Base stations serve as primary communication hubs, connecting mobile devices directly to the network infrastructure for seamless signal transmission. Relay stations extend network coverage by receiving and retransmitting signals, enhancing connectivity in areas where direct base station communication is weak or unavailable; explore the article to understand how these stations impact Your wireless experience.
Table of Comparison
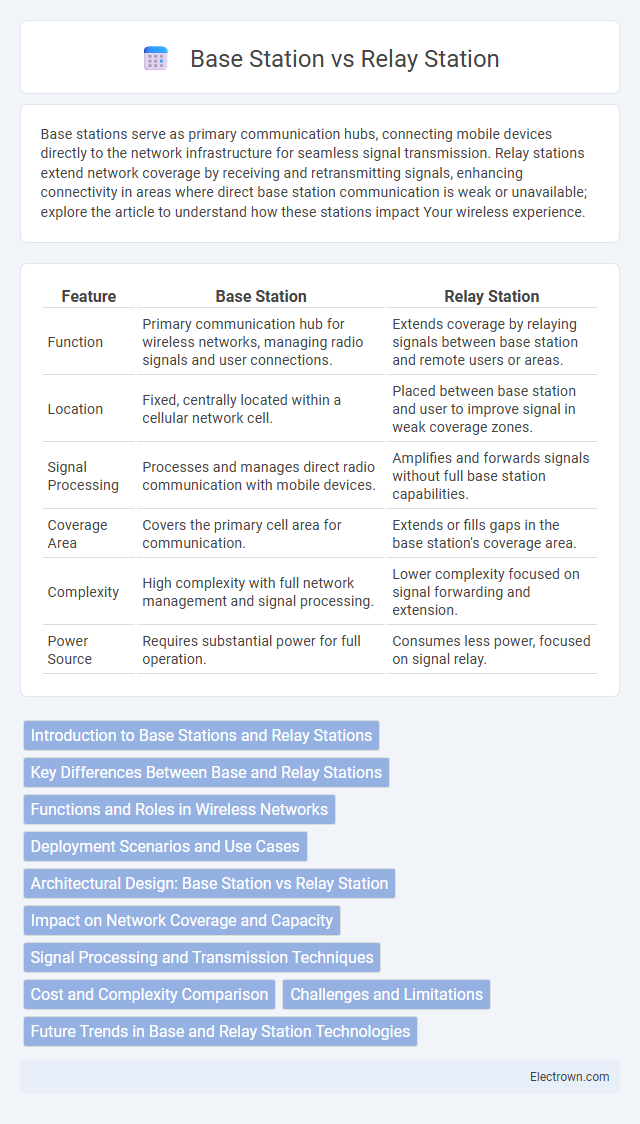
| Feature | Base Station | Relay Station |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Primary communication hub for wireless networks, managing radio signals and user connections. | Extends coverage by relaying signals between base station and remote users or areas. |
| Location | Fixed, centrally located within a cellular network cell. | Placed between base station and user to improve signal in weak coverage zones. |
| Signal Processing | Processes and manages direct radio communication with mobile devices. | Amplifies and forwards signals without full base station capabilities. |
| Coverage Area | Covers the primary cell area for communication. | Extends or fills gaps in the base station's coverage area. |
| Complexity | High complexity with full network management and signal processing. | Lower complexity focused on signal forwarding and extension. |
| Power Source | Requires substantial power for full operation. | Consumes less power, focused on signal relay. |
Introduction to Base Stations and Relay Stations
Base stations serve as primary communication hubs connecting mobile devices to the cellular network, managing radio resources, and facilitating data transmission. Relay stations extend network coverage by receiving signals from base stations and retransmitting them to areas with weak or no direct connection, enhancing signal strength and reducing dead zones. Your mobile experience relies on the seamless cooperation between base stations and relay stations to maintain consistent connectivity.
Key Differences Between Base and Relay Stations
Base stations serve as central communication hubs in cellular networks, managing direct connections with mobile devices and coordinating signal transmission, while relay stations function to extend coverage by receiving and retransmitting signals between base stations and mobile users. Base stations typically handle higher traffic loads and possess greater network control capabilities, whereas relay stations primarily enhance signal strength in areas with weak coverage without managing network access or authentication. The distinction lies in their operational roles: base stations are essential for core network access, whereas relay stations act as signal boosters to improve coverage and capacity.
Functions and Roles in Wireless Networks
Base stations serve as central communication hubs in wireless networks, managing direct connections between user devices and the core network, handling tasks such as signal transmission, reception, and network coordination. Relay stations extend network coverage by receiving signals from base stations and forwarding them to areas where direct signal propagation is weak or obstructed, effectively enhancing connectivity and signal quality in dead zones. Both entities are essential for maintaining seamless wireless communication; base stations establish primary network access while relay stations optimize coverage and throughput in challenging environments.
Deployment Scenarios and Use Cases
Base stations are typically deployed as fixed infrastructure in urban or rural areas to provide direct wireless communication coverage to mobile users, supporting macro-level network access with high capacity and broad geographic reach. Relay stations are used in challenging environments such as mountainous regions, dense urban canyons, or remote locations to extend coverage by receiving and retransmitting signals between a base station and users, enhancing signal quality and network reach without additional base station installation. Use cases for base stations include primary cellular network access and public safety communications, while relay stations are crucial for coverage extension, temporary event support, and filling coverage gaps in hard-to-reach areas.
Architectural Design: Base Station vs Relay Station
Base stations feature a complex architectural design integrating antennas, transceivers, and control units to manage direct communication with mobile devices and connect to the core network. Relay stations have a simpler design focused on receiving and retransmitting signals between the base station and mobiles to extend coverage without direct network control functions. Your network performance benefits from understanding that base stations serve as primary nodes while relay stations act as intermediate signal boosters within the cellular architecture.
Impact on Network Coverage and Capacity
Base stations serve as primary hubs in cellular networks, directly handling user connections to provide extensive coverage and high capacity for numerous simultaneous devices. Relay stations extend or fill coverage gaps by retransmitting signals between base stations and users, enhancing network reach without significantly increasing capacity. Your network's coverage is expanded with relay stations, but capacity improvements depend mainly on the base station's capabilities.
Signal Processing and Transmission Techniques
Base stations utilize advanced signal processing techniques such as Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) and Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) to enhance data transmission efficiency and capacity over direct wireless links. Relay stations primarily perform signal amplification and regeneration to extend coverage and improve signal quality without complex encoding or decoding processes. Signal transmission in base stations involves direct communication with mobile devices, whereas relay stations operate by receiving, processing, and forwarding signals between base stations and user equipment.
Cost and Complexity Comparison
Base stations typically involve higher initial capital expenditure due to sophisticated infrastructure, extensive spectrum usage, and powerful transmission equipment. Relay stations offer a cost-effective alternative by extending coverage with lower power consumption and simpler hardware, reducing both installation and maintenance expenses. The complexity of base stations is substantially greater, requiring advanced signal processing and network management, whereas relay stations operate with simpler protocols and limited processing capabilities.
Challenges and Limitations
Base stations face challenges such as limited coverage range and network congestion in densely populated areas, impacting overall communication quality. Relay stations experience limitations related to signal degradation and increased latency due to their dependence on retransmitting signals between base stations and end users. Your network's performance can be affected by these issues, requiring careful optimization to balance coverage and signal strength.
Future Trends in Base and Relay Station Technologies
Future trends in base station technologies emphasize the integration of advanced AI-driven network management and energy-efficient hardware to support 5G and emerging 6G connectivity standards. Relay stations are evolving with enhanced signal processing capabilities and adaptive beamforming techniques, enabling extended coverage and seamless communication in challenging environments. Your network infrastructure can benefit from these innovations by improving data throughput, reducing latency, and expanding service reach without significant new base station deployments.
Base station vs Relay station Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com