A downconverter shifts high-frequency signals to lower frequencies for easier processing, while an upconverter converts lower-frequency signals to higher frequencies for transmission. Discover how understanding these devices can optimize Your communication systems by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
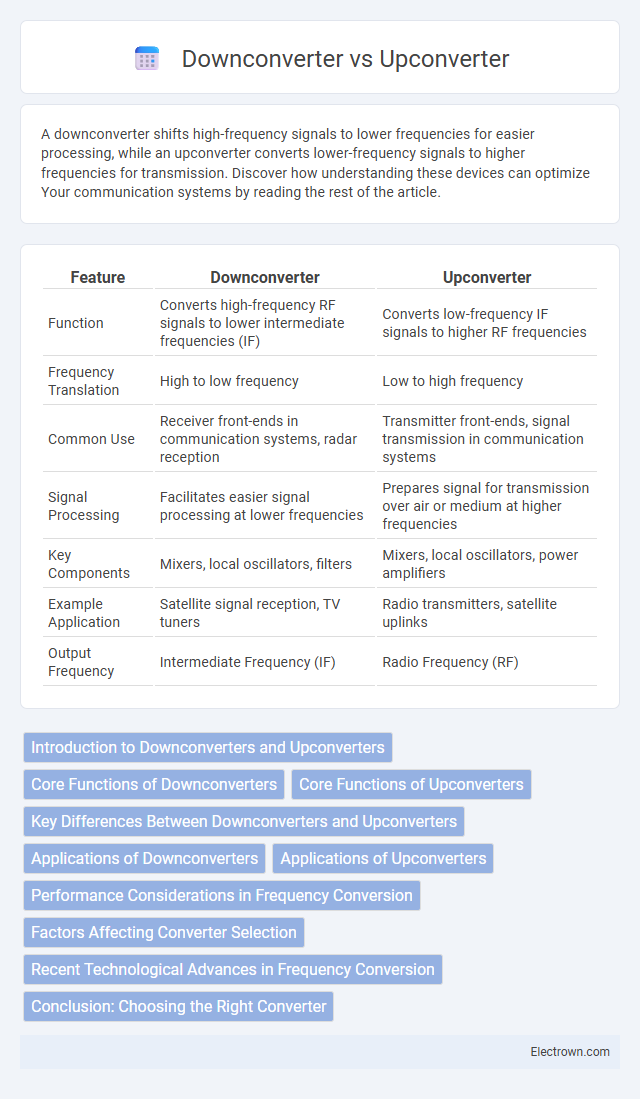
| Feature | Downconverter | Upconverter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts high-frequency RF signals to lower intermediate frequencies (IF) | Converts low-frequency IF signals to higher RF frequencies |
| Frequency Translation | High to low frequency | Low to high frequency |
| Common Use | Receiver front-ends in communication systems, radar reception | Transmitter front-ends, signal transmission in communication systems |
| Signal Processing | Facilitates easier signal processing at lower frequencies | Prepares signal for transmission over air or medium at higher frequencies |
| Key Components | Mixers, local oscillators, filters | Mixers, local oscillators, power amplifiers |
| Example Application | Satellite signal reception, TV tuners | Radio transmitters, satellite uplinks |
| Output Frequency | Intermediate Frequency (IF) | Radio Frequency (RF) |
Introduction to Downconverters and Upconverters
Downconverters and upconverters are critical components in radio frequency (RF) and communication systems, enabling signal frequency translation for effective transmission and reception. A downconverter shifts a higher frequency signal to a lower intermediate frequency (IF) or baseband, facilitating easier signal processing and demodulation. Conversely, an upconverter translates a lower frequency signal to a higher frequency, suitable for efficient transmission over airwaves or satellite links.
Core Functions of Downconverters
Downconverters primarily convert high-frequency signals to lower frequencies, enabling easier processing and analysis in communication systems. This frequency translation is crucial for reducing signal complexity and improving compatibility with standard receivers and digital circuits. Your system benefits from downconverters by enhancing signal clarity and minimizing noise during transmission and reception.
Core Functions of Upconverters
Upconverters play a crucial role in wireless communication by converting lower-frequency signals to higher frequencies, enabling efficient transmission over long distances and facilitating the use of smaller antennas. They are essential in satellite communications, radar systems, and broadcasting, where signal frequency elevation helps in reducing interference and improving signal quality. Your system's performance depends on selecting an upconverter that supports the desired frequency range and maintains signal integrity throughout the conversion process.
Key Differences Between Downconverters and Upconverters
Downconverters shift high-frequency signals to lower frequencies, simplifying signal processing and analysis, while upconverters convert low-frequency signals to higher frequencies for effective transmission and broadcasting. Downconverters are essential in receivers to bring incoming signals to intermediate frequencies, whereas upconverters are crucial in transmitters to modulate baseband signals onto carrier frequencies. The key difference lies in the direction of frequency translation: downconverters perform frequency downshifts, and upconverters perform frequency upshifts.
Applications of Downconverters
Downconverters are essential in satellite communication systems, where they convert high-frequency signals from the satellite to lower intermediate frequencies suitable for signal processing. They are widely used in radio receivers and radar systems to enable easier signal demodulation and analysis. Downconverters also play a critical role in wireless communication infrastructures, facilitating efficient data transmission by adapting frequency bands for optimal reception.
Applications of Upconverters
Upconverters are essential in satellite communication systems to shift lower-frequency baseband signals to higher microwave or RF frequencies for transmission through antennas. These devices play a critical role in radar systems by converting received intermediate frequencies to higher frequencies for further processing and signal amplification. Upconverters are also widely used in wireless communication infrastructure to facilitate frequency translation, enhancing signal reach and data throughput in cellular networks.
Performance Considerations in Frequency Conversion
Downconverters typically improve signal-to-noise ratio by lowering high-frequency signals to manageable intermediate frequencies, enhancing sensitivity and selectivity in receivers. Upconverters, essential for transmitting signals at higher frequencies, must maintain linearity to minimize distortion and spurious emissions for optimal performance. Your choice between these frequency converters will depend on balancing factors like conversion gain, noise figure, and linearity to meet specific application requirements.
Factors Affecting Converter Selection
Converter selection depends on factors such as frequency range, signal strength, and system compatibility. Downconverters are chosen when high-frequency signals need to be brought to a lower frequency for easier processing, while upconverters are used to shift low-frequency signals to higher frequencies for transmission. Your choice should align with the specific application requirements, including bandwidth, noise figure, and power consumption.
Recent Technological Advances in Frequency Conversion
Recent technological advances in frequency conversion have significantly enhanced the performance and efficiency of downconverters and upconverters used in wireless communication systems. Innovations in semiconductor materials, such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC), enable higher power handling and improved linearity in these frequency converters. Your signal processing benefits from these advancements by achieving lower noise figures and higher frequency stability, crucial for 5G and satellite communication applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Converter
Selecting the right converter depends on your specific communication needs, where a downconverter translates high-frequency signals to lower frequencies for easier processing, and an upconverter shifts low-frequency signals to higher frequencies for transmission. Your system requirements, such as signal type, frequency range, and application purpose, guide the decision between downconverters and upconverters. Understanding these technical distinctions ensures optimal performance and compatibility in your signal processing setup.
Downconverter vs Upconverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com