eARC offers enhanced audio quality and supports high-bitrate formats, making it ideal for immersive home theater experiences compared to the more basic ARC standard. Discover how upgrading to eARC can elevate your entertainment setup by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
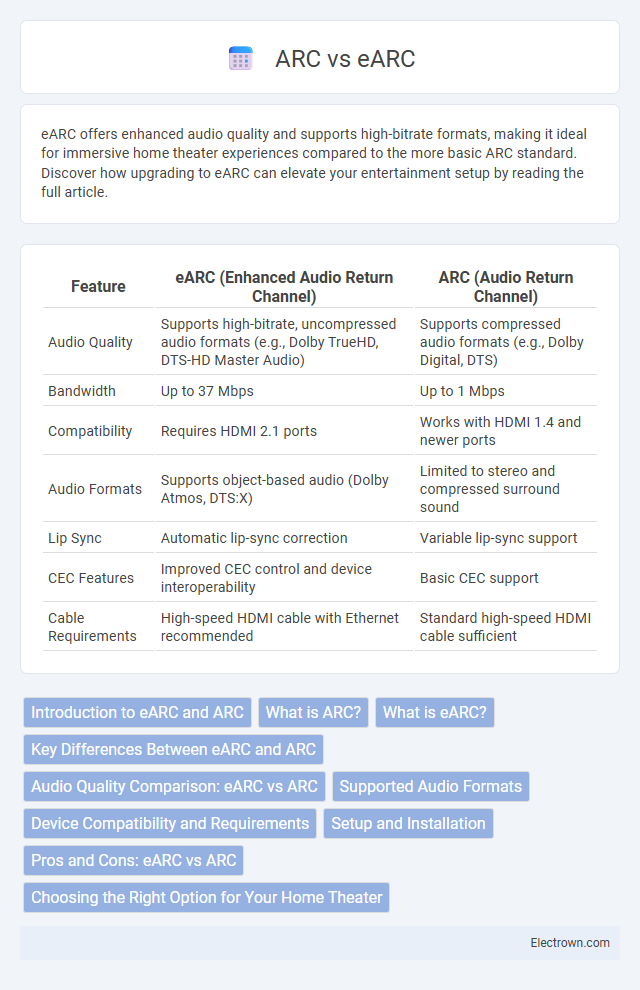
| Feature | eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) | ARC (Audio Return Channel) |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Quality | Supports high-bitrate, uncompressed audio formats (e.g., Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio) | Supports compressed audio formats (e.g., Dolby Digital, DTS) |
| Bandwidth | Up to 37 Mbps | Up to 1 Mbps |
| Compatibility | Requires HDMI 2.1 ports | Works with HDMI 1.4 and newer ports |
| Audio Formats | Supports object-based audio (Dolby Atmos, DTS:X) | Limited to stereo and compressed surround sound |
| Lip Sync | Automatic lip-sync correction | Variable lip-sync support |
| CEC Features | Improved CEC control and device interoperability | Basic CEC support |
| Cable Requirements | High-speed HDMI cable with Ethernet recommended | Standard high-speed HDMI cable sufficient |
Introduction to eARC and ARC
ARC (Audio Return Channel) and eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) are audio technologies designed to simplify sound connectivity between your TV and external audio devices like soundbars or AV receivers. ARC supports standard audio formats and basic lip-sync correction, while eARC offers higher bandwidth for lossless audio formats such as Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, ensuring superior sound quality. Understanding the differences between ARC and eARC helps you optimize your home entertainment audio experience.
What is ARC?
ARC (Audio Return Channel) is a feature in HDMI standards allowing audio signals to travel both ways between a TV and an audio device, eliminating the need for a separate audio cable. It supports compressed audio formats like Dolby Digital and DTS but has limited bandwidth, restricting high-quality audio formats. ARC simplifies home theater setups by enabling the TV to send audio to an external sound system through a single HDMI connection.
What is eARC?
eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) is an advanced version of ARC designed to transmit high-quality audio signals between your TV and external audio devices, such as soundbars or AV receivers. It supports uncompressed audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, enabling a superior home theater experience with richer sound quality. Unlike ARC, eARC offers greater bandwidth and faster data transfer to handle modern audio formats seamlessly.
Key Differences Between eARC and ARC
eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) supports higher bandwidth and advanced audio formats such as Dolby Atmos and DTS:X, while ARC (Audio Return Channel) is limited to basic stereo and compressed surround sound. eARC ensures better audio quality and lip-sync accuracy by utilizing a dedicated data channel in HDMI 2.1, whereas ARC operates through HDMI 1.4 or later with limited capabilities. Your home theater setup benefits from eARC when you require seamless transmission of uncompressed audio for an immersive entertainment experience.
Audio Quality Comparison: eARC vs ARC
Enhanced Audio Return Channel (eARC) delivers significantly higher audio quality compared to Audio Return Channel (ARC), supporting uncompressed high-bitrate formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio. ARC is limited to compressed audio signals such as Dolby Digital and DTS, which reduce the audio fidelity in home theater setups. eARC ensures seamless transmission of high-resolution audio formats including object-based audio like Dolby Atmos, providing a more immersive listening experience.
Supported Audio Formats
eARC supports a broader range of high-quality audio formats compared to ARC, including uncompressed 5.1 and 7.1 surround sound, Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio, and object-based audio formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. ARC typically transmits compressed audio formats such as Dolby Digital and DTS, limiting audio fidelity and channel count. Understanding these differences helps you choose the best connection for immersive home theater audio performance.
Device Compatibility and Requirements
eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) requires HDMI 2.1 ports on both the TV and audio device to support higher bandwidth and advanced audio formats such as DTS:X and Dolby Atmos, whereas ARC operates with HDMI 1.4 or higher, supporting basic audio formats. Devices compatible with eARC must also support the ARC protocol but with firmware updates or hardware upgrades often needed to enable full functionality. Compatibility limitations mean many older soundbars and TVs only support ARC, while newer high-end models offer eARC for enhanced audio performance and feature support.
Setup and Installation
eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) requires HDMI 2.1-compatible devices and cables for optimal setup and installation, ensuring high-bandwidth audio formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X are supported without compression. ARC (Audio Return Channel), compatible with HDMI 1.4 and above, offers simpler installation but limits audio quality and bandwidth, typically supporting compressed formats only. Your choice impacts the setup complexity and audio performance, with eARC demanding more advanced hardware but delivering superior sound experience.
Pros and Cons: eARC vs ARC
eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) offers higher bandwidth supporting uncompressed audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, providing superior sound quality compared to ARC, which supports compressed audio formats only. However, eARC requires compatible HDMI 2.1 hardware, making it less compatible with older devices where ARC remains widely supported and easier to implement. While ARC is sufficient for basic audio needs, eARC excels in delivering high-fidelity home theater experiences but may involve higher costs and device upgrades.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Home Theater
When choosing between eARC and ARC for your home theater, consider that eARC offers enhanced audio bandwidth and supports advanced formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X, providing superior sound quality compared to ARC's basic audio capabilities. Your decision should factor in the compatibility of your TV and audio devices, as eARC requires HDMI 2.1 standards, while ARC works with HDMI 1.4 or higher. Opting for eARC ensures future-proofing and richer audio experiences, making it the ideal choice for high-end setups.
eARC vs ARC Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com