LoRa and Sigfox are two leading low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, with LoRa offering greater flexibility through private network deployments and Sigfox providing a cost-effective, operator-managed global network. Understanding the differences in range, power consumption, and network infrastructure can help optimize Your IoT solution. Dive into the full article to explore which technology best fits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
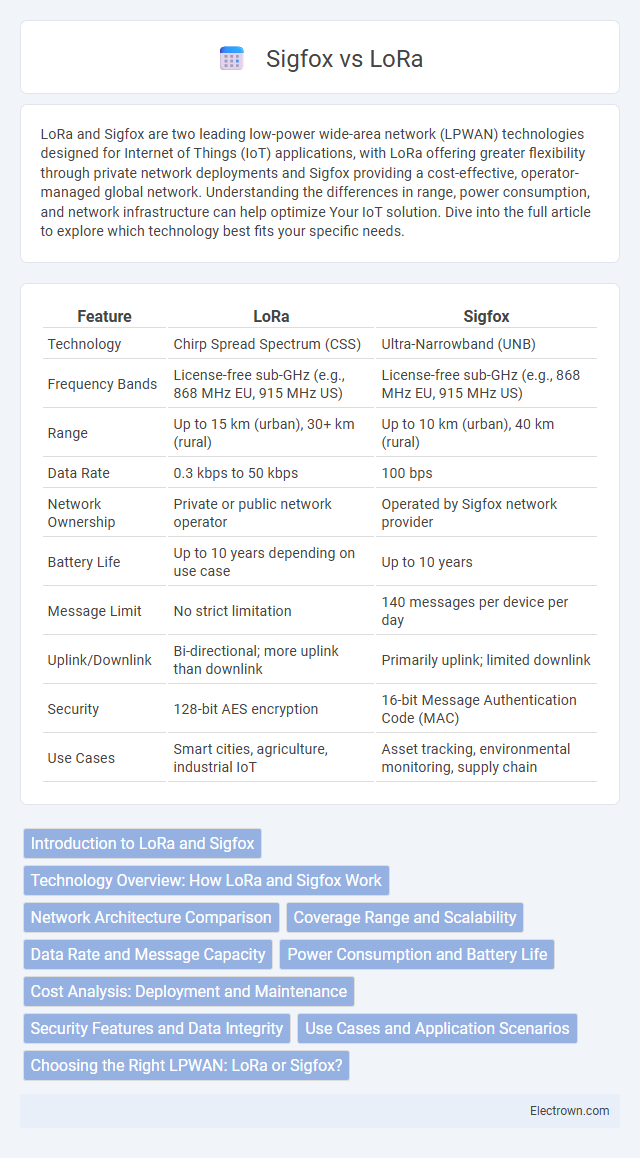
| Feature | LoRa | Sigfox |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) | Ultra-Narrowband (UNB) |
| Frequency Bands | License-free sub-GHz (e.g., 868 MHz EU, 915 MHz US) | License-free sub-GHz (e.g., 868 MHz EU, 915 MHz US) |
| Range | Up to 15 km (urban), 30+ km (rural) | Up to 10 km (urban), 40 km (rural) |
| Data Rate | 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps | 100 bps |
| Network Ownership | Private or public network operator | Operated by Sigfox network provider |
| Battery Life | Up to 10 years depending on use case | Up to 10 years |
| Message Limit | No strict limitation | 140 messages per device per day |
| Uplink/Downlink | Bi-directional; more uplink than downlink | Primarily uplink; limited downlink |
| Security | 128-bit AES encryption | 16-bit Message Authentication Code (MAC) |
| Use Cases | Smart cities, agriculture, industrial IoT | Asset tracking, environmental monitoring, supply chain |
Introduction to LoRa and Sigfox
LoRa and Sigfox are leading low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, offering extensive range and long battery life. LoRa, developed by Semtech, operates on unlicensed frequency bands and supports bidirectional communication with flexible network architecture, ideal for smart cities and agriculture. Sigfox uses ultra-narrowband modulation to provide energy-efficient, low-throughput connectivity with a global ready-made network, optimizing your devices for simple, cost-effective data transmission.
Technology Overview: How LoRa and Sigfox Work
LoRa operates using chirp spread spectrum modulation, enabling long-range, low-power communication ideal for IoT devices in smart cities and agriculture. Sigfox utilizes ultra-narrowband modulation, focusing on ultra-low energy consumption and extended battery life with low data rates suited for simple sensor networks. Both technologies leverage license-free sub-GHz ISM bands but differ significantly in network architecture, with LoRa supporting private and public networks and Sigfox relying on a global subscription-based network.
Network Architecture Comparison
LoRa employs a decentralized star-of-stars network architecture where gateways relay messages between end devices and a central network server, enabling flexible deployment and scalability for private or public networks. Sigfox uses a centralized star network design with base stations connected to a core network, optimized for low power and long-range communication with minimal data throughput. Your choice depends on the need for network control, scalability, and the specific IoT application requirements.
Coverage Range and Scalability
LoRa offers flexible coverage ranges typically up to 15 km in rural areas and 2-5 km in urban settings, making it ideal for diverse environments, while Sigfox provides a more limited range of about 3-10 km, optimized for low-power, wide-area network applications. In terms of scalability, LoRa supports private network deployments with extensive device connectivity and customization, enabling greater control over network expansion. Your choice between LoRa and Sigfox should consider LoRa's adaptability for large-scale deployments versus Sigfox's simplicity and energy-efficient operation within predefined coverage.
Data Rate and Message Capacity
LoRa offers a higher data rate ranging from 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps, enabling more detailed and frequent data transmissions compared to Sigfox's fixed 100 bps data rate. Sigfox supports up to 140 messages per device per day with a maximum payload of 12 bytes, limiting throughput and data complexity. LoRa supports larger payloads up to 243 bytes and allows flexible message capacity depending on network conditions, making it suitable for applications requiring varied data sizes and transmission frequencies.
Power Consumption and Battery Life
LoRa technology offers low power consumption with devices often achieving battery life spanning up to 10 years due to its adaptive data rate and efficient modulation techniques. Sigfox, designed for ultra-narrowband communication, typically enables even lower power usage, leading to battery lives that can exceed 10 years under optimal conditions. Both technologies prioritize energy efficiency, but Sigfox's simpler protocol and limited message payloads generally result in longer battery performance in comparable IoT deployments.
Cost Analysis: Deployment and Maintenance
LoRa offers a cost-efficient deployment with lower infrastructure expenses due to its use of unlicensed spectrum and the ability to build private networks, reducing reliance on third-party operators. Sigfox requires subscription fees for network access, leading to higher ongoing maintenance costs despite minimal hardware investment. Your choice should consider long-term operational expenses and control over network ownership to optimize total cost of ownership.
Security Features and Data Integrity
LoRa employs AES-128 encryption at both the network and application layers, ensuring strong security and data integrity for your IoT devices. Sigfox uses end-to-end encryption combined with unique device authentication, protecting data transfers against interception and tampering. Both technologies implement safeguards to maintain reliable and secure communication but differ in flexibility and scalability depending on application needs.
Use Cases and Application Scenarios
LoRa excels in smart city deployments, agriculture monitoring, and industrial IoT due to its long-range coverage and customizable private networks, supporting applications requiring low power and secure data transmission. Sigfox is well-suited for asset tracking, environmental monitoring, and simple sensor networks, benefiting from its wide global network and ultra-narrow band technology optimized for small, infrequent data packets. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize network flexibility and scalability (LoRa) or extensive global coverage with low device complexity (Sigfox).
Choosing the Right LPWAN: LoRa or Sigfox?
Choosing between LoRa and Sigfox depends on your project's range, data needs, and network availability. LoRa offers flexible private network deployment and higher data rates, ideal for customized IoT solutions requiring long range and low power consumption. Sigfox excels in simplicity with a global network and ultra-low power use, best suited for small, infrequent data transmissions over wide areas where operator coverage exists.
LoRa vs Sigfox Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com