NFC enables quick, simple file transfers over very short distances without pairing, while Bluetooth offers greater range and higher transfer speeds but requires device pairing. Discover how to choose the best option for your file-sharing needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
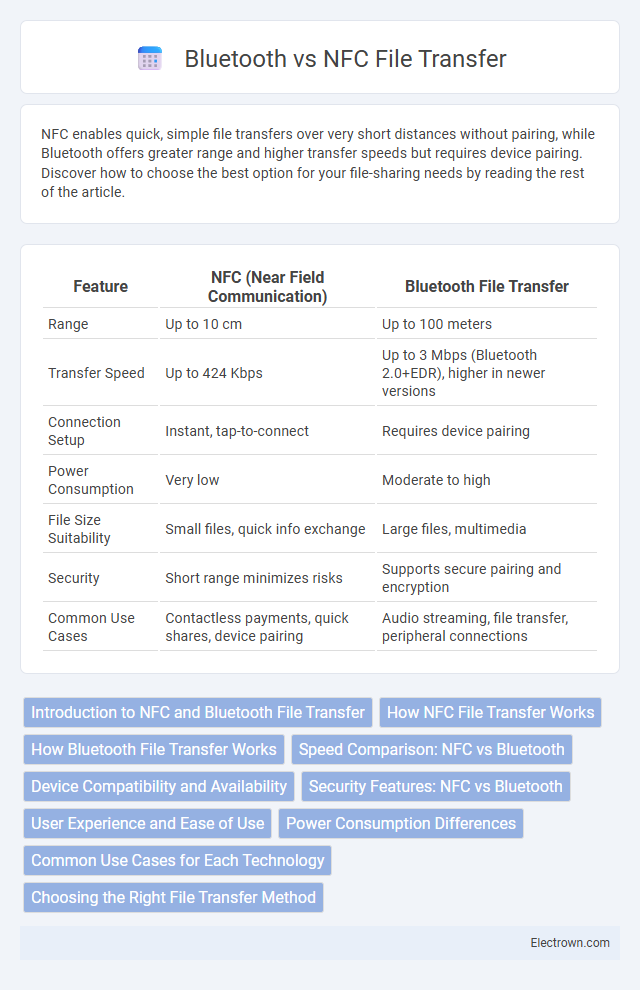
| Feature | NFC (Near Field Communication) | Bluetooth File Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Up to 10 cm | Up to 100 meters |
| Transfer Speed | Up to 424 Kbps | Up to 3 Mbps (Bluetooth 2.0+EDR), higher in newer versions |
| Connection Setup | Instant, tap-to-connect | Requires device pairing |
| Power Consumption | Very low | Moderate to high |
| File Size Suitability | Small files, quick info exchange | Large files, multimedia |
| Security | Short range minimizes risks | Supports secure pairing and encryption |
| Common Use Cases | Contactless payments, quick shares, device pairing | Audio streaming, file transfer, peripheral connections |
Introduction to NFC and Bluetooth File Transfer
NFC (Near Field Communication) enables quick and secure data transfer between devices within a few centimeters, ideal for contactless payments and pairing. Bluetooth File Transfer supports longer-range wireless communication, typically up to 10 meters, facilitating larger file exchanges like photos, videos, and documents. Both technologies complement each other by offering diverse connectivity options depending on range and data size requirements.
How NFC File Transfer Works
NFC file transfer works by establishing a close-range wireless connection when two NFC-enabled devices are tapped together, allowing data exchange through electromagnetic fields. Your device uses Near Field Communication to initiate pairing instantly without manual setup, making it faster than Bluetooth for initiating transfers. While NFC handles the connection handshake, the actual file transfer typically occurs via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi Direct for higher speeds.
How Bluetooth File Transfer Works
Bluetooth file transfer works by establishing a wireless connection between two devices using radio waves within the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Devices pair through a process involving device discovery, authentication, and secure link setup, enabling direct data exchange via the Bluetooth protocol stack, typically using the OBEX (Object Exchange) profile for file transfers. This method allows for relatively high data transfer speeds over distances up to 100 meters, making it suitable for sending large files compared to NFC's short-range, lower-speed communication.
Speed Comparison: NFC vs Bluetooth
NFC offers a data transfer speed of up to 424 kbps, making it ideal for quick, low-volume exchanges such as contact sharing or payment authentication. Bluetooth significantly outperforms NFC in speed, with Bluetooth 5.0 reaching up to 2 Mbps and the latest Bluetooth 5.2 supporting even higher rates, making it better suited for transferring larger files or streaming media. Your choice depends on whether rapid small data exchanges or faster large file transfers align best with your needs.
Device Compatibility and Availability
NFC (Near Field Communication) offers widespread compatibility with most modern smartphones, tablets, and some laptops, enabling quick and simple file transfers without pairing. Bluetooth, on the other hand, supports a broader range of devices including older smartphones, computers, headphones, and peripherals, making it more universally available for diverse hardware. While NFC excels in ease of use and instant connectivity, Bluetooth provides greater device compatibility and longer transfer range, essential for transferring larger files across various platforms.
Security Features: NFC vs Bluetooth
NFC offers enhanced security by enabling close-proximity data transfer within a range of about 4 centimeters, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized interception. Bluetooth employs encryption protocols like AES-128 but remains vulnerable to attacks such as bluejacking and bluesnarfing due to its longer communication range of up to 100 meters. Consequently, NFC's limited range and passive communication model provide superior protection against eavesdropping and unauthorized access compared to Bluetooth.
User Experience and Ease of Use
NFC enables instant file transfer with a simple tap, eliminating the need for device pairing and complex setup, which greatly enhances user experience and ease of use. Bluetooth, while offering higher data transfer rates and longer range, requires manual device discovery and pairing, adding steps that can complicate the process for users unfamiliar with the technology. Your choice between NFC and Bluetooth should consider the balance between convenience for quick, small transfers and the need for faster, larger data exchanges.
Power Consumption Differences
NFC consumes significantly less power than Bluetooth because it operates over very short distances and requires minimal energy for data transmission. Bluetooth, especially Bluetooth Classic and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), uses more power to maintain connections and achieve higher data transfer rates over longer distances. Your choice between NFC and Bluetooth for file transfer should consider the balance between power consumption and data transfer speed based on your device's battery capacity and usage scenario.
Common Use Cases for Each Technology
NFC is commonly used for quick, contactless data exchanges such as mobile payments, pairing devices, and sharing small files like contacts or photos with a simple tap. Bluetooth excels in transferring larger files, streaming audio to wireless headphones or speakers, and enabling continuous connections for peripherals like keyboards, mice, and fitness trackers. Both technologies complement each other by addressing distinct needs in short-range communication and file transfer scenarios.
Choosing the Right File Transfer Method
Choosing the right file transfer method depends on your priorities such as speed, range, and device compatibility. NFC offers quick, secure pairing with minimal setup, ideal for small files or contact sharing within close proximity under 10 cm. Bluetooth supports larger files over longer distances up to 100 meters but requires device pairing and may consume more power, making it suitable for transferring music, videos, or extensive data between your devices.
NFC vs Bluetooth File Transfer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com