MEMS microphones offer superior durability, smaller size, and consistent performance compared to electret microphones, which are typically bulkier and more prone to environmental degradation. Explore the rest of the article to discover which microphone best suits your audio needs.
Table of Comparison
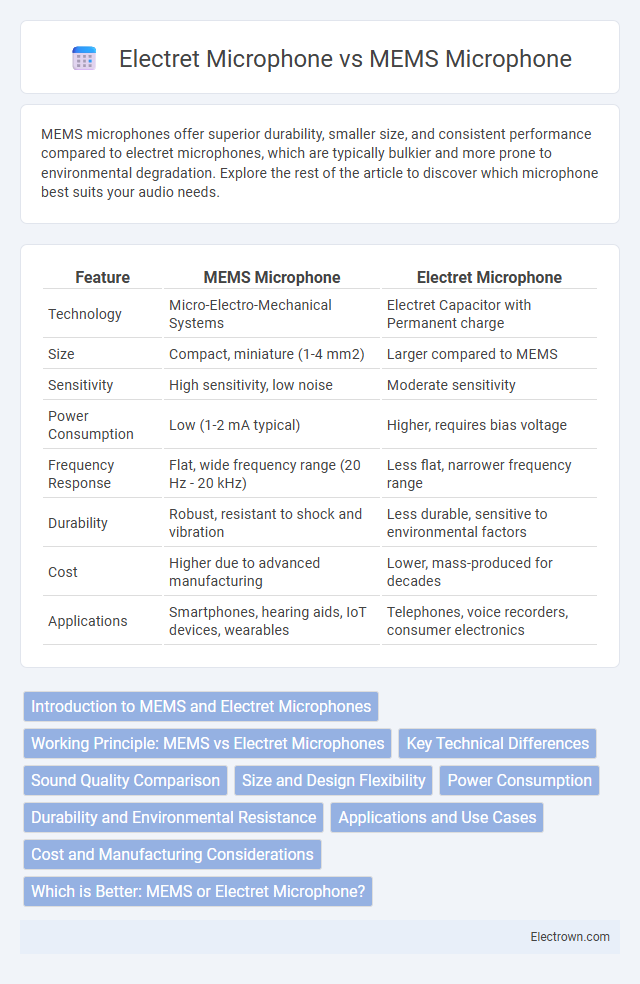
| Feature | MEMS Microphone | Electret Microphone |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems | Electret Capacitor with Permanent charge |
| Size | Compact, miniature (1-4 mm2) | Larger compared to MEMS |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity, low noise | Moderate sensitivity |
| Power Consumption | Low (1-2 mA typical) | Higher, requires bias voltage |
| Frequency Response | Flat, wide frequency range (20 Hz - 20 kHz) | Less flat, narrower frequency range |
| Durability | Robust, resistant to shock and vibration | Less durable, sensitive to environmental factors |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced manufacturing | Lower, mass-produced for decades |
| Applications | Smartphones, hearing aids, IoT devices, wearables | Telephones, voice recorders, consumer electronics |
Introduction to MEMS and Electret Microphones
MEMS microphones utilize micro-electromechanical systems technology to convert sound into electrical signals with high precision and compact size, making them ideal for modern smartphones and wearables. Electret microphones rely on a permanently charged material to capture sound, offering low cost and reliable performance typically found in traditional telephones and consumer electronics. Both types serve audio capture needs but differ significantly in design, sensitivity, and integration capabilities.
Working Principle: MEMS vs Electret Microphones
MEMS microphones operate using a micro-machined diaphragm and backplate forming a capacitive sensor that converts sound waves into electrical signals through changes in capacitance. Electret microphones utilize a permanently charged electret material combined with a flexible diaphragm and backplate, generating voltage variations in response to sound pressure changes. The MEMS design offers greater stability and sensitivity by leveraging semiconductor fabrication techniques, while electret microphones rely on static charge and mechanical variance for sound detection.
Key Technical Differences
MEMS microphones utilize microelectromechanical systems technology, offering superior sensitivity, smaller size, and lower power consumption compared to electret microphones, which rely on a permanently charged polymer film. MEMS devices provide a wider frequency response and better noise immunity due to their integrated ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) design. Your choice between MEMS and electret microphones should consider the application's demands on precision, size constraints, and environmental resilience.
Sound Quality Comparison
MEMS microphones offer superior sound quality compared to electret microphones due to their higher sensitivity and lower noise floor, resulting in clearer audio capture. Their advanced digital signal processing capabilities enhance frequency response and reduce distortion, delivering more accurate and consistent sound reproduction. Electret microphones, while cost-effective, generally exhibit higher self-noise and limited dynamic range, which can impact overall audio fidelity.
Size and Design Flexibility
MEMS microphones are significantly smaller than electret microphones, allowing for compact device integration and enhanced design flexibility in modern electronics. Their silicon-based structure enables easy customization and integration with other microdevices, making them ideal for space-constrained applications. Your choice of microphone can greatly impact the overall design, especially when miniaturization and versatile placement options are critical.
Power Consumption
MEMS microphones typically consume less power compared to electret microphones, making them ideal for battery-operated and portable devices. The low voltage operation of MEMS technology enhances energy efficiency without compromising audio quality. Electret microphones, while reliable, generally require higher bias voltage, resulting in greater power consumption during use.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
MEMS microphones offer superior durability and environmental resistance compared to electret microphones, as their solid-state construction withstands shock, vibration, and extreme temperatures more effectively. Electret microphones, relying on a delicate charged diaphragm, are more susceptible to moisture, dust, and aging, which can degrade performance over time. Your choice of microphone impacts long-term reliability, especially in harsh or variable environments where consistent audio quality is essential.
Applications and Use Cases
MEMS microphones are widely used in smartphones, hearing aids, and wearable devices due to their small size, low power consumption, and high sensitivity, making them ideal for noise-cancelling and voice recognition applications. Electret microphones remain popular in consumer electronics like telephones, laptops, and portable audio recorders, valued for their robustness and cost-effectiveness in general sound capture. MEMS technology excels in environments requiring miniaturization and integration with digital systems, whereas electret microphones are preferred for straightforward audio capture in less size-sensitive applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
MEMS microphones typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to batch fabrication on silicon wafers using semiconductor processes, leading to smaller size and greater integration capability. Electret microphones, while generally more affordable in raw component terms, require more manual assembly and calibration, increasing labor costs and limiting scalability. Your choice depends on balancing precision, production volume, and cost efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Which is Better: MEMS or Electret Microphone?
MEMS microphones offer superior performance with better noise immunity, smaller size, and greater durability compared to electret microphones, which rely on a charged diaphragm and can degrade over time. Your choice depends on application needs; MEMS is ideal for modern electronic devices requiring high precision and reliability, while electret microphones provide a cost-effective solution for simpler audio capture. Overall, MEMS microphones deliver enhanced sensitivity and consistency, making them a better choice for advanced audio applications.
MEMS Microphone vs Electret Microphone Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com