Heat sinks provide efficient passive cooling for CPUs and GPUs by dissipating heat through metal fins, while liquid cooling systems offer superior thermal performance by circulating coolant to absorb and transfer heat away from components. Explore the detailed comparison to find out which cooling solution best fits Your needs.
Table of Comparison
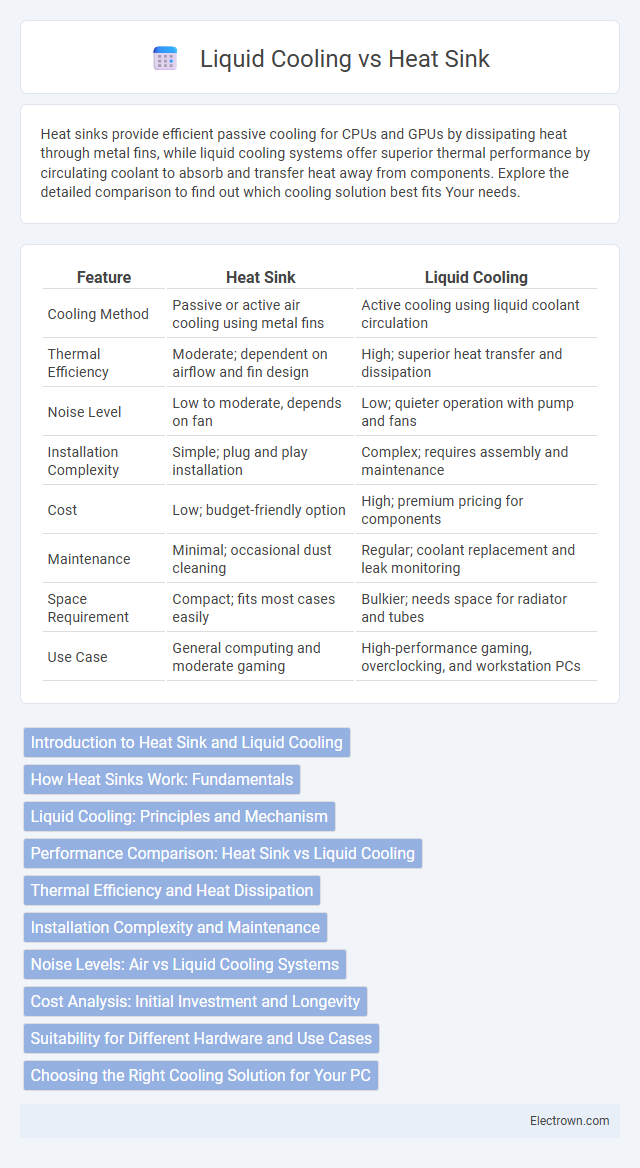
| Feature | Heat Sink | Liquid Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Passive or active air cooling using metal fins | Active cooling using liquid coolant circulation |
| Thermal Efficiency | Moderate; dependent on airflow and fin design | High; superior heat transfer and dissipation |
| Noise Level | Low to moderate, depends on fan | Low; quieter operation with pump and fans |
| Installation Complexity | Simple; plug and play installation | Complex; requires assembly and maintenance |
| Cost | Low; budget-friendly option | High; premium pricing for components |
| Maintenance | Minimal; occasional dust cleaning | Regular; coolant replacement and leak monitoring |
| Space Requirement | Compact; fits most cases easily | Bulkier; needs space for radiator and tubes |
| Use Case | General computing and moderate gaming | High-performance gaming, overclocking, and workstation PCs |
Introduction to Heat Sink and Liquid Cooling
Heat sinks are passive cooling solutions that dissipate heat through metal fins, commonly made of aluminum or copper, efficiently managing heat from CPUs, GPUs, and power electronics. Liquid cooling systems use coolant circulated through tubes and radiators to transfer heat away from components, offering superior thermal performance for high-power or overclocked devices. Your choice between a heat sink and liquid cooling depends on your system's thermal demands, space constraints, and noise preferences.
How Heat Sinks Work: Fundamentals
Heat sinks work by transferring heat away from electronic components through conduction, convection, and radiation. They are typically made of highly conductive materials like aluminum or copper, with fins that increase surface area for efficient heat dissipation into the surrounding air. The design maximizes airflow and thermal conductivity to prevent overheating and maintain optimal device performance.
Liquid Cooling: Principles and Mechanism
Liquid cooling operates by circulating coolant through a closed loop that absorbs heat from components via a water block, then transports it to a radiator where fans dissipate the heat into the surrounding air. This mechanism ensures more efficient heat transfer compared to traditional heat sinks, maintaining lower temperatures under heavy workloads. Your system benefits from enhanced thermal regulation, enabling higher performance and prolonged hardware lifespan.
Performance Comparison: Heat Sink vs Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling systems offer superior thermal management compared to traditional heat sinks by efficiently dissipating heat through a continuous liquid flow, resulting in lower CPU and GPU temperatures under heavy workloads. Heat sinks rely on passive or active air cooling, which may suffice for moderate performance but struggle to maintain stable temperatures during overclocking or high-performance gaming. Your system's cooling choice directly impacts component longevity and performance, with liquid cooling providing quieter operation and enhanced heat dissipation in demanding scenarios.
Thermal Efficiency and Heat Dissipation
Heat sinks provide reliable thermal efficiency by utilizing conductive materials like aluminum or copper to dissipate heat through convection and radiation, making them effective for moderate thermal loads. Liquid cooling systems outperform heat sinks in heat dissipation by circulating coolant fluid that absorbs and transfers heat away from the CPU or GPU more efficiently, supporting higher thermal loads and maintaining lower operating temperatures. The enhanced thermal conductivity of liquids combined with larger surface areas in radiators results in superior heat dissipation capabilities compared to traditional passive or active heat sinks.
Installation Complexity and Maintenance
Heat sinks offer straightforward installation with minimal tools required, making them accessible for most users. Liquid cooling systems, however, demand more complex setup involving mounting pumps, radiators, and tubing, often requiring experience to avoid leaks. Regular maintenance is simpler for heat sinks, typically limited to dust cleaning, whereas liquid cooling necessitates periodic coolant replacement and system checks to prevent component damage.
Noise Levels: Air vs Liquid Cooling Systems
Heat sinks with air cooling operate using fans that generate noticeable noise depending on the fan speed and size, often ranging between 20 to 40 decibels during typical use. Liquid cooling systems are generally quieter since they rely on fewer or slower-spinning fans and the liquid's efficiency in heat transfer reduces the need for high fan speeds. Your choice between the two affects noise levels significantly, with liquid cooling offering a quieter environment ideal for noise-sensitive setups.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Longevity
Heat sinks offer a lower initial investment compared to liquid cooling systems due to simpler design and fewer components. Liquid cooling generally involves higher upfront costs but can provide longer longevity and enhanced thermal performance, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Your choice should weigh the balance between budget constraints and the long-term efficiency benefits of each cooling method.
Suitability for Different Hardware and Use Cases
Heat sinks offer effective cooling for standard CPUs and GPUs in typical desktop setups, making them suitable for everyday computing and moderate gaming environments. Liquid cooling systems provide superior thermal performance, ideal for high-end gaming rigs, overclocked processors, and workstations handling intensive tasks like 3D rendering or video editing. Your choice should align with hardware demands and use cases, as liquid cooling excels in high-performance scenarios while heat sinks suffice for less demanding applications.
Choosing the Right Cooling Solution for Your PC
Choosing the right cooling solution for your PC depends on factors such as system performance, noise levels, and budget. Heat sinks offer reliable, low-maintenance cooling ideal for mid-range builds, while liquid cooling provides superior thermal performance suited for high-end gaming and overclocking setups. Evaluating your PC's workload, case compatibility, and maintenance preferences helps determine whether air or liquid cooling best meets your needs.
Heat Sink vs Liquid Cooling Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com