PCB trace antennas offer a cost-effective and compact solution by integrating directly onto the circuit board, providing good performance for short-range communication without additional components. Understanding the differences between trace and chip antennas can help you optimize your device's wireless connectivity, so explore the rest of the article for detailed insights.
Table of Comparison
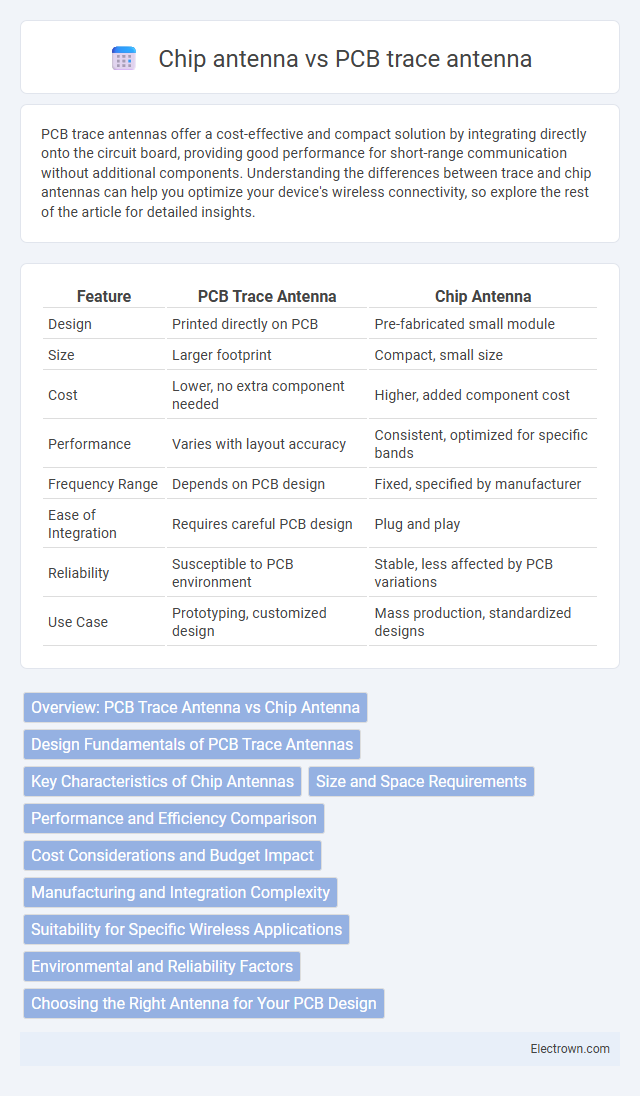
| Feature | PCB Trace Antenna | Chip Antenna |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Printed directly on PCB | Pre-fabricated small module |
| Size | Larger footprint | Compact, small size |
| Cost | Lower, no extra component needed | Higher, added component cost |
| Performance | Varies with layout accuracy | Consistent, optimized for specific bands |
| Frequency Range | Depends on PCB design | Fixed, specified by manufacturer |
| Ease of Integration | Requires careful PCB design | Plug and play |
| Reliability | Susceptible to PCB environment | Stable, less affected by PCB variations |
| Use Case | Prototyping, customized design | Mass production, standardized designs |
Overview: PCB Trace Antenna vs Chip Antenna
PCB trace antennas integrate directly onto the circuit board, offering a low-cost and compact solution with customizable shapes and sizes tailored for specific frequencies. Chip antennas provide a more compact, plug-and-play design with consistent performance and ease of replacement, suitable for space-constrained applications. While PCB trace antennas rely on layout precision, chip antennas offer more predictable radiation patterns and require less design optimization.
Design Fundamentals of PCB Trace Antennas
PCB trace antennas rely on the conductive pathways etched directly onto the board substrate, utilizing transmission line principles to optimize signal radiation. Key design fundamentals include trace dimensions, substrate material permittivity, and antenna geometry, which together influence resonance frequency and impedance matching. You must carefully balance these parameters to achieve efficient performance and minimize signal loss in your wireless applications.
Key Characteristics of Chip Antennas
Chip antennas feature compact, integrated designs optimized for space-constrained applications, offering consistent performance across various environments. They exhibit stable impedance matching and are designed to provide reliable radiating efficiency despite small form factors. Compared to PCB trace antennas, chip antennas generally enable easier tuning and better repeatability in mass production due to their standardized manufacturing process.
Size and Space Requirements
PCB trace antennas offer significant advantages in size and space efficiency by integrating directly onto the circuit board, reducing the need for additional components and keeping the overall device footprint minimal. Chip antennas, while compact and easy to implement as discrete components, often require extra PCB area for placement and matching circuitry, increasing space consumption. Designers frequently prefer PCB trace antennas for ultra-compact devices where minimizing space is critical without compromising antenna performance.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
PCB trace antennas offer cost-effective manufacturing and compact integration but generally exhibit lower efficiency and limited bandwidth due to their planar structure and substrate losses. Chip antennas provide better performance with higher gain and improved radiation patterns, enhancing signal quality and range in compact devices. Choosing between them depends on your design priorities, balancing cost constraints with the need for reliable wireless communication efficiency.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
PCB trace antennas generally offer lower production costs due to their integration directly onto the circuit board, eliminating the need for additional components or assembly steps. Chip antennas, while often more expensive upfront, provide consistent performance and reduced design complexity, potentially saving your budget on troubleshooting and iterative design modifications. Evaluating total cost impact involves balancing PCB trace antenna's economic manufacturing benefits against chip antenna's reliability and ease of integration in your specific application.
Manufacturing and Integration Complexity
PCB trace antennas offer simpler manufacturing and integration because they are etched directly onto the circuit board, reducing assembly steps and component costs. Chip antennas require precise placement and additional soldering, increasing production complexity and potential alignment issues. Your choice between these antennas impacts the overall manufacturing workflow and time-to-market efficiency.
Suitability for Specific Wireless Applications
PCB trace antennas offer excellent customization for specific wireless applications, allowing precise tuning for frequencies like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, which makes them ideal for compact, cost-sensitive designs. Chip antennas provide standardized performance with minimal design effort, making them suitable for rapid development and applications demanding consistent RF characteristics across multiple devices. Choosing between PCB trace and chip antennas depends on your project's requirements for size, frequency precision, and manufacturing complexity.
Environmental and Reliability Factors
PCB trace antennas offer superior environmental resilience due to their integration within the PCB substrate, providing enhanced protection against moisture, dust, and physical damage compared to chip antennas. Chip antennas, while compact and easy to replace, are more susceptible to environmental degradation and mechanical stress from external factors, potentially impacting long-term reliability. Your choice between these antenna types should consider the device's operating environment and durability requirements to ensure consistent performance.
Choosing the Right Antenna for Your PCB Design
Selecting the right antenna for your PCB design depends on factors such as size constraints, frequency range, and performance requirements. PCB trace antennas offer a compact and cost-effective solution with customizable designs directly integrated into the board, ideal for space-limited applications. Chip antennas provide consistent performance with a smaller footprint and easier integration, making them suitable for advanced IoT devices and complex RF environments.
PCB trace antenna vs Chip antenna Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com