An EMI filter is designed specifically to suppress electromagnetic interference affecting electronic devices, while an EMC filter provides broader protection by ensuring electromagnetic compatibility and reducing both emissions and susceptibility of equipment. Discover how understanding the differences between EMI and EMC filters can enhance Your device's performance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
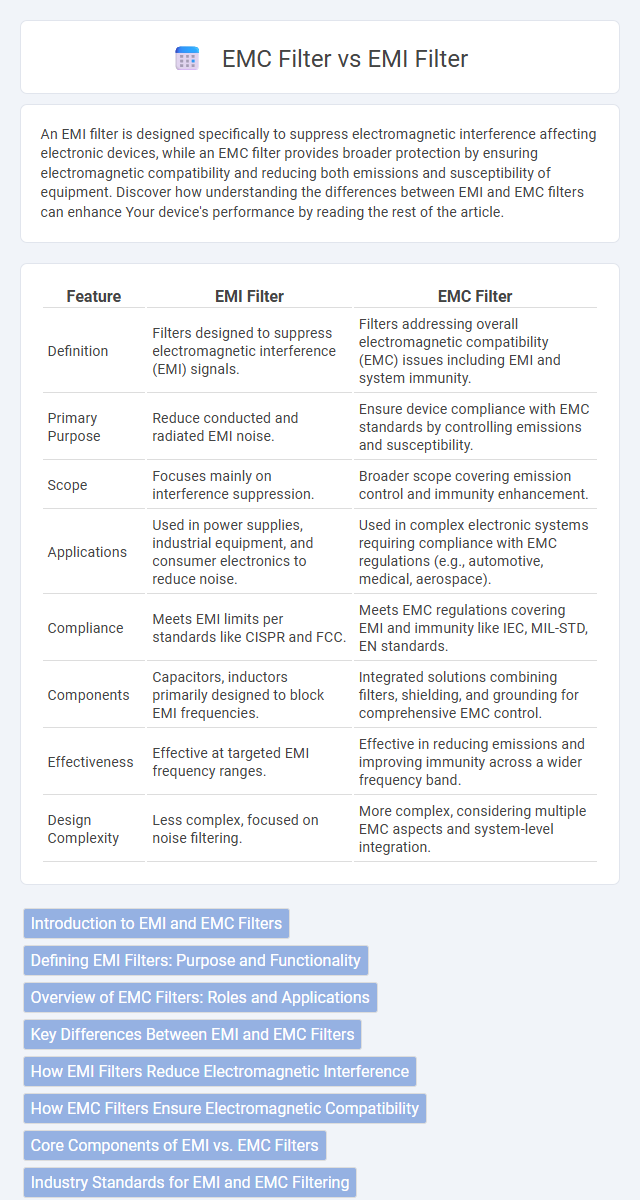
| Feature | EMI Filter | EMC Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Filters designed to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI) signals. | Filters addressing overall electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) issues including EMI and system immunity. |
| Primary Purpose | Reduce conducted and radiated EMI noise. | Ensure device compliance with EMC standards by controlling emissions and susceptibility. |
| Scope | Focuses mainly on interference suppression. | Broader scope covering emission control and immunity enhancement. |
| Applications | Used in power supplies, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics to reduce noise. | Used in complex electronic systems requiring compliance with EMC regulations (e.g., automotive, medical, aerospace). |
| Compliance | Meets EMI limits per standards like CISPR and FCC. | Meets EMC regulations covering EMI and immunity like IEC, MIL-STD, EN standards. |
| Components | Capacitors, inductors primarily designed to block EMI frequencies. | Integrated solutions combining filters, shielding, and grounding for comprehensive EMC control. |
| Effectiveness | Effective at targeted EMI frequency ranges. | Effective in reducing emissions and improving immunity across a wider frequency band. |
| Design Complexity | Less complex, focused on noise filtering. | More complex, considering multiple EMC aspects and system-level integration. |
Introduction to EMI and EMC Filters
EMI filters are designed to suppress electromagnetic interference signals generated by electronic devices, ensuring compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. EMC filters, while similar, emphasize broader system-level protection by controlling both emissions and susceptibility to electromagnetic disturbances. Both types of filters incorporate components such as inductors, capacitors, and resistors to mitigate noise and maintain stable device operation within regulatory limits.
Defining EMI Filters: Purpose and Functionality
EMI filters are designed to suppress electromagnetic interference that can disrupt electronic devices by blocking unwanted high-frequency noise signals. They function by attenuating conducted emissions from power lines and signal cables, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and protecting sensitive equipment. Your electronic system benefits from enhanced performance and reduced susceptibility to electromagnetic disturbances when EMI filters are correctly implemented.
Overview of EMC Filters: Roles and Applications
EMC filters are designed to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure compliance with electromagnetic compatibility standards by filtering conducted emissions and improving signal integrity. These filters play a crucial role in protecting sensitive electronic equipment in industries such as telecommunications, automotive, and medical devices. Your choice of an EMC filter depends on specific requirements like frequency range, current rating, and environmental conditions to effectively minimize EMI and enhance device performance.
Key Differences Between EMI and EMC Filters
EMI filters are designed primarily to suppress electromagnetic interference by blocking or attenuating high-frequency noise signals, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. EMC filters encompass a broader scope, aiming to improve electromagnetic compatibility by reducing both the emission and susceptibility of electronic devices to electromagnetic disturbances. The key difference lies in EMI filters focusing on noise suppression, while EMC filters integrate EMI filtering with measures to enhance overall system immunity and reliability.
How EMI Filters Reduce Electromagnetic Interference
EMI filters reduce electromagnetic interference by blocking or attenuating unwanted high-frequency noise signals in electrical circuits, ensuring cleaner power supply and signal integrity. They typically employ passive components such as inductors, capacitors, and resistors arranged to create low-pass filters that prevent noise from entering or exiting electronic devices. This filtering process enhances electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) by minimizing disruptions in sensitive electronic equipment and communication systems.
How EMC Filters Ensure Electromagnetic Compatibility
EMC filters reduce electromagnetic interference by attenuating both conducted and radiated noise, ensuring devices meet regulatory emission limits. They incorporate components such as inductors and capacitors designed to suppress high-frequency disturbances, preventing disturbances from affecting sensitive equipment. Effective EMC filters maintain electromagnetic compatibility by minimizing the emission and susceptibility of electronic systems within their operational environment.
Core Components of EMI vs. EMC Filters
EMI filters primarily consist of inductors, capacitors, and resistors designed to suppress electromagnetic interference by blocking high-frequency noise signals. EMC filters incorporate these same core components but are engineered to ensure overall electromagnetic compatibility by both attenuating interference and maintaining proper operation of electronic devices within regulatory standards. Understanding the specific core components in your filter choice ensures effective noise reduction and regulatory compliance for your electronic systems.
Industry Standards for EMI and EMC Filtering
EMI filters and EMC filters adhere to stringent industry standards such as CISPR 22, IEC 61000-4-2, and MIL-STD-461 to ensure effective suppression of electromagnetic interference and compatibility. EMI filters target high-frequency noise mitigation according to these benchmarks, while EMC filters focus on broader electromagnetic compatibility requirements including immunity and emission levels. Your selection depends on compliance needs with these standards to maintain device performance and regulatory approval.
Applications: Where to Use EMI or EMC Filters
EMI filters are primarily used in electronic devices and equipment to suppress high-frequency electromagnetic interference, ensuring compliance with emission standards. EMC filters, on the other hand, are designed for comprehensive electromagnetic compatibility, addressing both emission and susceptibility issues in industrial machinery, medical devices, and communication systems. Your choice depends on whether the focus is on reducing emitted noise (EMI filter) or achieving overall compatibility and immunity in complex environments (EMC filter).
Choosing the Right Filter: EMI vs. EMC Considerations
Selecting the appropriate filter requires understanding that EMI filters target electromagnetic interference specifically to prevent unwanted signal disruption, while EMC filters address broader electromagnetic compatibility to ensure devices operate without mutual interference. EMI filters are ideal for reducing high-frequency noise in sensitive electronic circuits, whereas EMC filters provide comprehensive suppression across conducted and radiated emissions to meet regulatory standards. Evaluating device requirements, frequency ranges, and compliance criteria guides the choice between EMI and EMC filters for optimal performance and protection.
EMI Filter vs EMC Filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com