POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) relies on traditional copper wires for voice communication, offering reliability with limited features, while VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) uses internet connectivity to provide flexible, cost-effective calling with advanced functionalities. Discover how Your business can benefit from understanding the differences between POTS and VoIP by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
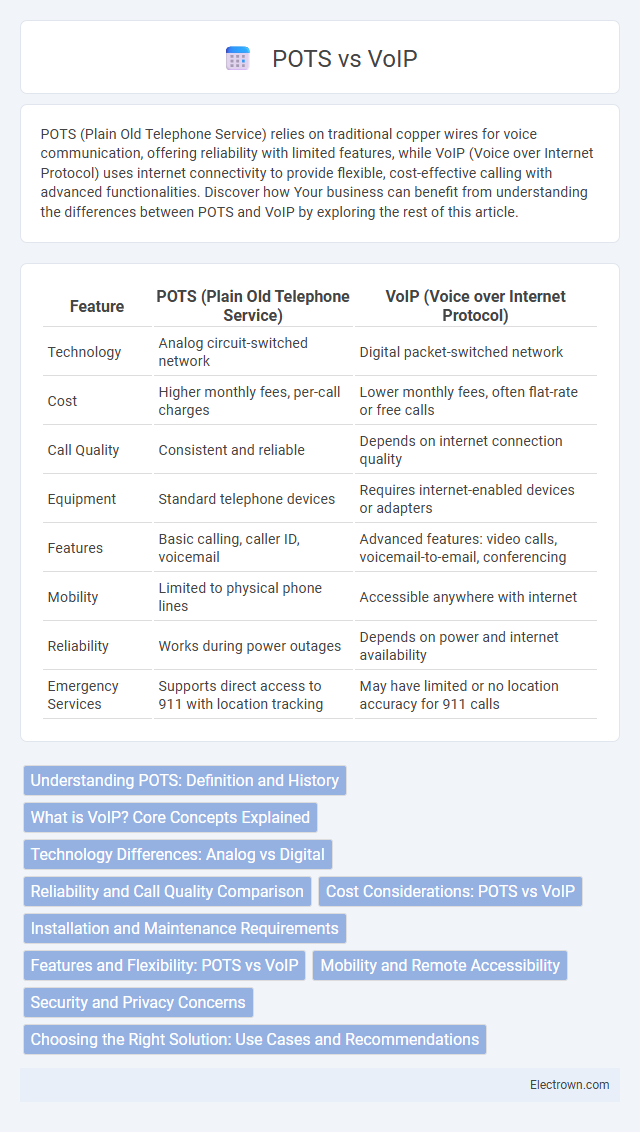
| Feature | POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) | VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Analog circuit-switched network | Digital packet-switched network |
| Cost | Higher monthly fees, per-call charges | Lower monthly fees, often flat-rate or free calls |
| Call Quality | Consistent and reliable | Depends on internet connection quality |
| Equipment | Standard telephone devices | Requires internet-enabled devices or adapters |
| Features | Basic calling, caller ID, voicemail | Advanced features: video calls, voicemail-to-email, conferencing |
| Mobility | Limited to physical phone lines | Accessible anywhere with internet |
| Reliability | Works during power outages | Depends on power and internet availability |
| Emergency Services | Supports direct access to 911 with location tracking | May have limited or no location accuracy for 911 calls |
Understanding POTS: Definition and History
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) refers to the traditional analog voice transmission technology that has been the standard for telephone communications since the late 19th century. Its infrastructure relies on circuit-switched networks and copper wires, providing reliable voice service with minimal latency. Understanding POTS helps you appreciate the evolution of telephony and how modern VoIP systems offer more flexibility and cost-efficiency by leveraging internet protocols.
What is VoIP? Core Concepts Explained
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) is a technology that enables voice communication over the internet by converting analog voice signals into digital data packets. It relies on core concepts such as packet switching, IP networks, and codecs for compression and decompression of audio. Unlike POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service), which uses traditional circuit-switched telephony networks, VoIP leverages broadband connections and software-based communication platforms to deliver flexible, cost-effective voice services.
Technology Differences: Analog vs Digital
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) uses analog signal transmission, relying on traditional copper wire infrastructure to carry voice as continuous electrical waves. VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) converts voice into digital data packets that are transmitted over IP networks, enabling higher flexibility and integration with internet services. Understanding these fundamental technology differences helps you choose the right communication system for reliability or advanced digital features.
Reliability and Call Quality Comparison
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) offers high reliability and consistent call quality due to its dedicated circuit-switched network, ensuring stable voice transmission even during power outages or network congestion. VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) depends on internet connectivity, which can introduce latency, jitter, and packet loss, potentially affecting call clarity and reliability in areas with poor bandwidth or unstable connections. Your choice between POTS and VoIP should consider the critical need for uninterrupted service and voice quality in your communication setup.
Cost Considerations: POTS vs VoIP
Traditional POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) incurs higher monthly fees and charges for long-distance calls compared to VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), which leverages Internet connectivity to reduce costs significantly. VoIP systems offer scalable pricing models based on the number of users and minutes used, often including free internal calls and more affordable international rates. Maintenance expenses are generally lower for VoIP due to software-based updates, whereas POTS requires physical line repairs and infrastructure investments.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) installation involves physical wiring and requires professional technicians to set up copper lines, making it a time-consuming process compared to VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), which only needs an internet connection and compatible devices. Maintenance for POTS includes regular line checks, physical repairs, and addressing service disruptions caused by weather or infrastructure issues, whereas VoIP maintenance is primarily software-based, involving updates and network troubleshooting that can often be performed remotely. VoIP systems offer greater flexibility with lower installation and maintenance costs due to reliance on existing IP networks and minimal hardware requirements.
Features and Flexibility: POTS vs VoIP
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) provides reliable voice communication with basic features like caller ID and voicemail but lacks flexibility for advanced functionalities. VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) offers a wide range of features such as video conferencing, call forwarding, virtual voicemail, and integration with other digital tools, enhancing overall communication capabilities. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize traditional reliability or the flexibility and scalability of modern VoIP services.
Mobility and Remote Accessibility
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) offers limited mobility and remote accessibility as it relies on fixed landline connections, restricting users to a specific physical location for calls. VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) enhances mobility by enabling calls from any internet-connected device, supporting remote work and on-the-go communication. Your business benefits from VoIP's flexibility, allowing seamless connectivity whether you're at home, in the office, or traveling.
Security and Privacy Concerns
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) offers inherent security advantages due to its analog signal transmission, making it less vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks compared to VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), which relies on internet connectivity. VoIP systems require robust encryption protocols like TLS and SRTP to protect voice data from interception, but they remain susceptible to malware, DoS attacks, and eavesdropping if not properly secured. Privacy concerns in VoIP also stem from potential data breaches and metadata tracking by service providers, whereas POTS typically limits data collection and unauthorized access risks.
Choosing the Right Solution: Use Cases and Recommendations
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) remains ideal for businesses requiring reliable, low-latency voice communication with minimal setup, especially in areas with unstable internet connectivity, while VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) offers scalable, cost-effective solutions with advanced features like video conferencing, call routing, and integration with CRM systems. Small businesses and remote teams benefit from VoIP's flexibility and mobility, whereas emergency services and organizations prioritizing uninterrupted service rely on POTS for its consistent power supply and simpler infrastructure. Evaluating network stability, budget constraints, feature needs, and scalability helps determine the right telephony solution for each use case.
POTS vs VoIP Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com