E-ink displays provide a paper-like reading experience with low power consumption and excellent outdoor visibility, while LCD displays offer vibrant colors and faster refresh rates suitable for multimedia use. Discover which display technology best suits your needs by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
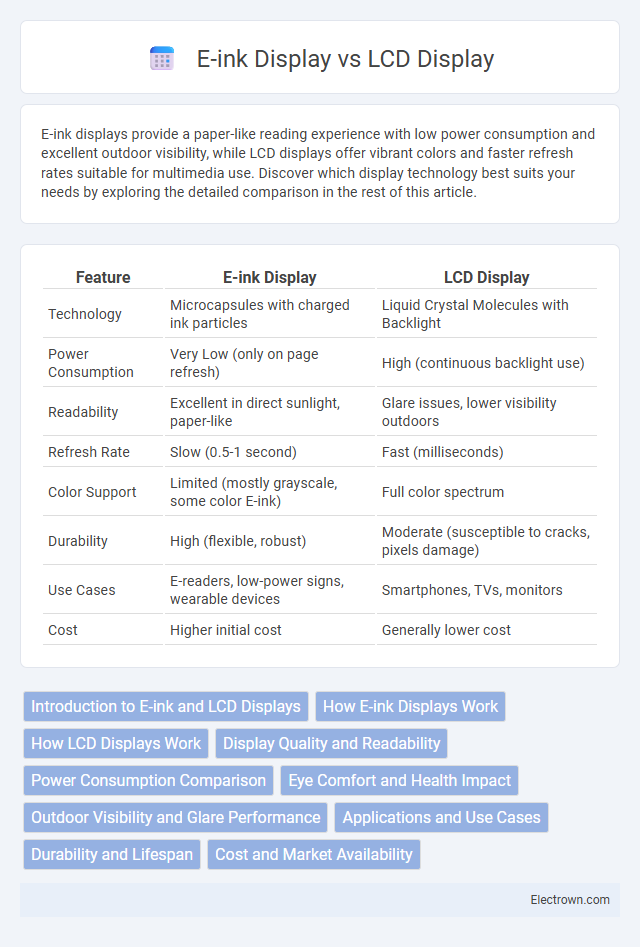
| Feature | E-ink Display | LCD Display |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Microcapsules with charged ink particles | Liquid Crystal Molecules with Backlight |
| Power Consumption | Very Low (only on page refresh) | High (continuous backlight use) |
| Readability | Excellent in direct sunlight, paper-like | Glare issues, lower visibility outdoors |
| Refresh Rate | Slow (0.5-1 second) | Fast (milliseconds) |
| Color Support | Limited (mostly grayscale, some color E-ink) | Full color spectrum |
| Durability | High (flexible, robust) | Moderate (susceptible to cracks, pixels damage) |
| Use Cases | E-readers, low-power signs, wearable devices | Smartphones, TVs, monitors |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to E-ink and LCD Displays
E-ink displays use microcapsules filled with charged particles that respond to electric fields, producing high-contrast, paper-like images with minimal power consumption. LCD displays rely on liquid crystal molecules manipulated by backlight to render vibrant colors and sharp images, ideal for dynamic multimedia use. Understanding these technologies helps you choose the right screen for reading comfort or multimedia performance.
How E-ink Displays Work
E-ink displays operate using microcapsules filled with positively charged white particles and negatively charged black particles suspended in a clear fluid, which rearrange to form images when an electric field is applied. This technology mimics the appearance of ink on paper by reflecting ambient light instead of emitting its own, resulting in reduced power consumption and minimal eye strain. Your choice of an E-ink display ensures enhanced readability in bright sunlight and extended battery life compared to traditional LCD screens.
How LCD Displays Work
LCD displays operate by manipulating liquid crystals sandwiched between two polarizing filters and glass layers; when an electric current passes through these crystals, they align to either block or allow light to pass, creating images. Backlighting is essential for LCD screens, providing illumination that shines through the liquid crystal layer to produce visible colors and brightness. This technology results in vibrant color reproduction and fast refresh rates but consumes more power compared to E-ink displays.
Display Quality and Readability
E-ink displays offer superior readability due to their paper-like appearance and lack of glare, making them ideal for prolonged reading in various lighting conditions. LCD displays provide vibrant colors and high resolution, suitable for multimedia content but may cause eye strain during extended use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize eye comfort and natural reading experience (E-ink) or rich visuals and animation (LCD).
Power Consumption Comparison
E-ink displays consume significantly less power than LCD displays due to their bi-stable nature, requiring energy only when refreshing the image. LCDs rely on a constant backlight, leading to continuous power usage, especially during prolonged screen activity. This efficiency makes E-ink ideal for devices prioritizing battery longevity, such as e-readers and low-power smart devices.
Eye Comfort and Health Impact
E-ink displays emit no light and rely on ambient lighting, reducing eye strain and minimizing blue light exposure compared to LCD displays, which use backlighting that can cause fatigue and disrupt sleep patterns. The reflective nature of E-ink closely mimics paper, offering a comfortable reading experience especially during extended use. In contrast, prolonged exposure to LCD screens can lead to digital eye strain symptoms such as dryness, headaches, and blurred vision.
Outdoor Visibility and Glare Performance
E-ink displays offer superior outdoor visibility by mimicking paper, reducing glare and making content easily readable even under direct sunlight, unlike traditional LCD displays that often suffer from reflection and washed-out colors. LCD screens rely on backlighting which can cause significant glare, hindering clear viewing in bright environments, whereas your eyes experience less strain with E-ink technology during prolonged outdoor use. This makes E-ink displays ideal for devices used primarily outside, such as e-readers, while LCDs remain better suited for vibrant multimedia in controlled lighting conditions.
Applications and Use Cases
E-ink displays excel in e-readers and low-power devices, offering superior readability in bright sunlight and extended battery life, ideal for digital books and wearable technology. LCD displays dominate in smartphones, tablets, and monitors, providing vibrant colors and fast refresh rates necessary for video streaming, gaming, and interactive applications. Both technologies cater to specific needs, with E-ink favored for static content and prolonged usage, while LCDs support dynamic, multimedia-rich environments.
Durability and Lifespan
E-ink displays boast superior durability and lifespan compared to LCD displays due to their non-backlit technology and minimal power consumption, which reduces wear on components. LCD displays rely on backlighting and organic materials that degrade faster, leading to shorter overall longevity. Devices equipped with E-ink screens are typically more resistant to screen burn-in and can maintain image integrity for years under proper usage conditions.
Cost and Market Availability
E-ink displays generally have higher initial manufacturing costs due to specialized technology but offer cost efficiency in long-term usage for devices like e-readers. LCD displays benefit from mass production and widespread adoption, resulting in lower prices and extensive market availability across smartphones, monitors, and TVs. The affordability and accessibility of LCD technology make it the dominant choice in consumer electronics, while E-ink remains niche for low-power display applications.
E-ink Display vs LCD Display Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com