Yagi antennas provide high gain and directivity ideal for long-distance communication, while log-periodic antennas offer wide bandwidth and consistent performance over a range of frequencies. Discover the key differences to determine which antenna best suits your needs in the full article.
Table of Comparison
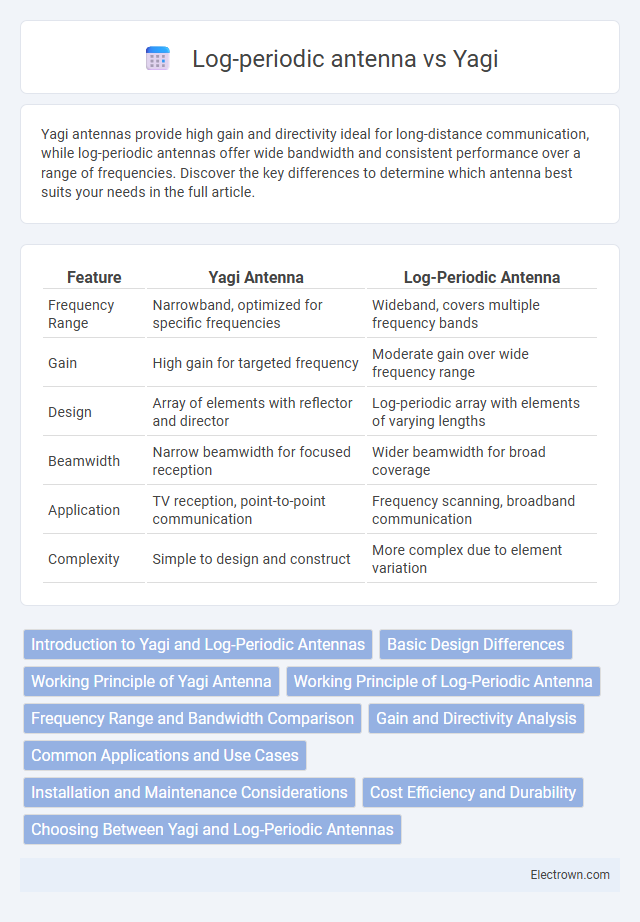
| Feature | Yagi Antenna | Log-Periodic Antenna |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | Narrowband, optimized for specific frequencies | Wideband, covers multiple frequency bands |
| Gain | High gain for targeted frequency | Moderate gain over wide frequency range |
| Design | Array of elements with reflector and director | Log-periodic array with elements of varying lengths |
| Beamwidth | Narrow beamwidth for focused reception | Wider beamwidth for broad coverage |
| Application | TV reception, point-to-point communication | Frequency scanning, broadband communication |
| Complexity | Simple to design and construct | More complex due to element variation |
Introduction to Yagi and Log-Periodic Antennas
Yagi antennas feature a driven element, reflector, and multiple directors designed to provide high gain and directivity, making them ideal for targeted signal reception. Log-periodic antennas consist of a series of elements with varying lengths and spacing, enabling wideband frequency coverage and consistent performance across a broad spectrum. Both antenna types serve distinct roles in communication systems, with Yagi antennas optimized for narrowband applications and Log-periodic antennas suited for broadband requirements.
Basic Design Differences
Yagi antennas feature a fixed set of elements including a driven element, reflector, and several directors arranged in a linear fashion to focus signal reception or transmission in one direction. Log-periodic antennas consist of multiple elements of varying lengths and spacing, allowing for wideband frequency coverage with consistent gain across frequencies. Understanding these basic design differences is crucial for choosing the right antenna to optimize Your signal strength and frequency range needs.
Working Principle of Yagi Antenna
The Yagi antenna operates on the principle of directional gain by using multiple elements, including a driven element, reflector, and one or more directors, to focus radio waves in a specific direction. This arrangement creates constructive interference in the forward direction, enhancing signal strength and reception while minimizing interference from other directions. Your choice of a Yagi antenna can significantly improve signal quality for applications requiring targeted, long-distance communication.
Working Principle of Log-Periodic Antenna
The working principle of a log-periodic antenna relies on a series of dipole elements with varying lengths and spacing that reproduce similar electrical characteristics over a wide frequency range. Each element resonates at a different frequency, allowing the antenna to maintain consistent gain and impedance as the operating frequency changes. Your communication system benefits from this frequency agility, making log-periodic antennas ideal for applications requiring broadband performance compared to the narrowband Yagi antenna.
Frequency Range and Bandwidth Comparison
Yagi antennas are designed for narrow frequency ranges, typically providing high gain within a limited bandwidth, making them ideal for specific, single-frequency applications such as TV reception or amateur radio. In contrast, Log-periodic antennas offer a wide frequency range and broad bandwidth, supporting multiple frequencies simultaneously, which suits applications like broadband communication and signal monitoring. The trade-off involves Yagi antennas delivering stronger signal focus at chosen frequencies, while Log-periodic antennas ensure versatility over a broad spectrum with moderate gain.
Gain and Directivity Analysis
Yagi antennas typically offer higher gain and more focused directivity due to their fixed element structure, making them ideal for long-range, point-to-point communication. Log-periodic antennas provide wider bandwidth with moderate gain and less directivity, allowing for multi-frequency applications and broader signal coverage. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize maximum signal strength (gain) with narrow beamwidth (Yagi) or flexible frequency operation with moderate gain (Log-periodic).
Common Applications and Use Cases
Yagi antennas excel in long-distance point-to-point communication and television broadcasting due to their high gain and directional focus, making them ideal for fixed-location setups. Log-periodic antennas offer a wider frequency range and frequency-independent performance, which suits them well for applications such as signal monitoring, spectrum analysis, and broadband communication. Your choice between these antennas depends on whether you prioritize narrowband high gain or broadband versatility for your specific application needs.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Yagi antennas require precise alignment toward the signal source during installation to maximize directional gain, making initial setup more critical but simpler once positioned. Log-periodic antennas offer broader bandwidth and less sensitivity to exact positioning, which can ease installation in variable signal environments but may require more frequent inspection for element integrity. Both antenna types benefit from regular maintenance checks to ensure element stability and corrosion prevention, especially in harsh weather conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Durability
Yagi antennas generally offer higher cost efficiency due to their simpler design and easier manufacturing process, making them more affordable for most use cases. Log-periodic antennas provide superior durability under harsh environmental conditions because of their robust construction and materials suited for prolonged outdoor exposure. Your choice depends on whether budget constraints or long-term reliability in challenging settings are the primary priorities.
Choosing Between Yagi and Log-Periodic Antennas
Choosing between Yagi and log-periodic antennas depends on your specific application and frequency requirements. Yagi antennas provide higher gain and better directivity for narrowband signals, making them ideal for targeting specific frequencies, while log-periodic antennas offer wideband frequency coverage with moderate gain, suitable for multi-frequency use. Your decision should consider the trade-off between gain, bandwidth, and size to optimize signal reception for your communication system.
Yagi vs Log-periodic antenna Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com