CDMA and TDMA are two distinct multiple access technologies used in mobile communication, where CDMA allows multiple users to share the same frequency band simultaneously through unique codes, while TDMA divides the frequency into time slots assigned to different users. Understanding the differences between these technologies can help you choose the best option for your communication needs--explore the full article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
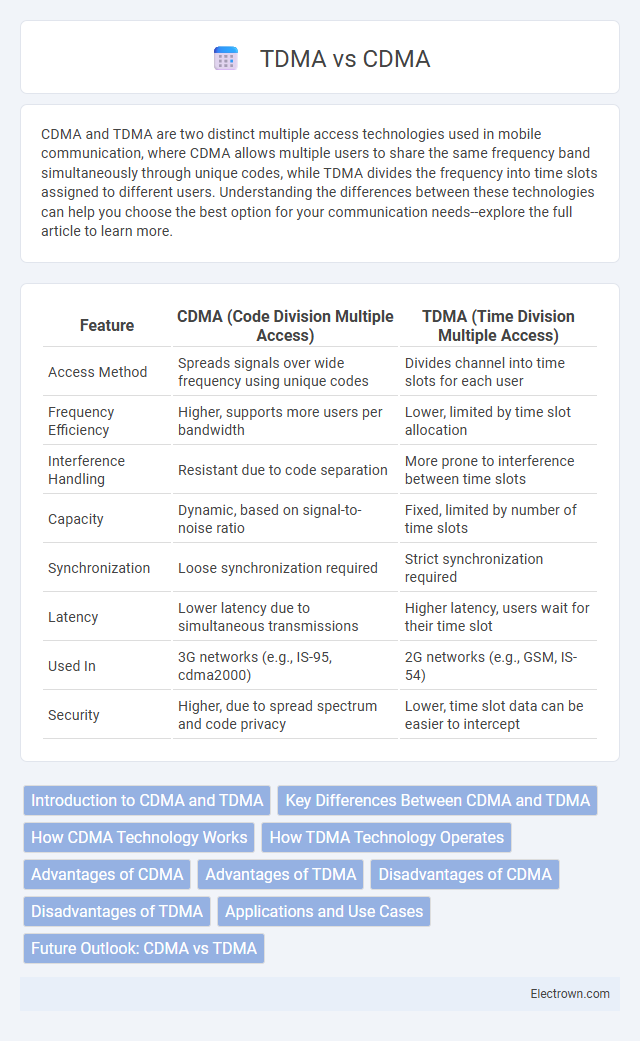
| Feature | CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) | TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) |
|---|---|---|
| Access Method | Spreads signals over wide frequency using unique codes | Divides channel into time slots for each user |
| Frequency Efficiency | Higher, supports more users per bandwidth | Lower, limited by time slot allocation |
| Interference Handling | Resistant due to code separation | More prone to interference between time slots |
| Capacity | Dynamic, based on signal-to-noise ratio | Fixed, limited by number of time slots |
| Synchronization | Loose synchronization required | Strict synchronization required |
| Latency | Lower latency due to simultaneous transmissions | Higher latency, users wait for their time slot |
| Used In | 3G networks (e.g., IS-95, cdma2000) | 2G networks (e.g., GSM, IS-54) |
| Security | Higher, due to spread spectrum and code privacy | Lower, time slot data can be easier to intercept |
Introduction to CDMA and TDMA
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) and TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) are two fundamental technologies used in wireless communication to enable multiple users to share the same frequency spectrum. CDMA employs spread-spectrum technology, assigning unique codes to each user to simultaneously transmit over the entire bandwidth, enhancing capacity and security. TDMA allocates distinct time slots to each user within a frequency channel, allowing sequential transmissions that optimize spectrum efficiency and reduce interference.
Key Differences Between CDMA and TDMA
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) uses spread-spectrum technology allowing multiple users to share the same frequency band simultaneously by assigning unique codes, while TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) divides the frequency into time slots allocated to different users sequentially. CDMA offers better spectral efficiency and higher capacity due to its ability to handle multiple signals over the same channel, whereas TDMA provides simpler implementation and lower power consumption by separating users in time. The key differences also include CDMA's resistance to interference and multipath fading, contrasting with TDMA's susceptibility to signal delay variations and timing synchronization requirements.
How CDMA Technology Works
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) technology works by assigning unique codes to each communication channel, allowing multiple users to share the same frequency band simultaneously without interference. It spreads the signal over a wide spectrum using a process called spread spectrum, enhancing security and resistance to noise. Unlike TDMA, which divides access by time slots, CDMA enables all users to transmit at the same time, improving capacity and efficiency in cellular networks.
How TDMA Technology Operates
TDMA technology operates by dividing each cellular channel into multiple time slots, allowing several users to share the same frequency without interference by transmitting in rapid succession. Each user is assigned a specific time slot for sending and receiving data, maximizing channel efficiency and reducing signal collision. Your mobile device synchronizes precisely with these time slots to ensure seamless communication within the TDMA network.
Advantages of CDMA
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) offers superior capacity and spectrum efficiency compared to TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access), enabling more simultaneous users within the same bandwidth. Its use of spread-spectrum technology provides enhanced security and resistance to interference and multipath fading, improving call quality and reliability. Your mobile experience benefits from CDMA's ability to support soft handoffs, reducing dropped calls during transitions between cell towers.
Advantages of TDMA
TDMA offers increased spectral efficiency by dividing a single frequency into multiple time slots, allowing more users to share the same channel without interference. It provides better power control and reduced interference compared to CDMA, enhancing voice quality and battery life in mobile devices. TDMA's structured time division simplifies network synchronization and supports predictable latency, benefiting real-time voice and data transmission.
Disadvantages of CDMA
CDMA suffers from the near-far problem, where strong signals can overshadow weaker ones, reducing overall system efficiency. It requires complex power control mechanisms to manage interference and maintain call quality. Additionally, CDMA systems face challenges with capacity limitations in high-density environments due to increased noise and signal distortion.
Disadvantages of TDMA
TDMA suffers from limitations including strict time synchronization requirements, which increases system complexity and potential latency. It also exhibits lower spectral efficiency compared to CDMA due to the fixed time slot allocation, leading to underutilization during varying traffic loads. Interference and signal degradation in multipath environments further reduce TDMA's overall performance and reliability.
Applications and Use Cases
CDMA technology is predominantly used in 3G cellular networks such as Verizon and Sprint, offering improved capacity and security for voice and data transmission in mobile communications. TDMA finds extensive use in 2G networks like GSM, supporting moderate data rates and efficient spectrum utilization for voice-centric applications internationally. CDMA suits dense urban environments with high user density, while TDMA is favored in regions prioritizing standardized global interoperability and network scalability.
Future Outlook: CDMA vs TDMA
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) continues to dominate in modern cellular networks due to its superior spectral efficiency, higher capacity, and better resistance to interference compared to TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access). TDMA's future outlook is limited primarily to legacy systems and niche applications, as 4G and 5G technologies favor CDMA-based and OFDMA-based techniques for enhanced data throughput and network performance. The ongoing evolution toward 5G and beyond solidifies CDMA's role in enabling advanced mobile broadband and IoT connectivity.
CDMA vs TDMA Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com