Switch-mode power supplies offer higher efficiency and lighter weight by converting power through high-frequency switching, while linear power supplies provide cleaner, more stable output with less electromagnetic interference but at the cost of greater heat dissipation and lower efficiency. Discover which power supply suits Your specific applications and requirements in the detailed comparison ahead.
Table of Comparison
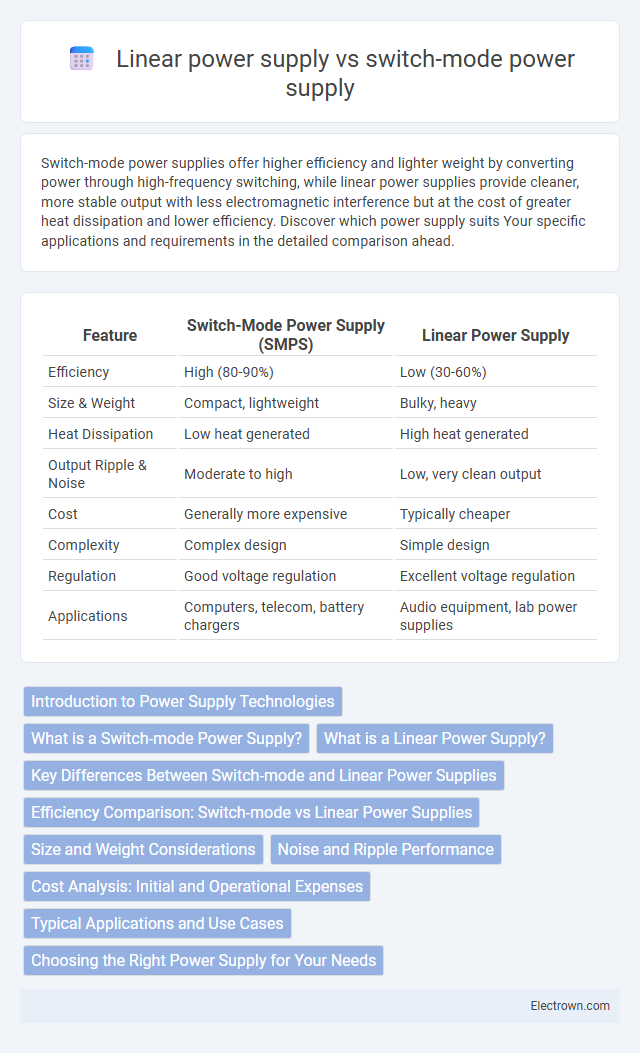
| Feature | Switch-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) | Linear Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (80-90%) | Low (30-60%) |
| Size & Weight | Compact, lightweight | Bulky, heavy |
| Heat Dissipation | Low heat generated | High heat generated |
| Output Ripple & Noise | Moderate to high | Low, very clean output |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically cheaper |
| Complexity | Complex design | Simple design |
| Regulation | Good voltage regulation | Excellent voltage regulation |
| Applications | Computers, telecom, battery chargers | Audio equipment, lab power supplies |
Introduction to Power Supply Technologies
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) and linear power supplies serve as essential technologies for converting electrical power efficiently and reliably in electronic devices. SMPS use high-frequency switching regulators to convert voltage with minimal energy loss, making them lighter and more compact compared to linear power supplies, which rely on linear regulation and dissipate excess voltage as heat. Understanding the differences in efficiency, size, and electromagnetic interference helps you select the appropriate power supply technology for your specific application needs.
What is a Switch-mode Power Supply?
A switch-mode power supply (SMPS) is an electronic power converter that efficiently transforms electrical power using high-frequency switching components such as transistors and inductors. It regulates output voltage by rapidly switching the input power on and off while controlling energy storage elements, resulting in reduced heat dissipation and higher efficiency compared to linear power supplies. SMPS units are widely utilized in applications requiring compact size, lightweight design, and energy efficiency, including computers, telecommunications, and industrial equipment.
What is a Linear Power Supply?
A linear power supply converts AC voltage to a lower DC voltage using a transformer followed by a rectifier and a linear regulator to maintain a steady output. It provides clean, low-noise power ideal for sensitive electronic devices but is less efficient and bulkier compared to switch-mode power supplies. Your choice of a linear power supply benefits applications requiring minimal electrical noise and stable voltage regulation.
Key Differences Between Switch-mode and Linear Power Supplies
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) operate by rapidly switching transistors on and off to regulate voltage efficiently, resulting in higher efficiency and smaller size compared to linear power supplies, which use resistive voltage regulation. Linear power supplies provide cleaner, low-noise output ideal for sensitive analog circuits, but generate more heat and are less energy-efficient. SMPS are preferred in compact, modern electronic devices due to their light weight and efficiency, while linear power supplies are chosen for applications requiring minimal electrical noise.
Efficiency Comparison: Switch-mode vs Linear Power Supplies
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) achieve significantly higher efficiency, often between 80% to 95%, by rapidly switching on and off to regulate voltage with minimal energy loss. Linear power supplies typically operate at 40% to 60% efficiency due to continuous voltage regulation through dissipative components that generate heat. Choosing a switch-mode power supply can improve Your device's energy efficiency and reduce thermal management requirements compared to linear alternatives.
Size and Weight Considerations
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) are significantly smaller and lighter than linear power supplies due to their high-frequency switching operation, which allows the use of smaller transformers and components. Linear power supplies rely on heavy transformers and large heat sinks, resulting in bulkier and heavier units. The compact size and reduced weight of SMPS make them ideal for applications with space and weight constraints, such as portable devices and modern electronics.
Noise and Ripple Performance
Switch-mode power supplies generate higher noise and ripple due to their high-frequency switching, which can interfere with sensitive electronic circuits, while linear power supplies offer significantly lower noise and ripple levels, making them ideal for precision applications. You can reduce unwanted interference in audio or RF equipment by choosing linear power supplies, despite their lower efficiency and larger size compared to switch-mode designs. Noise spectrum analysis typically shows switch-mode power supplies with ripple frequencies in the tens to hundreds of kHz range, whereas linear power supplies maintain a stable, low-noise output with ripple often below a few millivolts.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operational Expenses
Switch-mode power supplies typically have higher initial costs due to complex circuitry but offer lower operational expenses through superior energy efficiency and reduced heat dissipation. Linear power supplies feature lower upfront costs with simpler designs but incur higher ongoing energy costs because of wasted power as heat. Your choice should balance budget constraints with long-term energy savings for optimal cost efficiency.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Switch-mode power supplies are ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and compact size, such as consumer electronics, computers, and LED lighting. Linear power supplies excel in audio equipment, laboratory instruments, and sensitive analog devices due to their low noise and stable voltage output. Your choice depends on whether efficiency or clean power is more critical for your specific use case.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Needs
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) offer higher efficiency, smaller size, and lighter weight compared to linear power supplies, making them ideal for applications requiring compact design and minimal heat dissipation. Linear power supplies provide cleaner, low-noise output voltage, which suits sensitive audio or medical equipment where signal integrity is crucial. Understanding your specific power requirements, including efficiency, noise sensitivity, and physical size constraints, is essential to choosing the right power supply for your needs.
Switch-mode power supply vs linear power supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com