LCD and LED screens differ primarily in backlighting technology, with LED displays offering improved color accuracy, energy efficiency, and thinner profiles due to their use of light-emitting diodes compared to traditional cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFL) in LCDs. Discover how these distinctions impact your viewing experience and which option suits your needs best by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
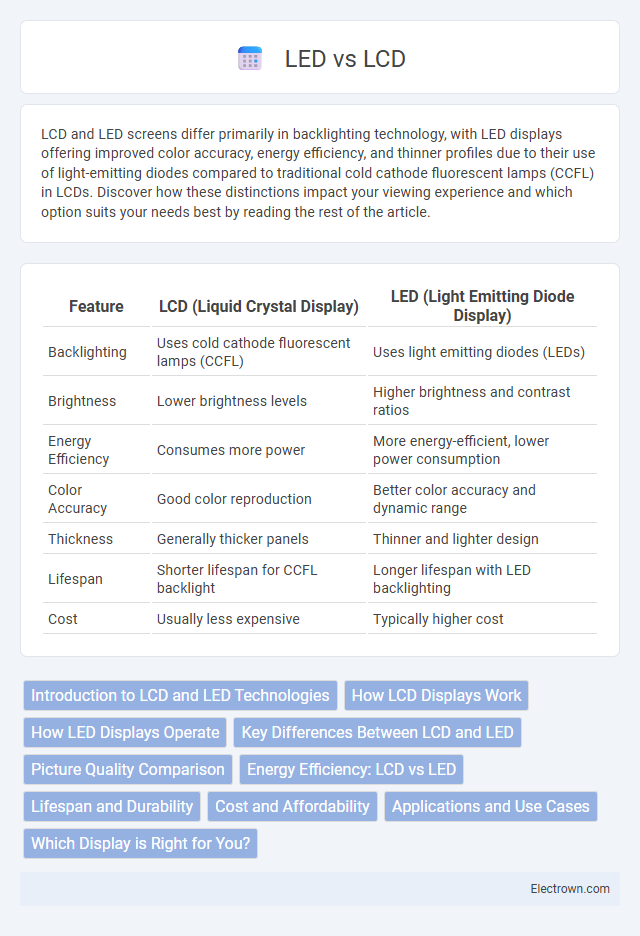
| Feature | LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) | LED (Light Emitting Diode Display) |
|---|---|---|
| Backlighting | Uses cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFL) | Uses light emitting diodes (LEDs) |
| Brightness | Lower brightness levels | Higher brightness and contrast ratios |
| Energy Efficiency | Consumes more power | More energy-efficient, lower power consumption |
| Color Accuracy | Good color reproduction | Better color accuracy and dynamic range |
| Thickness | Generally thicker panels | Thinner and lighter design |
| Lifespan | Shorter lifespan for CCFL backlight | Longer lifespan with LED backlighting |
| Cost | Usually less expensive | Typically higher cost |
Introduction to LCD and LED Technologies
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology uses liquid crystals to modulate light and create images by blocking or allowing light to pass through each pixel. LED (Light Emitting Diode) displays use LEDs as a direct backlight source or as individual pixels to produce brighter and more energy-efficient images. Understanding these fundamental differences helps you choose the right display based on image quality, power consumption, and application needs.
How LCD Displays Work
LCD displays work by using liquid crystals that align to control light passage through the screen, creating images by blocking or allowing light from a backlight to pass through each pixel. These crystals do not emit light themselves, relying on the backlight to produce visible images. Understanding how LCD technology operates helps you make an informed decision between LCD and LED displays based on your viewing needs and lighting conditions.
How LED Displays Operate
LED displays operate by using light-emitting diodes to produce images through individual pixels that emit light when an electric current passes through them. Unlike traditional LCDs that rely on a backlight, LED displays incorporate these diodes directly behind or within the screen, enhancing brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency. Your viewing experience benefits from sharper colors and deeper blacks due to the precise control of each LED pixel's illumination.
Key Differences Between LCD and LED
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens use a fluorescent backlight to illuminate pixels, while LED (Light Emitting Diode) displays employ LED backlighting, resulting in better brightness and energy efficiency. LED screens offer superior color accuracy, thinner panels, and improved contrast ratios compared to traditional LCDs. The response time in LED displays is generally faster, making them ideal for gaming and high-definition video playback.
Picture Quality Comparison
LED displays offer superior picture quality compared to traditional LCD screens by utilizing light-emitting diodes that provide higher brightness and better contrast ratios. LCDs rely on cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) for backlighting, which result in less vibrant colors and lower dynamic range. The advanced LED technology allows for deeper blacks and more vivid color reproduction, enhancing the overall viewing experience.
Energy Efficiency: LCD vs LED
LED displays consume significantly less energy than traditional LCDs because LEDs use light-emitting diodes for backlighting, which are more efficient than the cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) used in many LCDs. Modern LED TVs can reduce power consumption by up to 40% compared to older LCD models, making them a more eco-friendly choice. The energy-saving advantages of LED backlighting contribute to lower electricity bills and decreased environmental impact over the device's lifespan.
Lifespan and Durability
LED displays generally have a longer lifespan and greater durability compared to traditional LCD screens because LED technology uses light-emitting diodes that last up to 50,000 hours, whereas LCDs typically last around 30,000 hours. Your device's exposure to heat and usage intensity can impact the lifespan, but LEDs maintain brightness and color accuracy better over time under regular conditions. Durable design elements in LED panels also make them more resistant to physical damage and environmental factors than standard LCDs.
Cost and Affordability
LCD TVs generally have a lower upfront cost compared to LED TVs due to their simpler backlighting technology, making them more affordable for budget-conscious buyers. LED TVs, while typically priced higher, offer better energy efficiency and longer lifespan, which can result in lower long-term expenses. For consumers prioritizing initial affordability, LCD remains a cost-effective choice, whereas LED provides more value over time through durability and performance.
Applications and Use Cases
LCD technology is widely used in devices like computer monitors, smartphones, and digital watches due to its energy efficiency and sharp image quality. LED displays, offering superior brightness and contrast ratios, are preferred for outdoor digital billboards, television screens, and large-format displays where visibility under various lighting conditions is crucial. Depending on Your needs, LCD suits indoor, low-power applications while LED excels in environments requiring high visibility and vibrant colors.
Which Display is Right for You?
Choosing between LCD and LED displays depends on your specific needs and viewing preferences. LED screens, a type of LCD with LED backlighting, offer better contrast, energy efficiency, and thinner designs, making them ideal for vibrant visuals and modern aesthetics. Your decision should consider factors like budget, room lighting, and desired picture quality to select the display that best enhances your viewing experience.
LCD vs LED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com