DIP switches offer easy, reliable, and customizable settings for electronic devices without soldering, while jumpers require physical placement of connectors on pins to configure hardware options. Explore the rest of the article to understand which option best suits Your project's needs and applications.
Table of Comparison
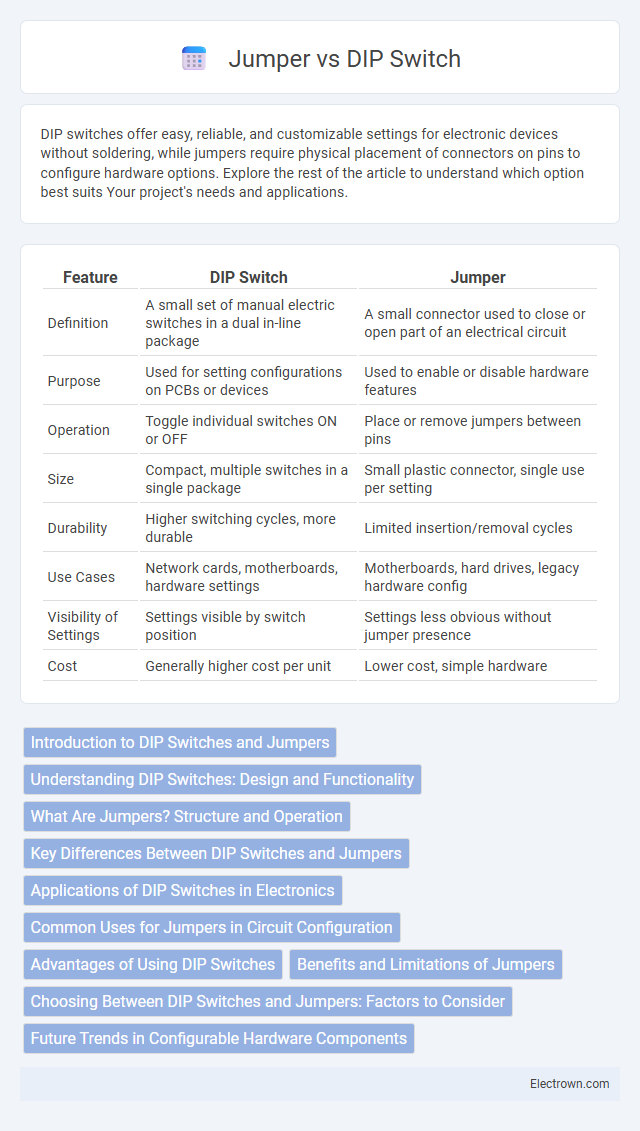
| Feature | DIP Switch | Jumper |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A small set of manual electric switches in a dual in-line package | A small connector used to close or open part of an electrical circuit |
| Purpose | Used for setting configurations on PCBs or devices | Used to enable or disable hardware features |
| Operation | Toggle individual switches ON or OFF | Place or remove jumpers between pins |
| Size | Compact, multiple switches in a single package | Small plastic connector, single use per setting |
| Durability | Higher switching cycles, more durable | Limited insertion/removal cycles |
| Use Cases | Network cards, motherboards, hardware settings | Motherboards, hard drives, legacy hardware config |
| Visibility of Settings | Settings visible by switch position | Settings less obvious without jumper presence |
| Cost | Generally higher cost per unit | Lower cost, simple hardware |
Introduction to DIP Switches and Jumpers
DIP switches and jumpers are essential components used to configure settings on electronic devices. DIP switches offer multiple binary options in a compact form, allowing precise control over device behavior without soldering. Jumpers provide a simple method for setting hardware configurations by physically connecting pins, making it easy to change settings on your circuit board.
Understanding DIP Switches: Design and Functionality
DIP switches feature a series of small manual electrical toggles mounted on a dual in-line package, allowing for the easy configuration of circuit settings without soldering. These switches provide precise binary selection, enabling users to control hardware options like device addressing and mode selection efficiently. Their compact design ensures reliable functionality in various electronic applications where quick and repeatable adjustments are necessary.
What Are Jumpers? Structure and Operation
Jumpers are small connectors that sit on pairs of pins on a circuit board to enable or disable specific hardware functions by completing an electrical circuit. Their simple structure consists of a plastic cap with a conductive metal inside, which you manually place over the pins to configure device settings. Jumpers provide a reliable, tactile way to alter hardware options, making hardware customization straightforward without the need for software changes.
Key Differences Between DIP Switches and Jumpers
DIP switches provide multiple individual switch settings on a small package, allowing precise control of circuit functions without the need for soldering or hardware changes. Jumpers consist of small connectors placed over pairs of pins to open or close circuits, typically used for configuration on PCBs and requiring physical repositioning to alter settings. DIP switches offer more granular and user-friendly configuration options, while jumpers are simpler but less flexible for frequent changes.
Applications of DIP Switches in Electronics
DIP switches are widely used in electronics for setting hardware configurations, such as selecting device modes, enabling or disabling features, and addressing peripherals in embedded systems and circuit boards. These switches offer reliable manual control in applications including communication devices, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics. Compared to jumpers, DIP switches provide more convenient, compact, and reusable options for setting multiple binary options without the need to remove physical connectors.
Common Uses for Jumpers in Circuit Configuration
Jumpers are commonly used in circuit configuration to set hardware options such as enabling or disabling features on motherboards, selecting voltage levels, or configuring device modes. They provide a simple and reliable method for permanent or semi-permanent connections without soldering, allowing for easy customization and troubleshooting. Your devices benefit from the flexibility jumpers offer in adjusting settings without needing specialized tools.
Advantages of Using DIP Switches
DIP switches offer precise and customizable configuration options, allowing you to easily set and change multiple circuit settings without soldering. They provide reliable electrical isolation and reduce the risk of accidental short circuits compared to jumpers. Their compact design makes them ideal for space-constrained applications, enhancing device durability and maintenance efficiency.
Benefits and Limitations of Jumpers
Jumpers provide a low-cost, reliable method for configuring hardware settings on motherboards, hard drives, and other devices, allowing easy electrical connection changes without additional power. Their major benefit lies in simplicity and durability under various environmental conditions, but their limitations include vulnerability to physical wear, difficulty in reconfiguration without tools, and a lack of fine-grained control compared to DIP switches. Jumpers are less suited for frequent changes or settings requiring multiple options, making them ideal for permanent or semi-permanent hardware configurations.
Choosing Between DIP Switches and Jumpers: Factors to Consider
Choosing between DIP switches and jumpers depends on factors such as ease of use, space constraints, and configuration frequency. DIP switches offer a more straightforward and reliable method for frequently changing settings without removing components, while jumpers require physical repositioning that may be less convenient but save PCB space. Consider the application's need for quick adjustments, available board area, and user accessibility when deciding between these configuration options.
Future Trends in Configurable Hardware Components
Future trends in configurable hardware components emphasize increased integration of DIP switches and jumpers with digital interfaces for enhanced flexibility and remote configurability. DIP switches maintain popularity for simple, low-cost binary settings, while jumpers evolve towards automated detection and adjustment mechanisms within modular hardware systems. Advancements in IoT and embedded systems drive demand for hybrid configurations combining physical toggles with software-controlled settings to optimize user control and system adaptability.
DIP switch vs Jumper Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com