Surface mount resistors offer compact size and efficient heat dissipation ideal for high-density circuit boards, while wirewound resistors provide superior precision and higher power handling capabilities due to their coiled wire construction. Explore the differences in performance, applications, and durability to determine which resistor best suits your project needs.
Table of Comparison
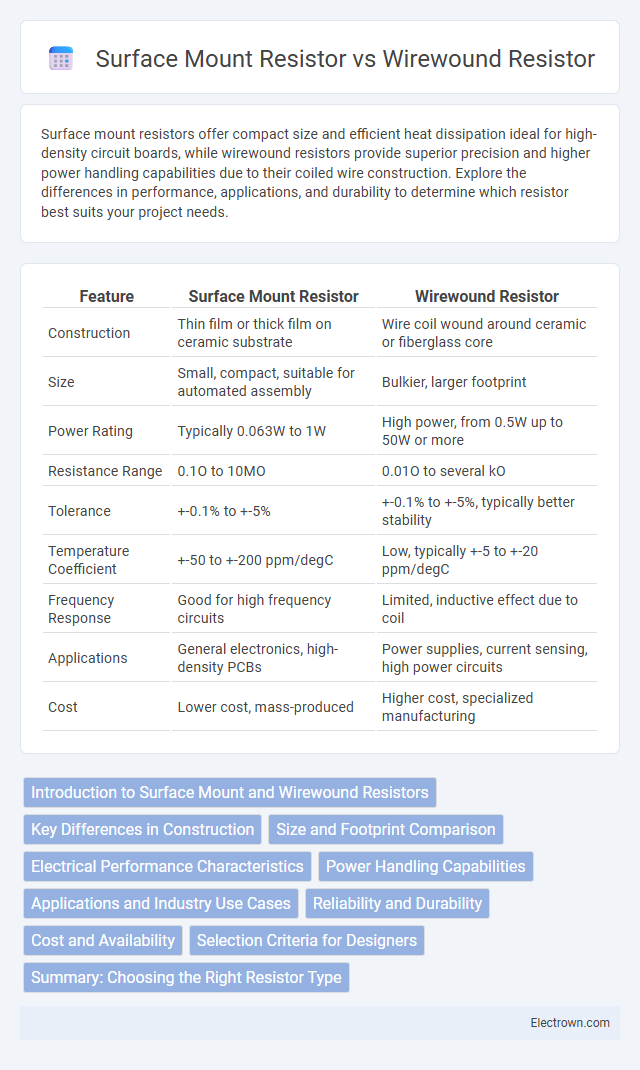
| Feature | Surface Mount Resistor | Wirewound Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Thin film or thick film on ceramic substrate | Wire coil wound around ceramic or fiberglass core |
| Size | Small, compact, suitable for automated assembly | Bulkier, larger footprint |
| Power Rating | Typically 0.063W to 1W | High power, from 0.5W up to 50W or more |
| Resistance Range | 0.1O to 10MO | 0.01O to several kO |
| Tolerance | +-0.1% to +-5% | +-0.1% to +-5%, typically better stability |
| Temperature Coefficient | +-50 to +-200 ppm/degC | Low, typically +-5 to +-20 ppm/degC |
| Frequency Response | Good for high frequency circuits | Limited, inductive effect due to coil |
| Applications | General electronics, high-density PCBs | Power supplies, current sensing, high power circuits |
| Cost | Lower cost, mass-produced | Higher cost, specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Surface Mount and Wirewound Resistors
Surface mount resistors offer compact size and high-frequency performance, ideal for modern electronics requiring efficient space utilization and automated assembly. Wirewound resistors, characterized by a coil of wire wrapped around a core, provide high power dissipation and precision in applications demanding stability under high temperature and load. Your choice depends on the specific electrical and thermal requirements of the circuit, balancing size and performance constraints.
Key Differences in Construction
Surface mount resistors feature a thin film or metal oxide layer deposited on a ceramic base, resulting in a compact and lightweight design ideal for automated PCB assembly. Wirewound resistors consist of a metal wire, usually nichrome, wound around a ceramic or fiberglass core, offering superior power handling and precision stability in high-power applications. The fundamental construction variances influence their electrical characteristics, thermal performance, and suitability across diverse electronic circuits.
Size and Footprint Comparison
Surface mount resistors feature a compact size and minimal footprint, typically measuring between 0402 and 1206 package sizes, making them ideal for high-density circuit boards. Wirewound resistors are physically larger due to their construction, often requiring more board space and increased height, which can limit their use in compact or densely populated designs. The smaller footprint of surface mount resistors enhances automated assembly and allows for higher component density compared to the bulkier wirewound resistors.
Electrical Performance Characteristics
Surface mount resistors offer precise resistance values with low parasitic inductance and capacitance, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. Wirewound resistors provide excellent power handling and superior thermal stability but exhibit higher inductance that can affect performance in high-frequency circuits. Choosing the right resistor depends on your circuit's frequency requirements and power dissipation needs.
Power Handling Capabilities
Surface mount resistors typically handle power ratings from 1/16 watt to 1 watt, making them suitable for low to moderate power applications. Wirewound resistors excel in high power handling, often rated between 1 watt to several hundred watts, due to their construction with resistive wire wound around a ceramic core. This design enables wirewound resistors to dissipate heat more efficiently, making them ideal for circuits requiring significant power dissipation.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Surface mount resistors are commonly used in compact electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and automotive electronics due to their small size and high-frequency performance. Wirewound resistors find applications in power regulation, industrial equipment, and audio systems where high precision, power dissipation, and stability under thermal stress are critical. Industries such as consumer electronics, aerospace, and heavy machinery rely on surface mount resistors for miniaturized circuits, while power plants and manufacturing automation use wirewound resistors for robust, high-power applications.
Reliability and Durability
Surface mount resistors offer high reliability due to their stable construction and are resistant to vibration and mechanical shock, making them suitable for compact electronic devices. Wirewound resistors excel in durability, capable of withstanding high power loads and extreme temperature variations without significant drift, ideal for power electronics and industrial applications. Both types provide reliable performance, but wirewound resistors outperform in power handling and longevity under harsh conditions.
Cost and Availability
Surface mount resistors are generally more cost-effective and widely available due to automated manufacturing processes and high demand in compact electronic devices. Wirewound resistors tend to be more expensive because of their complex construction and are often less readily stocked, especially in smaller sizes. Your choice should consider budget constraints and component accessibility for efficient project execution.
Selection Criteria for Designers
Surface mount resistors offer compact size, high-frequency performance, and ease of automated assembly, ideal for dense PCB layouts and precision applications. Wirewound resistors provide superior power handling, thermal stability, and low noise, making them suitable for high-power circuits and environments demanding reliability under stress. Your selection depends on balancing space constraints, power requirements, and the electrical characteristics essential for your specific design.
Summary: Choosing the Right Resistor Type
Surface mount resistors offer compact size, high-frequency performance, and automated assembly benefits, making them ideal for densely packed electronic circuits. Wirewound resistors provide superior power dissipation, precision, and thermal stability, suitable for high-power or high-accuracy applications. Selecting between surface mount and wirewound resistors depends on the specific requirements for size, power rating, tolerance, and thermal management in the intended design.
Surface mount resistor vs wirewound resistor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com