The 433MHz frequency band offers better penetration through obstacles and longer range in open areas, making it suitable for simple remote controls and sensor networks, while 868MHz provides higher data rates, less interference, and is ideal for urban environments and advanced IoT applications. Explore the differences further to understand which frequency best suits your wireless communication needs.
Table of Comparison
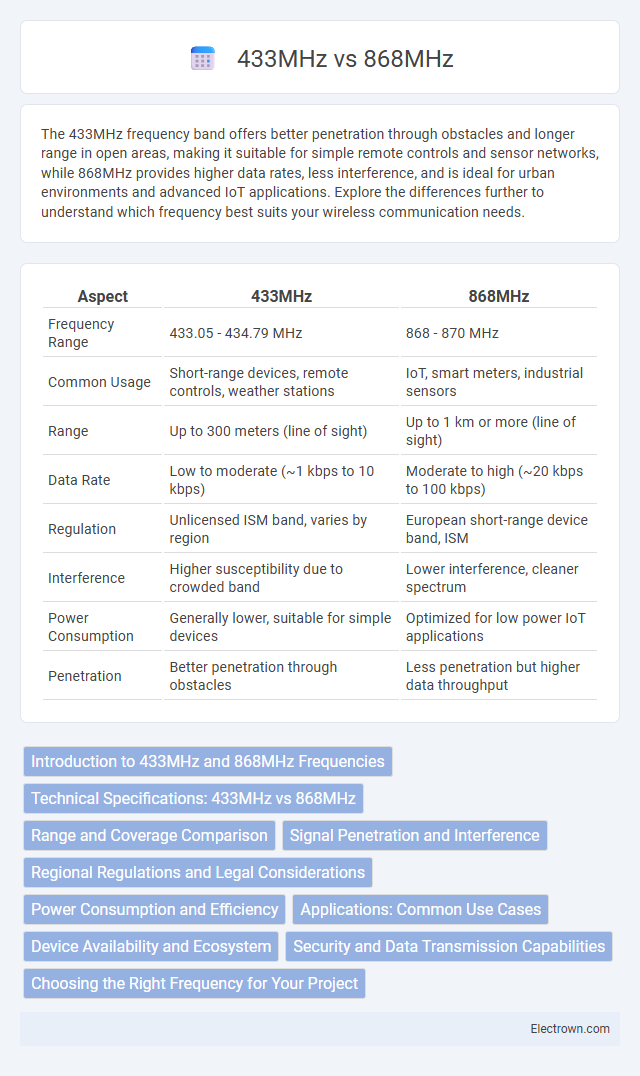
| Aspect | 433MHz | 868MHz |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 433.05 - 434.79 MHz | 868 - 870 MHz |
| Common Usage | Short-range devices, remote controls, weather stations | IoT, smart meters, industrial sensors |
| Range | Up to 300 meters (line of sight) | Up to 1 km or more (line of sight) |
| Data Rate | Low to moderate (~1 kbps to 10 kbps) | Moderate to high (~20 kbps to 100 kbps) |
| Regulation | Unlicensed ISM band, varies by region | European short-range device band, ISM |
| Interference | Higher susceptibility due to crowded band | Lower interference, cleaner spectrum |
| Power Consumption | Generally lower, suitable for simple devices | Optimized for low power IoT applications |
| Penetration | Better penetration through obstacles | Less penetration but higher data throughput |
Introduction to 433MHz and 868MHz Frequencies
433MHz and 868MHz frequencies are commonly used in wireless communication, especially for IoT devices, remote controls, and sensor networks. The 433MHz band offers longer range and better penetration through obstacles due to its lower frequency, while the 868MHz band provides higher data rates and less congestion in Europe. Both frequencies are part of the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) bands, with 433MHz widely used globally and 868MHz primarily designated for Europe.
Technical Specifications: 433MHz vs 868MHz
433MHz operates within the ISM band with lower data rates, longer range, and better obstacle penetration, ideal for simple remote controls; 868MHz offers higher data rates, shorter range, and improved bandwidth suitable for IoT and wireless sensor networks in Europe. The 433MHz band typically supports modulation schemes like ASK and FSK with output power limits around 10mW, while 868MHz supports advanced modulation methods such as LoRa and OFDM, allowing up to 25mW output power under European regulations. Your choice depends on application requirements like range, data throughput, and regional regulatory constraints.
Range and Coverage Comparison
The 868MHz frequency band typically offers better range and coverage compared to 433MHz due to its lower susceptibility to interference and improved signal penetration through obstacles. While 433MHz can provide reliable short-range communication in cluttered environments, 868MHz supports longer distances, making it ideal for rural or wide-area applications. Your choice between these frequencies should consider specific range requirements and environmental factors to optimize wireless performance.
Signal Penetration and Interference
433MHz signals offer better penetration through walls and obstacles due to their lower frequency, making them more suitable for indoor and urban environments with dense structures. In contrast, 868MHz frequencies experience higher attenuation but face less interference from common devices such as garage remotes and cordless phones, providing a cleaner spectrum in many regions. Your choice between these bands should balance the need for penetration versus interference resilience based on the specific application environment.
Regional Regulations and Legal Considerations
The 433MHz frequency band is commonly used in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa, often categorized under the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) bands with limited power output restrictions to avoid interference. The 868MHz band is primarily designated for Europe and offers wider bandwidth and higher power allowances, regulated under ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) standards to support more robust communication systems. Compliance with regional regulations is crucial for legal operation, as unauthorized use of these frequencies can lead to fines and equipment confiscation.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
433MHz frequency generally offers lower power consumption due to its longer wavelength, which allows signals to travel farther with less energy, making it efficient for low-power, long-range applications. In contrast, 868MHz provides higher data rates but typically consumes more power, as it requires stronger transmission signals to maintain efficiency over similar distances. When optimizing Your device for power efficiency, 433MHz is often preferred for battery-powered IoT applications needing extended range and minimal energy use.
Applications: Common Use Cases
433MHz frequency is widely used for short-range applications like garage door openers, remote keyless entry systems, and low-power wireless sensor networks due to its good penetration and longer range in indoor environments. 868MHz is commonly adopted in Europe for IoT devices, smart metering, industrial automation, and home security systems, offering better data rates and reduced interference in densely populated areas. Both frequencies support wireless communication protocols, but 868MHz generally provides enhanced performance for urban and industrial applications with moderate range and higher data throughput.
Device Availability and Ecosystem
The 868MHz frequency band offers a broader range of devices with advanced features due to its widespread adoption in Europe, providing a richer ecosystem for IoT applications. In contrast, the 433MHz band has limited device availability but benefits from simpler designs and longer-range capabilities in rural or low-interference environments. Your choice depends on the balance between device variety and specific deployment needs related to regional frequency regulations and ecosystem support.
Security and Data Transmission Capabilities
433MHz frequency offers longer range and better penetration through obstacles but is more prone to interference due to crowded ISM bands, potentially compromising data integrity. 868MHz provides higher data transmission rates and enhanced security protocols with reduced interference, making it ideal for secure applications such as IoT and wireless sensor networks. Devices operating at 868MHz benefit from improved encryption standards and lower latency, ensuring reliable and secure data communication.
Choosing the Right Frequency for Your Project
Choosing the right frequency for your project depends on factors like range, interference, and regulatory compliance. The 433MHz band offers better penetration through obstacles and longer range, making it ideal for rural or indoor applications, whereas 868MHz provides higher data rates and less interference, suitable for urban environments and IoT devices. Assessing local regulations and the specific needs of your wireless communication will ensure optimal performance and reliability.
433MHz vs 868MHz Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com