CMOS sensors offer lower power consumption and faster processing speeds, making them ideal for high-speed photography and mobile devices, while CCD sensors provide superior image quality and better low-light performance due to their charge transfer efficiency. Discover the detailed comparison to choose the best sensor for your photography needs.
Table of Comparison
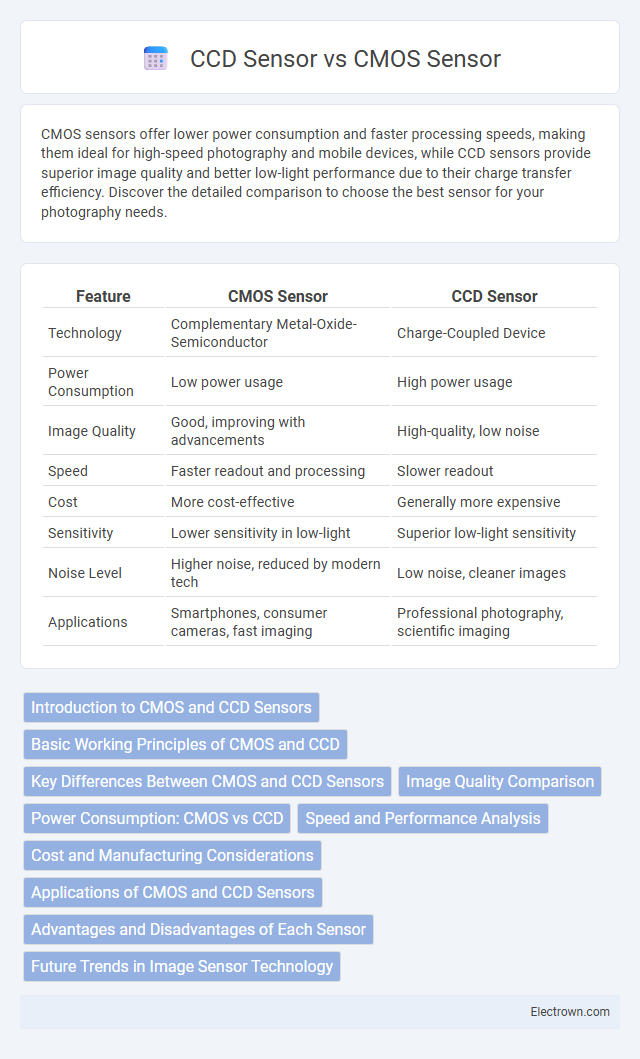
| Feature | CMOS Sensor | CCD Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor | Charge-Coupled Device |
| Power Consumption | Low power usage | High power usage |
| Image Quality | Good, improving with advancements | High-quality, low noise |
| Speed | Faster readout and processing | Slower readout |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Generally more expensive |
| Sensitivity | Lower sensitivity in low-light | Superior low-light sensitivity |
| Noise Level | Higher noise, reduced by modern tech | Low noise, cleaner images |
| Applications | Smartphones, consumer cameras, fast imaging | Professional photography, scientific imaging |
Introduction to CMOS and CCD Sensors
CMOS sensors, known for their low power consumption and faster processing speeds, are widely used in smartphones and digital cameras for high-quality image capture. CCD sensors excel in producing high-resolution images with superior light sensitivity, making them ideal for scientific imaging and professional photography. Understanding the differences between CMOS and CCD sensors can help you choose the right technology based on your imaging needs and device compatibility.
Basic Working Principles of CMOS and CCD
CMOS sensors operate by converting light into electrons using photodiodes on each pixel, then amplifying and processing signals directly within the pixel, enabling faster readout and lower power consumption. CCD sensors transfer accumulated charge across the chip to a single output node for conversion to voltage, which results in higher image quality but slower processing and higher power use. The difference in charge handling and signal processing fundamentally distinguishes CMOS's integration and speed advantages from CCD's superior light sensitivity and noise performance.
Key Differences Between CMOS and CCD Sensors
CMOS sensors use individual transistors at each pixel for faster readout speeds, while CCD sensors transfer charge across the chip to a single output node, resulting in higher image quality with less noise. CMOS sensors consume less power and are more cost-effective, making them ideal for mobile devices and consumer electronics, whereas CCD sensors excel in professional photography and scientific applications due to superior light sensitivity and dynamic range. Your choice between CMOS and CCD sensors should depend on the balance between speed, power efficiency, and image quality required for your specific use case.
Image Quality Comparison
CMOS sensors typically offer faster readout speeds and lower power consumption, while CCD sensors are renowned for superior light sensitivity and lower noise levels, resulting in higher image quality especially in low-light conditions. CCD sensors often produce images with better color accuracy and less distortion, making them ideal for applications requiring precise image clarity. Your choice depends on whether speed and efficiency or maximum image quality under challenging lighting is the priority.
Power Consumption: CMOS vs CCD
CMOS sensors consume significantly less power than CCD sensors, making them ideal for battery-powered devices like smartphones and digital cameras. The lower power consumption of CMOS sensors results from their on-chip signal processing capabilities, which reduce the need for external circuitry. CCD sensors, while offering high image quality, require more power due to charge transfer operations and external analog processing.
Speed and Performance Analysis
CMOS sensors offer faster readout speeds and lower power consumption compared to CCD sensors, making them ideal for high-speed imaging applications such as video recording and continuous shooting. CCD sensors typically provide higher image quality with lower noise levels, especially in low-light conditions, but they operate at slower speeds due to their charge transfer process. Your choice between CMOS and CCD sensors should balance the need for speed with the desired image quality based on your specific use case.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
CMOS sensors are generally more cost-effective to produce due to their compatibility with standard semiconductor manufacturing processes, allowing for integration with other electronics on a single chip, which reduces assembly complexity and overall expenses. CCD sensors require specialized fabrication techniques that increase production costs and typically involve separate processing circuits, leading to higher material and manufacturing expenditures. The widespread availability and scalability of CMOS technology make it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications demanding high volume and efficient manufacturing.
Applications of CMOS and CCD Sensors
CMOS sensors are widely used in smartphone cameras, automotive applications, and consumer electronics due to their low power consumption, fast readout speeds, and cost-effectiveness. CCD sensors excel in scientific imaging, astrophotography, and medical devices where high image quality, low noise, and superior light sensitivity are critical. When selecting your imaging technology, consider CMOS for versatility and speed, while choosing CCD for precision and low-noise performance in specialized applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Sensor
CMOS sensors offer lower power consumption, faster readout speeds, and cheaper manufacturing costs, making them ideal for smartphones and high-speed applications, though they tend to have higher noise levels and lower image quality compared to CCD sensors. CCD sensors provide superior image quality with better light sensitivity and lower noise, which benefits professional photography and scientific imaging, but they consume more power, are more expensive to produce, and have slower readout speeds. The choice between CMOS and CCD sensors depends on the specific requirements for image quality, power efficiency, and cost constraints in various applications.
Future Trends in Image Sensor Technology
Future trends in image sensor technology highlight CMOS sensors surpassing CCD sensors due to lower power consumption, faster readout speeds, and enhanced integration capabilities with AI processing. Innovations such as backside illumination (BSI) and stacked sensor architectures in CMOS sensors drive higher sensitivity and resolution, meeting demands in smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and medical imaging. Your choice of image sensor will increasingly rely on these advancements to deliver superior image quality and efficient performance in evolving digital imaging applications.
CMOS Sensor vs CCD Sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com