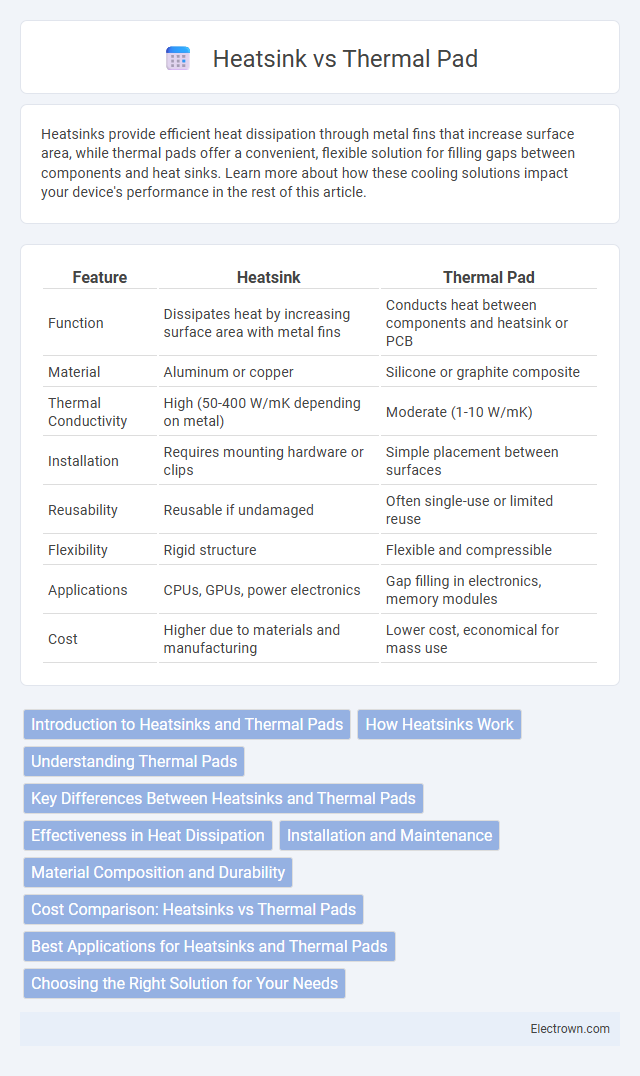
| Feature | Heatsink | Thermal Pad |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Dissipates heat by increasing surface area with metal fins | Conducts heat between components and heatsink or PCB |
| Material | Aluminum or copper | Silicone or graphite composite |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (50-400 W/mK depending on metal) | Moderate (1-10 W/mK) |
| Installation | Requires mounting hardware or clips | Simple placement between surfaces |
| Reusability | Reusable if undamaged | Often single-use or limited reuse |
| Flexibility | Rigid structure | Flexible and compressible |
| Applications | CPUs, GPUs, power electronics | Gap filling in electronics, memory modules |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and manufacturing | Lower cost, economical for mass use |
Introduction to Heatsinks and Thermal Pads
Heatsinks and thermal pads are essential components in managing device temperatures by enhancing heat dissipation from electronic components. A heatsink, typically made of aluminum or copper, absorbs and disperses heat away from critical parts, while thermal pads provide a conductive interface that fills gaps between a heatsink and the component for improved thermal transfer. Selecting the right combination can significantly improve your device's performance and longevity by preventing overheating.
How Heatsinks Work
Heatsinks dissipate heat by increasing surface area exposed to air, allowing heat from electronic components to transfer efficiently into the surrounding environment. Made typically from aluminum or copper, their fins improve airflow which accelerates cooling through convection. This passive heat dissipation prevents overheating, maintaining optimal device performance and longevity.
Understanding Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are soft, electrically insulating materials designed to fill air gaps and improve heat transfer between electronic components and heatsinks. Unlike heatsinks, which dissipate heat through metal fins, thermal pads enhance thermal conductivity by conforming to irregular surfaces, reducing thermal resistance. Their efficiency depends on thermal conductivity ratings, typically measured in W/mK, with higher values indicating better heat transfer performance.
Key Differences Between Heatsinks and Thermal Pads
Heatsinks are metal components designed to dissipate heat from electronic devices by increasing surface area and enhancing airflow, while thermal pads are soft, compliant materials that fill gaps between heat sources and heatsinks to improve thermal conductivity. Heatsinks actively cool by transferring heat to the surrounding air, whereas thermal pads act as thermal interface materials, ensuring efficient heat transfer between components. The key difference lies in their function: heatsinks manage heat dissipation, and thermal pads optimize thermal contact and reduce thermal resistance.
Effectiveness in Heat Dissipation
Heatsinks offer superior effectiveness in heat dissipation by providing a larger surface area and utilizing materials like aluminum or copper to rapidly transfer heat away from components. Thermal pads serve as an interface to fill gaps between heat-generating parts and heatsinks, improving thermal conductivity but generally performing less efficiently than direct heatsink contact. For optimal thermal management, you may need to combine both to ensure your device maintains lower temperatures under heavy use.
Installation and Maintenance
Heatsinks require precise placement and secure mounting, often using screws or clips, to ensure optimal thermal contact, while thermal pads offer a simpler, adhesive-backed installation that conforms easily to surface irregularities. Maintaining a heatsink involves regular cleaning to remove dust buildup, which can impede heat dissipation, whereas thermal pads may need periodic replacement as they degrade or lose conductivity over time. Your choice between these solutions should consider the ease of installation and the frequency of maintenance required for effective cooling performance.
Material Composition and Durability
Heatsinks are typically made from aluminum or copper, offering excellent thermal conductivity and long-lasting performance in dissipating heat from electronic components. Thermal pads consist of silicone or other polymer-based materials infused with thermally conductive fillers, providing flexible and durable interfaces for uneven surfaces but generally lower thermal conductivity than heatsinks. Your choice depends on balancing the durability of rigid metal heatsinks against the adaptable material composition of thermal pads for effective thermal management.
Cost Comparison: Heatsinks vs Thermal Pads
Heatsinks typically incur higher upfront costs compared to thermal pads due to their complex manufacturing and larger material requirements, especially for those made of copper or aluminum alloys. Thermal pads offer a cost-effective solution with lower prices and easier installation, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications or mass production. Your choice depends on balancing performance needs with budget constraints, as heatsinks provide superior heat dissipation but at a greater cost.
Best Applications for Heatsinks and Thermal Pads
Heatsinks excel in high-performance applications requiring efficient heat dissipation such as CPUs, GPUs, and power components in computers and industrial equipment. Thermal pads are ideal for filling uneven surfaces and gaps between components and heat sinks, frequently used in mobile devices, LED systems, and compact electronics where consistent pressure and thermal conductivity are crucial. Choosing the right solution ensures optimal thermal management, protecting Your devices from overheating and performance degradation.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting between a heatsink and a thermal pad depends on the specific thermal management requirements and device architecture. Heatsinks excel in dissipating high heat loads through passive airflow, making them ideal for CPUs and GPUs with significant thermal output. Thermal pads provide versatile, easy-to-install thermal interface solutions for moderate heat transfer, ensuring gap filling and electrical isolation in compact or irregularly shaped components.
Heatsink vs Thermal Pad Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com