Zigbee and Z-Wave are leading wireless communication protocols designed for smart home automation, with Zigbee offering higher data rates and broader device compatibility, while Z-Wave provides longer range and better interoperability among certified devices. Discover which protocol best fits Your smart home needs by exploring their key differences and benefits throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
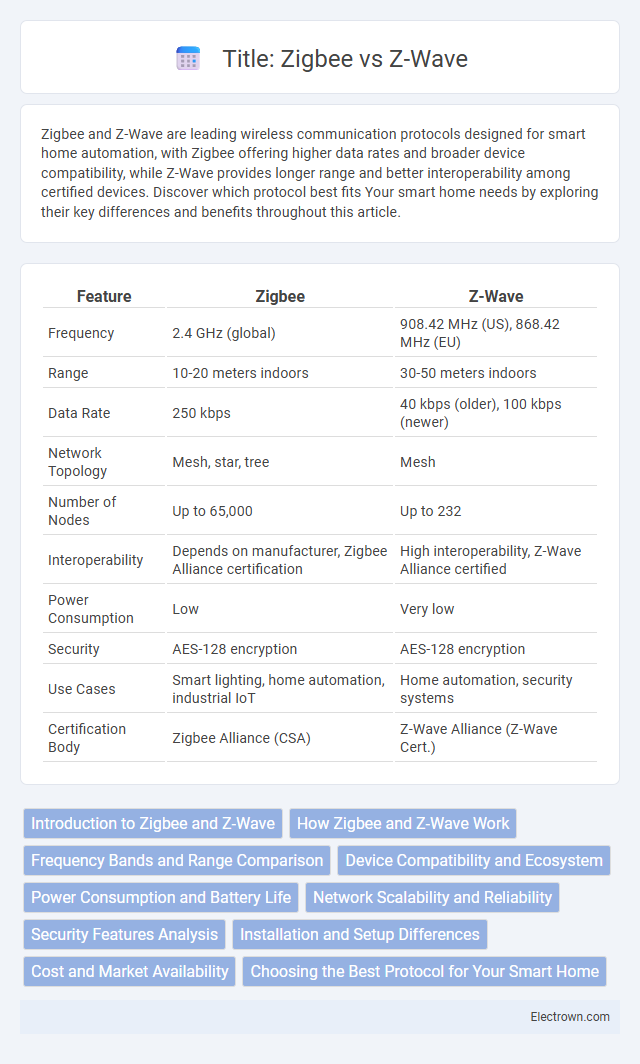
| Feature | Zigbee | Z-Wave |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 GHz (global) | 908.42 MHz (US), 868.42 MHz (EU) |
| Range | 10-20 meters indoors | 30-50 meters indoors |
| Data Rate | 250 kbps | 40 kbps (older), 100 kbps (newer) |
| Network Topology | Mesh, star, tree | Mesh |
| Number of Nodes | Up to 65,000 | Up to 232 |
| Interoperability | Depends on manufacturer, Zigbee Alliance certification | High interoperability, Z-Wave Alliance certified |
| Power Consumption | Low | Very low |
| Security | AES-128 encryption | AES-128 encryption |
| Use Cases | Smart lighting, home automation, industrial IoT | Home automation, security systems |
| Certification Body | Zigbee Alliance (CSA) | Z-Wave Alliance (Z-Wave Cert.) |
Introduction to Zigbee and Z-Wave
Zigbee and Z-Wave are leading wireless communication protocols designed for smart home automation, with Zigbee operating on the 2.4 GHz frequency and Z-Wave using the sub-1 GHz band, offering less interference and longer range. Zigbee supports a higher data rate up to 250 kbps, enabling faster communication between connected devices, whereas Z-Wave prioritizes reliability and interoperability with over 3,000 certified products worldwide. Your choice depends on device compatibility, network size, and specific smart home needs, as both protocols excel in low-power, mesh network architectures.
How Zigbee and Z-Wave Work
Zigbee operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, utilizing mesh networking to enable devices to communicate via short-range, low-power radio frequencies primarily in the 2.4 GHz band. Z-Wave functions on a proprietary protocol using the sub-1 GHz frequency band, favoring reduced interference and longer range, with a mesh network that allows devices to relay signals to extend coverage. Both technologies rely on secure, low-latency communication protocols optimized for smart home automation but differ in frequency, network capacity, and device interoperability.
Frequency Bands and Range Comparison
Zigbee operates primarily on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, offering a global standard with a maximum range of approximately 10-20 meters indoors. Z-Wave utilizes sub-1 GHz frequencies (908.42 MHz in the US and 868.42 MHz in Europe), which provides better penetration through walls and longer range of about 30-50 meters indoors. Your choice between Zigbee and Z-Wave can impact network reliability and device compatibility based on these frequency and range characteristics.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem
Zigbee offers broad device compatibility due to its open standard and widespread adoption among numerous manufacturers, creating a diverse and expansive ecosystem ideal for various smart home applications. Z-Wave operates on a proprietary protocol with a more limited but highly interoperable device range, ensuring reliable communication within its tightly controlled ecosystem. Your choice between Zigbee and Z-Wave depends on the importance of device variety versus seamless interoperability in your smart home network.
Power Consumption and Battery Life
Zigbee and Z-Wave both excel in low power consumption, but Zigbee operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard at 2.4 GHz, allowing faster data rates and slightly higher power use, which can reduce battery life in some devices. Z-Wave uses sub-1 GHz frequencies, typically resulting in better range and lower interference, leading to longer battery life for comparable devices. Your choice between Zigbee and Z-Wave can significantly impact battery performance, especially in battery-operated smart home sensors and switches.
Network Scalability and Reliability
Zigbee supports large mesh networks with up to 65,000 devices, providing extensive scalability for complex smart home setups, while Z-Wave networks typically handle up to 232 devices, making it more suitable for medium-sized environments. Both protocols use mesh networking to enhance reliability by routing signals through multiple devices, but Zigbee's higher device limit offers greater flexibility for future expansion. Your smart home system's network performance depends on choosing the right protocol based on the scale and robustness required.
Security Features Analysis
Zigbee employs AES-128 encryption for securing data transmissions, leveraging a distributed network architecture that enhances resilience against single points of failure and potential attacks. Z-Wave also uses AES-128 encryption but integrates a secure inclusion process called SmartStart, which simplifies device onboarding while preventing unauthorized access to the network. Both protocols offer robust security mechanisms; however, Z-Wave's centralized controller model provides more straightforward network monitoring and threat mitigation compared to Zigbee's mesh topology.
Installation and Setup Differences
Zigbee devices typically support self-healing mesh networks, allowing automatic device discovery and easier integration with existing smart home hubs, while Z-Wave devices require a primary controller for network setup and tend to have simpler pairing processes. Zigbee operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency, which may lead to interference in environments crowded with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth devices, whereas Z-Wave functions on sub-1 GHz frequencies, reducing signal interference and improving range. Installation of Zigbee can be more complex due to compatibility variations among manufacturers, but its widespread adoption promotes versatility, unlike Z-Wave's standardized protocol that ensures seamless interoperability but with fewer device options.
Cost and Market Availability
Zigbee devices generally offer lower costs due to widespread adoption and manufacturing scale, making them more budget-friendly for smart home installations. Z-Wave products, while often pricier, benefit from a dedicated frequency band that reduces interference, appealing to users prioritizing reliability over cost. Market availability favors Zigbee with broader support from numerous manufacturers and integration in popular hubs, though Z-Wave maintains strong presence in high-end security and automation niches.
Choosing the Best Protocol for Your Smart Home
Zigbee and Z-Wave are leading wireless protocols designed to enhance smart home connectivity through reliable, low-power communication. Zigbee operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency with faster data rates and a larger ecosystem, while Z-Wave uses sub-GHz frequencies for extended range and minimal interference. Your choice depends on device compatibility, network size, and interference considerations to ensure seamless smart home automation.
Zigbee vs Z-Wave Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com